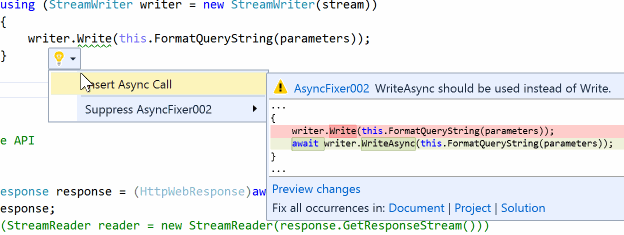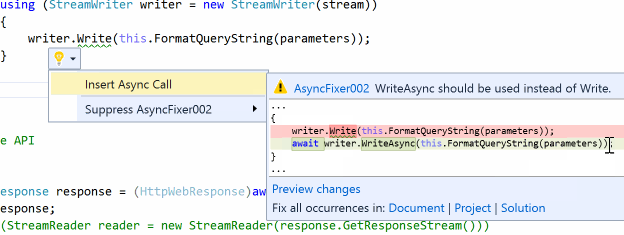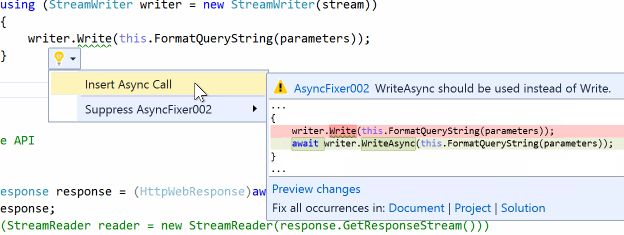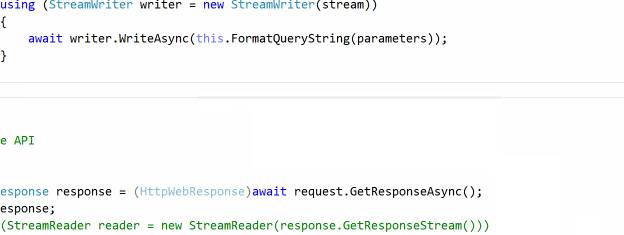
AsyncFixer helps developers in finding and correcting common async/await misuses (i.e., anti-patterns). It currently detects 5 common kinds of async/await misuses and fixes 3 of them via program transformations. AsyncFixer has been tested with thousands of open-source C# projects and successfully handles many corner cases. It is also one of the most common analyzers used in C# projects from Microsoft.
AsyncFixer will work just in the IDE and work as an analyzer on every project you open in Visual Studio. It can also operate in batch mode to correct all misuses in the document, project, or solution. You can download the VSIX from here.
If you want AsyncFixer to deploy as a NuGet package and work as a project-local analyzer that participates in builds, you can use the nuget package. Attaching an analyzer to a project means that the analyzer travels with the project to source control and so it is easy to apply the same rule for the team. You can download the nuget package from here.
Here are async/await misuses (i.e., anti-patterns) that AsyncFixer can currently detect:
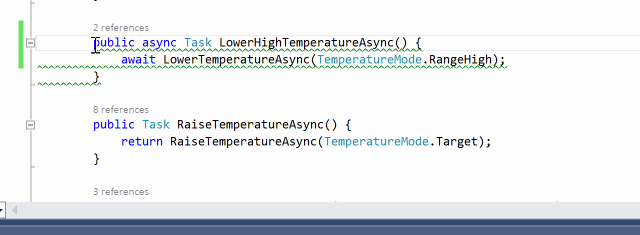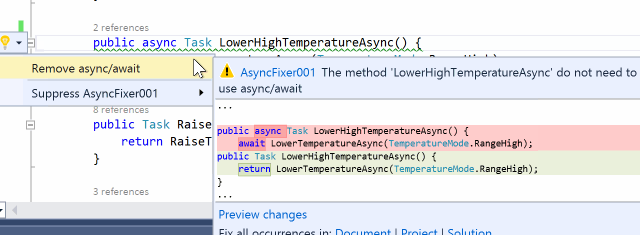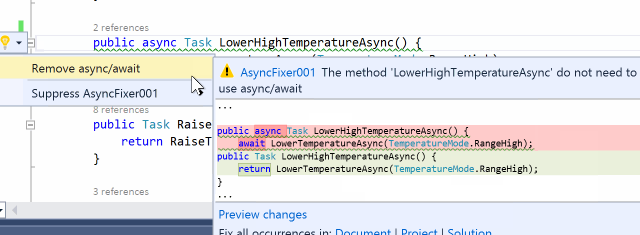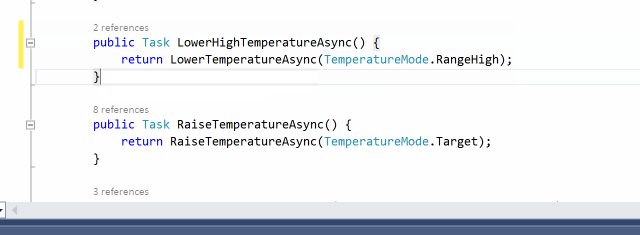
There are some async methods where there is no need to use async/await keywords. It is important to detect this kind of misuse because adding the async modifier comes at a price. AsyncFixer automatically removes async/await keywords from those methods.
