This repository has been archived by the owner on Aug 2, 2021. It is now read-only.
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 110
network: Suggest peer by address space gap #2065
Merged
Merged
Conversation
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
…ot address, renamed findPeerPo to peerPo
…unt(). Several minor comments and fixes
…ubchannel. Some PR comments. Fixed TestEachBinBaseUses so it is more stable
acud
approved these changes
Jan 7, 2020
zelig
approved these changes
Jan 11, 2020
There was a problem hiding this comment.
Choose a reason for hiding this comment
The reason will be displayed to describe this comment to others. Learn more.
conflict needs resolved, otherwise lgtm
Sign up for free
to subscribe to this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in.
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
This suggestion is invalid because no changes were made to the code.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is closed.
Suggestions cannot be applied while viewing a subset of changes.
Only one suggestion per line can be applied in a batch.
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
Applying suggestions on deleted lines is not supported.
You must change the existing code in this line in order to create a valid suggestion.
Outdated suggestions cannot be applied.
This suggestion has been applied or marked resolved.
Suggestions cannot be applied from pending reviews.
Suggestions cannot be applied on multi-line comments.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is queued to merge.
Suggestion cannot be applied right now. Please check back later.
This PR is based on #1869 which is based on a fork that we do not have access to. Thanks to @kortatu for these changes.
I have merged master and resolved conflicts best to my knowledge.
Original PR description is copied bellow.
This PR propose an improved method for suggesting peers for connecting. Whenever a peer of a given bin needs to be added, instead of taking the first
callable, the method suggest the peer which covers a bigger address space. The method is implemented but is not currently attached to the main code (so it is only used in unit tests). Attaching it is just replacing the call to the current function.(This was built on top of Kademlia load balancing pr #1757).
This is extracted from network/README.md:
Address space gaps
In order to optimize Kademlia load balancing, performance and peer suggestion, we define the concept of
address space gapor simplygap.A
gapis a portion of the overlay address space in which the current node does not know any peer. It could be represented as a range of addresses:0xxx, meaning0000-0111The
proximity order of a gaporgap pois the proximity order of that address space with respect to the nearest peer(s) in the kademlia connected table (and considering also the current node address). For example if the node address is0000, the gap of addresses1xxxhas proximity order 0. However the proximity order of the gap01xxhas po 1.The
