简单实现一个基于btree索引的小玩具,文件存放磁盘中,实现简单的查询和插入功能,代码还有点乱;
- node(>= v9.0.0)
- lru-cache(用来做page缓存)
npm install fudb;- 创建一个db并且写入数据的操作:
const fudb = require('fudb');
const fn = async (itemNum) => {
const db = await fudb.Create('js', 'name');
for (let i = 0; i < itemNum; i += 1) {
await db.put({
name: `funer80900090009${i}`,
sex: `${{ 0: 'female', 1: 'male', 2: 'shemale' }[i % 3]}`,
className: `super${i}`,
}); // eslint-disable-line
}
await db.flush();
}
fn(100);这样就在该项目目录下生成一个js目录,里面有连个文件
js.db和js.index,分别为原始数据文件,索引文件;注意一点由于简化实现,添加数据单条要小于一定值(1kb);
- 打开一个该类型的文件:
const fudb = require('fudb');
const fn = async () => {
const db = await fudb.Connect('js');
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i += 1) {
const result = await db.findByKey('name', `funer80900090009${i}`);
console.log(result);
if (!result) {
throw new Error('error!');
}
}
}
fn();- 范围查询:
const fudb = require('fudb');
const fn = async () => {
const db = await fudb.Connect('js');
db.range('name', { lt: 'funer809000900091', gt: 'funer809000900091' }).then((data) => {
console.log('count', data.total());
console.log('ids', data.cells);
data.fetch().then((details) => {
details.forEach((d) => {
console.log('detail', fudb.Parse(d));
});
});
});
}
fn();注意查询的时候必须要有{lt:, gt:},暂不支持单边的查找,以后慢慢支持;
range函数返回的是一个Promise; 且该方法是先统计btree的id的个数,并未实际获取真实的rawdata,该Promise返回的数据为:
{
count: () => {}, // 返回range查询的item总数,这里是统计的id的数量
cells: [{id: 'xxx'}],// 返回为包含id的对象数组
fetch: async() => {} // 通过索引id去加载rawdata
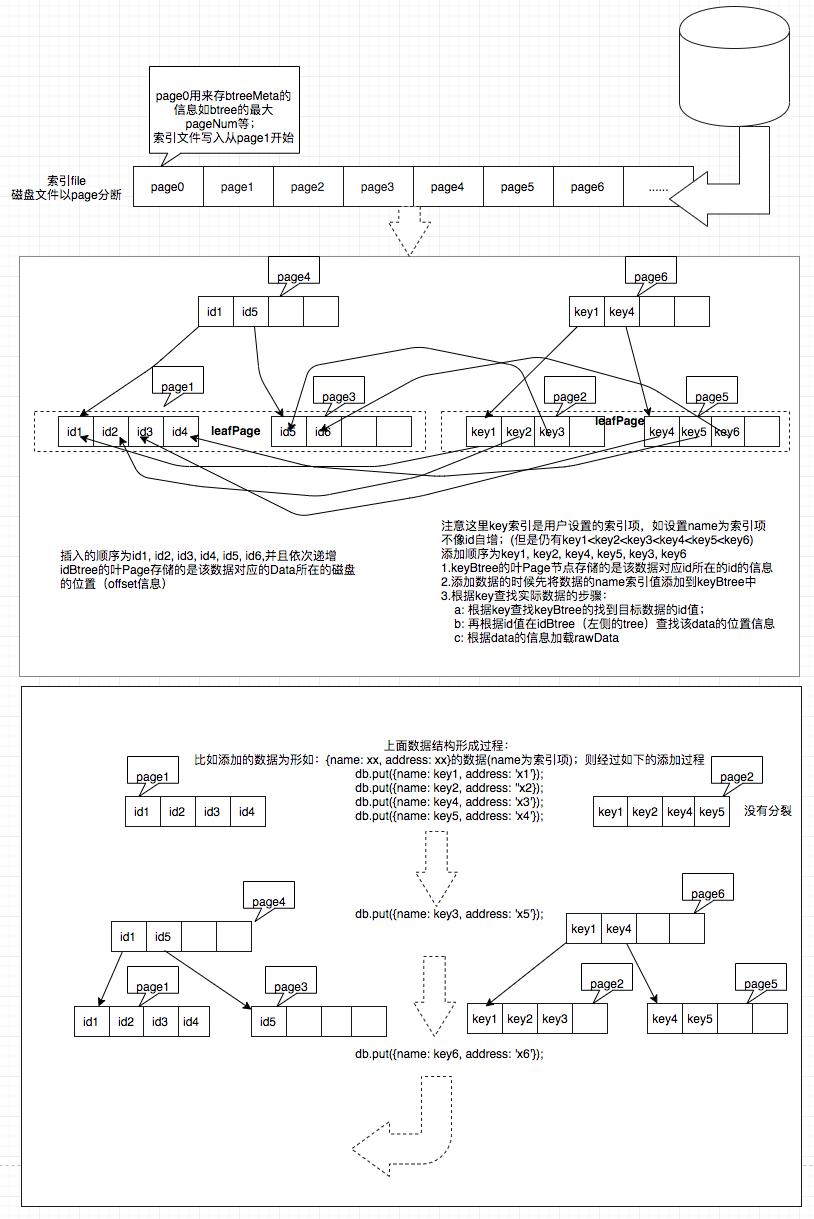
}由两个文件组成,一个为data文件,一个为index文件; index里有一个id组成的btree和user定义组成的一个btree;
id是由内部按照时间生成的一自增的对象,形如:{timeId: xxx, count: xxx}, 生成自增id的算法;这里有个假定:就是一秒内添加的速度不能大于256 * 256;
// generate auto incresed id and the length of id : 6
let count = 0; // less than 256 * 256
let id = 0;
const IdGen = function () {
let timeId = +new Date();
timeId = ~~(timeId / 1000);
if (timeId > id) {
count = 0;
id = timeId;
} else {
count += 1;
}
return {
timeId,
count,
};
};- 实现删除的操作(进行中)
- 不限制1kb的数据大小
- 实现page缓存处理,不用
lru-cache依赖 - 完善代码