Developers use some potentially long-running or blocking operations inside async methods even though there are corresponding asynchronous versions of these methods in .NET or third-party libraries. Some examples for such operations: Task.Wait(), Task.Result, StreamReader.ReadToEnd(), Thread.Sleep(), etc.
AsyncFixer automatically replaces those operations with their corresponding asynchronous operations and inserts an await expression. For instance, it converts Thread.Sleep(...) to await Task.Delay(...).
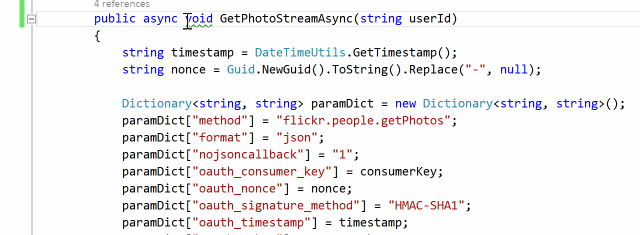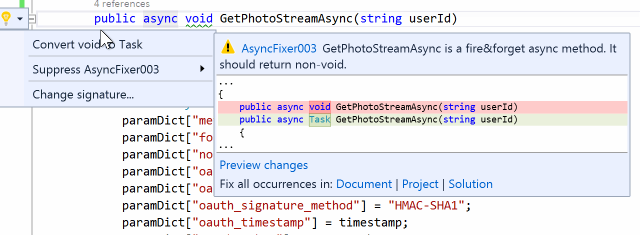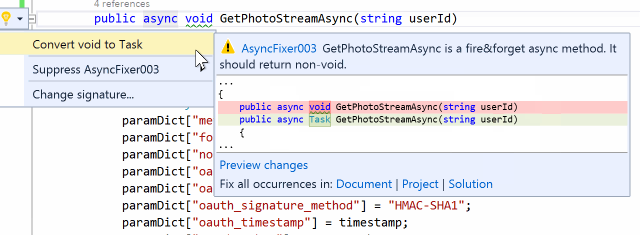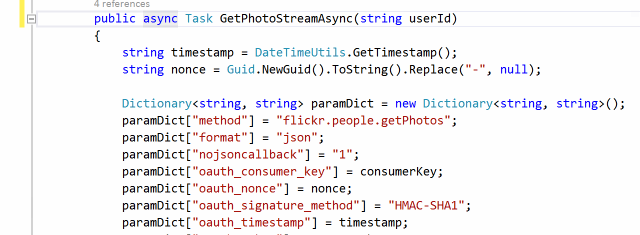
Some async methods and delegates are fire-and-forget, which return void. Unless a method is only called as an event handler, it must be awaitable. Otherwise, it is a code smell because it complicates control flow and makes error detection/correction difficult. Unhandled exceptions in those async-void methods and delegates will crash the process as well.
AsyncFixer automatically converts void to Task.
Inside a using block, developers insert a fire-and-forget async call which uses a disposable object as a parameter or target object. It can cause potential exceptions or wrong results. Here is an example:
static void foo()
{
var newStream = new FileStream("file.txt", FileMode.Create);
using (var stream = new FileStream("newfile.txt", FileMode.Open))
{
newStream.CopyToAsync(stream);
}
}
We copy the contents of the file to another file above. If the file size is big enough to make CopyToAsync take non-trivial duration, we will have ObjectDisposedException because Stream will be implicitly disposed due to the using block before CopyToAsync is finished. To fix the issue, we need to await asynchronous operations involving disposable objects inside using blocks:
await newStream.CopyToAsync(stream);
Downcasting from a nested task to a task or awaiting a nested task is dangerous. There is no way to wait for and get the result of the child task. This usually occurs when mixing async/await keywords with the old threading APIs such as TaskFactory.StartNew. Here is an example:
async Task foo()
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello");
await Task.Factory.StartNew(() => Task.Delay(1000)); // StartNew call returns a nested task: Task<Task>
Console.WriteLine("World");
}
A developer might expect one-second latency between "Hello" and "World" lines. However, those strings will be printed instantaneously without any latency. The reason is that we await a nested task, which is the return type of StartNew call. When we await the nested task, the return value is the inner task that is the result of Task.Delay call. As we do not await the inner task, we do not see the effect of the delay call. There are three possible fixes:
- We can await the inner task as well:
await (await Task.Factory.StartNew(() => Task.Delay(1000)));
- We can use
Unwrapto expose the inner task to theawaitexpression:
await Task.Factory.StartNew(() => Task.Delay(1000)).Unwrap();
- If you do not have reasons to use
TaskFactory.StartNewsuch asTaskCreationOptionsand a customTaskScheduler, we should always useTask.Runto automatically unwrap the inner task.
await Task.Run(() => Task.Delay(1000));