size of a gapis defined as the number of addresses that could fit in it. If the area of the whole address space is 1, thesize of a gapcould be defined from thegap poas1 / 2 ^ (po + 1). For example, our previous1xxxgap has a size of1 / (2 ^ 1) = 1/2. The size of01xxis1 / (2 ^ 2) = 1/4.In order to increment performance of content retrieval and delivery the node should minimize the size of its gaps, because this means that it knows peers near almost all addresses. If the minimum
gapin the kademlia table is 4, it means that whatever look up or forwarding done will be at least 4 po far away. On the other hand, if the node has a 0 pogap, it means that for half the addresses, the next jump will be still 0 po away!.Gaps for peer suggestion
The current kademlia bootstrap algorithm try to fill in the bins (or po spaces) until some level of saturation is reached.
In the process of doing that, the
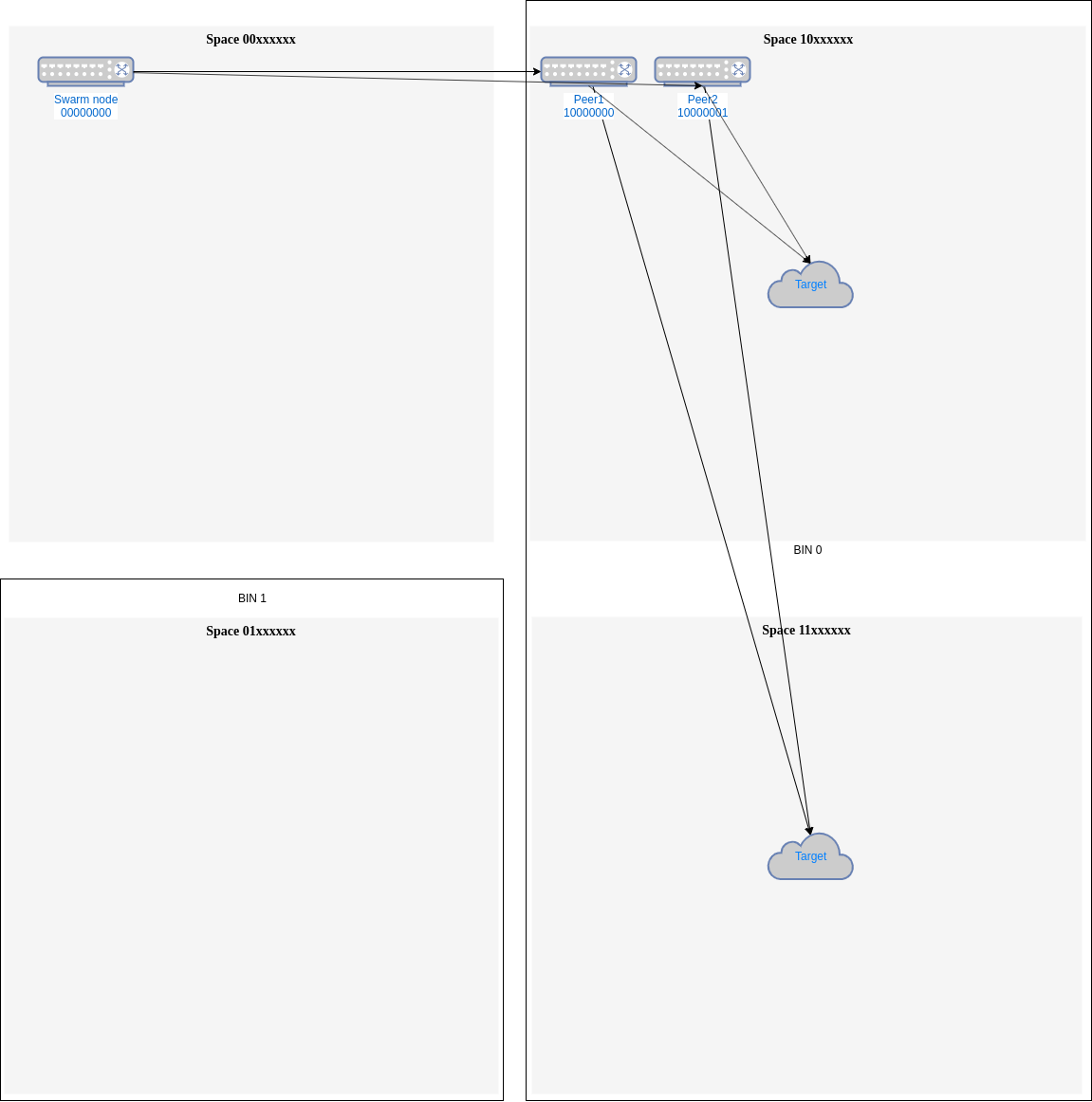
gapswill diminish, but not in the optimal way.For example, if the node address is
00000000, it is connected only with one peer in bin 010000000and the known addresses for bin 0 are:10000001and11000000. The current algorithm we will take the firstcallableone, so for example, it may suggest10000001as next peer. This is not optimal, as the biggestgapin bin 0 will still be po 1 =>11xxxxxx. If however, the algorithm is improved searching for a peer which covers a biggergap,11000000wouldbe selected and now the biggest
gapswill be po2 =>111xxxxand101xxxx.Additionally, even though the node does not have an address in a particular
gap, it could still select the furthest away from the current peers so it covers a biggergap. In the previous example with node00000000and one peer already connected10000000, if the known addresses are10000001and1001000, the best suggestion would be the last one, because it is po 3from the nearest peer as opposed to
10000001that is only po 7 away. The best case will cover agapof po 3 size (1/16 of area or 16 addresses) and the other one just po 7 size (1/256 area or 1 address).Gaps and load balancing
One additional benefit in considering
gapsis load balancing. If the target addresses are distributed randomly (although address popularity is another problem that can also be studied from thegapperspective), the request willbe automatically load balanced if we try to connect to peers covering the bigger
gaps. Continuing with our example, if in bin 0 we have peers10000000and10000001(Fig. 1), almost all addresses in space1xxxxxxx, that is, half of the addresses will have the same distance from both peers. If we need to send to some of those address we will need to use one of those peers. This could be done randomly, always the first or with some load balancing accounting to use the leastused one.
Fig.1 - Closer peers needs an external Load Balancing mechanism
This last method will still be useful, but if the
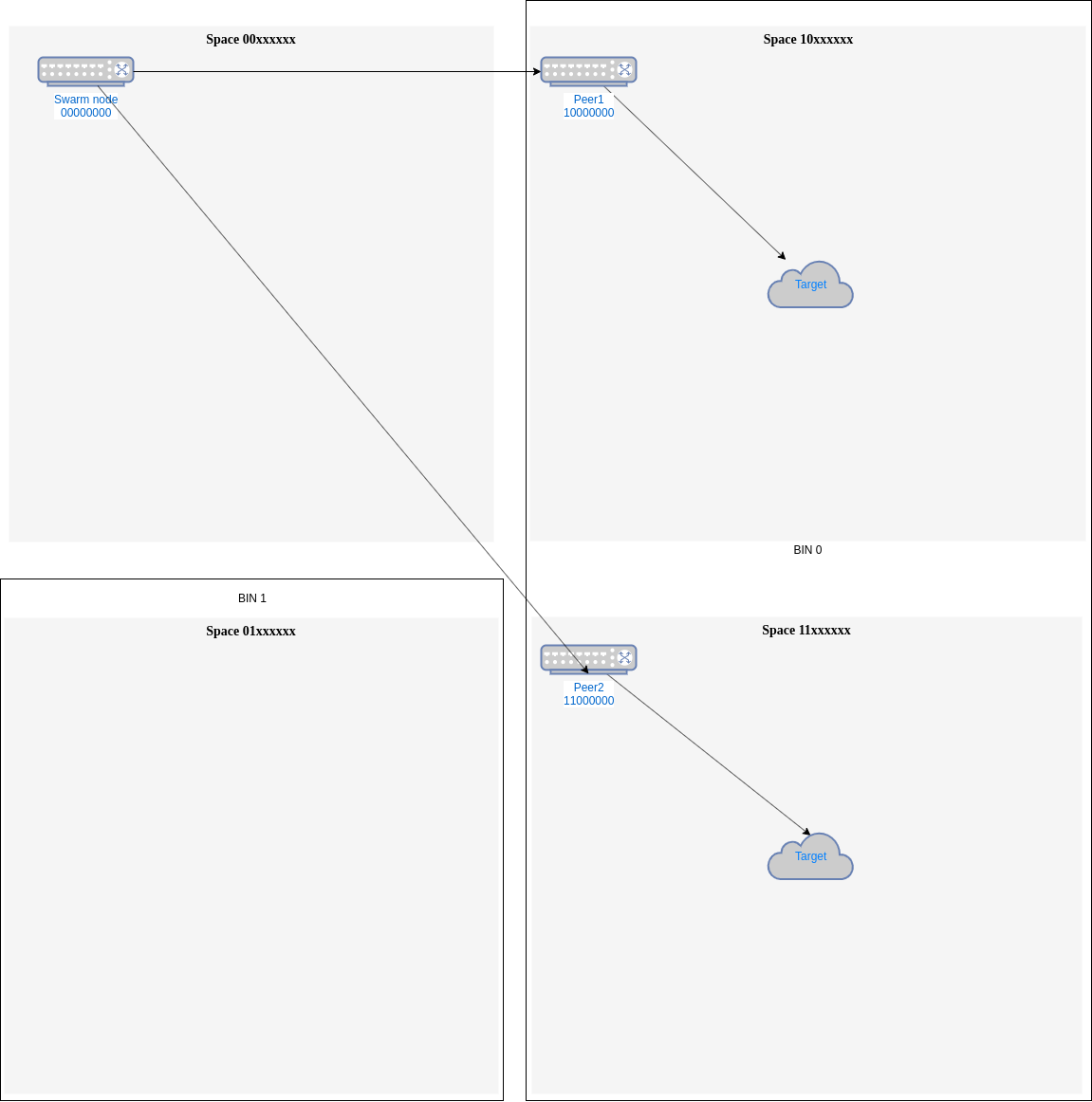
gapfilling strategy is used, most probably both peers will be separated enough that they never compete for an address and a natural load balancing will be made among them (for example,10000000and11000000will be used each for half the addresses in bin 0 (Fig. 2)).Fig.2 - Peers chosen by space address gap have a natural load balancing
Implementation
The search for gaps can be done easily using a proximity order tree or
pot. Traversing the bins of a node, agapis found if there is some of the po's missing starting from furthest (left). In each level the starting po to search for is the parent po (not 0, because in the second level, under a node of po=0, the minimum po that could be found is 1).Implementation of the function that looks for the bigger Gap in a
potcan be seen inpot.BiggestAddressGap. That function returns the biggest gap in the form of a po anda node under the gap can be found.
This function is used in
kademlia.suggestPeerInBinByGap, which it returns a BzzAddress in a particular bin which fills up the biggest address gap. This function is not used inSuggestPeer, but it will be enough to replace the call tosuggestPeerInBinwith the new one.Further improvements
Instead of the size of a gap, maybe it could be more interesting to see the rationbetween size and number of current peers serving that gap. If we have
ncurrent peers that are equidistant to a particular gap of sizes, the load of each of these peers will be on averages/n.We can define a gap's
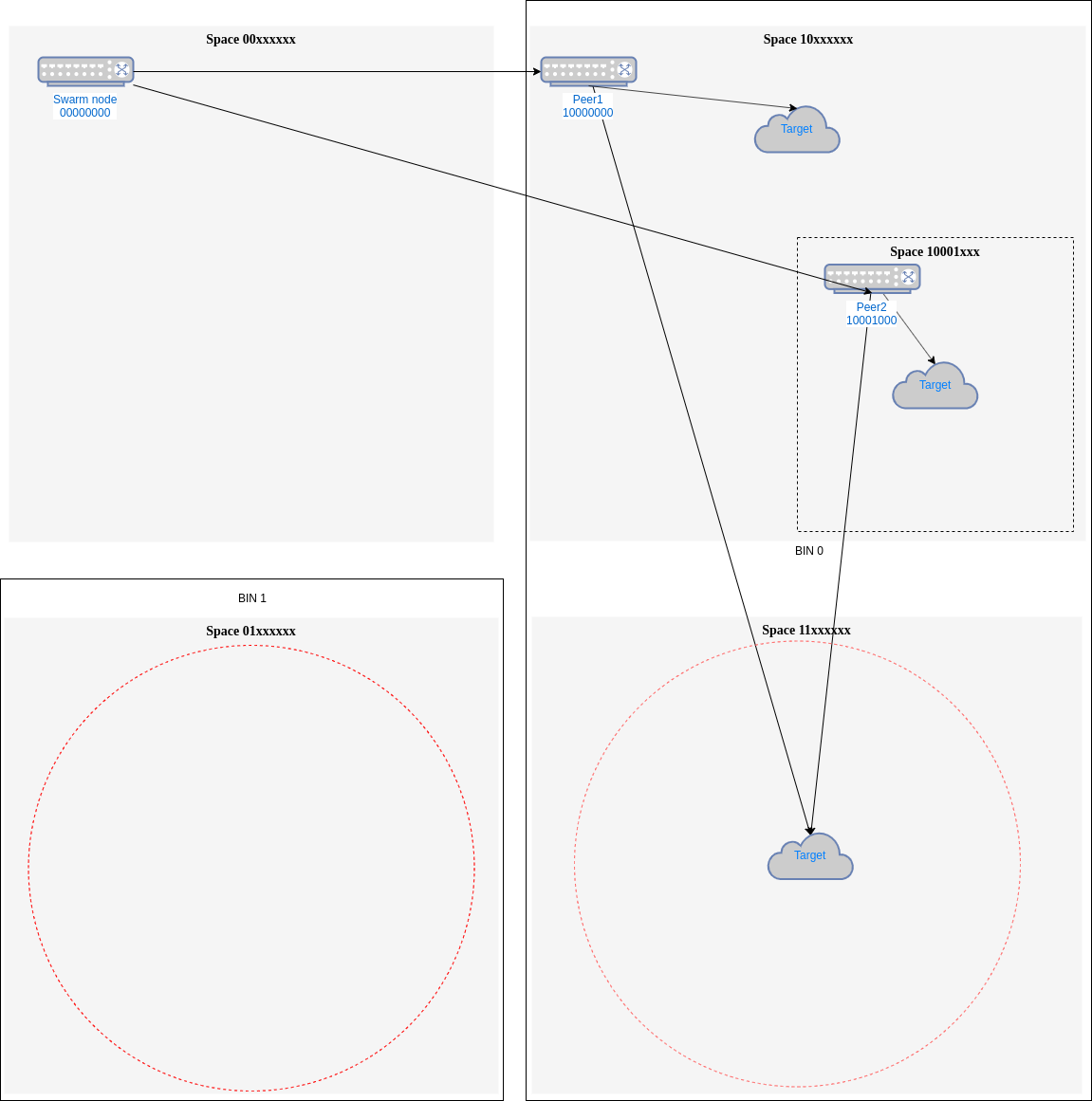
temperatureas that numbers/n. When looking for new peers to connect, instead of looking for bigger gaps we could look forhottergaps.For example, if in our first example, we can't find a peer in
11xxxxxxand we instead, used the best peer, we could end with the configuration in Fig. 3.Fig. 3 - Comparing gaps temperature
Here we still have
11xxxxxxas the biggest gap (po=1, size 1/4), same size as01xxxxxx. But if consider temperature,01xxxxxxis hotter because is served only by our node00000000, being its temperature is(1/4)/ 1 = 1/4. However,11xxxxxxis now served by two peers, so its temperature is(1/4) / 2 = 1/8, and that will mean that we will select01xxxxxxas the hotter one.There is a way of implementing temperature calculation so its cost it is the same as looking for biggest gap. Temperature can be calculated on the fly as the gap is found using a
pot.Other metrics could be considered in the temperature, as recently number of requests per address space, performance of current peers...