Two definitions of Machine Learning are offered. Arthur Samuel described it as: "the field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed." This is an older, informal definition.
Tom Mitchell provides a more modern definition: "A computer program is said to learn from experience E with respect to some class of tasks T and performance measure P, if its performance at tasks in T, as measured by P, improves with experience E."
Example: playing checkers.
E = the experience of playing many games of checkers
T = the task of playing checkers.
P = the probability that the program will win the next game.
In general, any machine learning problem can be assigned to one of two broad classifications:
Supervised learning , Unsupervised learning and Reinforcement learning.
Supervised learning is a type of machine learning method in which we provide sample labeled data to the machine learning system in order to train it, and on that basis, it predicts the output.
The system creates a model using labeled data to understand the datasets and learn about each data, once the training and processing are done then we test the model by providing a sample data to check whether it is predicting the exact output or not.
The goal of supervised learning is to map input data with the output data. The supervised learning is based on supervision, and it is the same as when a student learns things in the supervision of the teacher. The example of supervised learning is spam filtering. Supervised learning can be grouped further in two categories of algorithms:
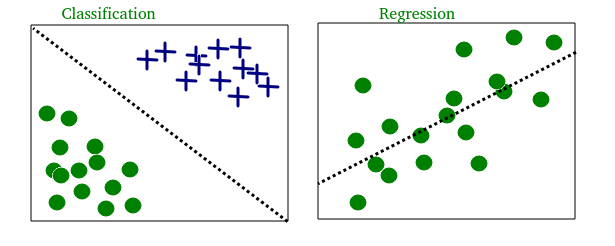
ClassificationRegression
Example:
(a) Regression - Given a picture of a person, we have to predict their age on the basis of the given picture
(b) Classification - Given a patient with a tumor, we have to predict whether the tumor is malignant or benign.
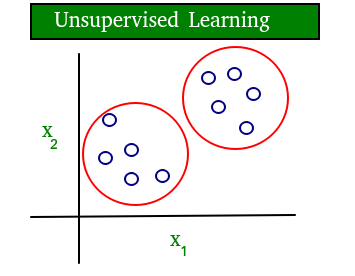
Unsupervised learning is a learning method in which a machine learns without any supervision.
The training is provided to the machine with the set of data that has not been labeled, classified, or categorized, and the algorithm needs to act on that data without any supervision. The goal of unsupervised learning is to restructure the input data into new features or a group of objects with similar patterns.
We can derive this structure by clustering the data based on relationships among the variables in the data.
With unsupervised learning there is no feedback based on the prediction results.
In unsupervised learning, we don't have a predetermined result. The machine tries to find useful insights from the huge amount of data. It can be further classifieds into two categories of algorithms:
ClusteringAssociation
Reinforcement learning is a feedback-based learning method, in which a learning agent gets a reward for each right action and gets a penalty for each wrong action. The agent learns automatically with these feedbacks and improves its performance. In reinforcement learning, the agent interacts with the environment and explores it. The goal of an agent is to get the most reward points, and hence, it improves its performance.
The robotic dog, which automatically learns the movement of his arms, is an example of Reinforcement learning.
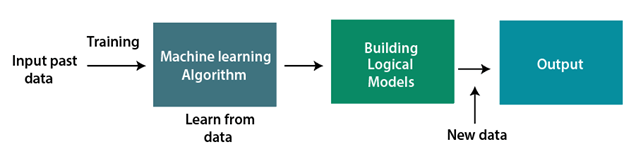
A Machine Learning system learns from historical data, builds the prediction models, and whenever it receives new data, predicts the output for it. The accuracy of predicted output depends upon the amount of data, as the huge amount of data helps to build a better model which predicts the output more accurately.
Data Gathering: To train a machine learning model we need data. Thus, data gathering is the first and foremost step in the machine learning lifecycle wherein data is collected from various sources and integrated together to create a combined set of data known as the dataset.Data Preprocessing: After the data set is ready it undergoes data preprocessing in which the data is transformed, or encoded so that the machine can easily read and parse it.Data Wrangling: Real-world applications have various errors and issues like missing values, duplicate data, invalid data, and noise that can hamper the training model and the final outcome. Hence, it is extremely important to deal with such issues and make the raw data understandable so that it can be easily understood by the machine learning algorithm. This process is known as data wrangling.Data Analysis: Once the data is ready to be processed it is used to build a machine learning model using numerous analytical techniques.Training Model: After data analysis, the model is trained using various algorithms so that it can understand the provided patterns, features, and rules. This allows the model to improve its performance and efficiency.Test Model: Once the model is trained it undergoes testing where it is checked for its accuracy and efficiency.Deployment: Finally the model is deployed in the form of a real-world application.
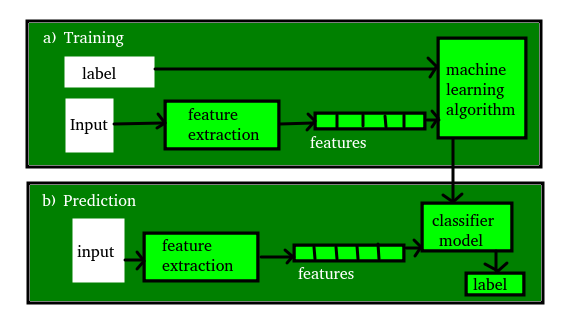
A model is a specific representation learned from data by applying some machine learning algorithm. A model is also called hypothesis.
A feature is an individual measurable property of our data. A set of numeric features can be conveniently described by a feature vector. Feature vectors are fed as input to the model. For example, in order to predict a fruit, there may be features like color, smell, taste, etc. Note: Choosing informative, discriminating and independent features is a crucial step for effective algorithms. We generally employ a feature extractor to extract the relevant features from the raw data.
A target variable or label is the value to be predicted by our model. For the fruit example discussed in the features section, the label with each set of input would be the name of the fruit like apple, orange, banana, etc.
The idea is to give a set of inputs(features) and it’s expected outputs(labels), so after training, we will have a model (hypothesis) that will then map new data to one of the categories trained on.
Once our model is ready, it can be fed a set of inputs to which it will provide a predicted output(label).
A dataset is a collection of data in which data is arranged in some order. A dataset can contain any data from a series of an array to a database table
A tabular dataset can be understood as a database table or matrix, where each column corresponds to a particular variable, and each row corresponds to the fields of the dataset. The most supported file type for a tabular dataset is "Comma Separated File," or CSV. But to store a "tree-like data," we can use the JSON file more efficiently.
Example:
| Country | Age | Salary | Purchased |
|---|---|---|---|
| India | 38 | 48000 | No |
| France | 43 | 45000 | Yes |
| Germany | 30 | 54000 | No |
| France | 48 | 65000 | No |
| Germany | 40 | Yes | |
| India | 35 | 58000 | Yes |
NOTE:
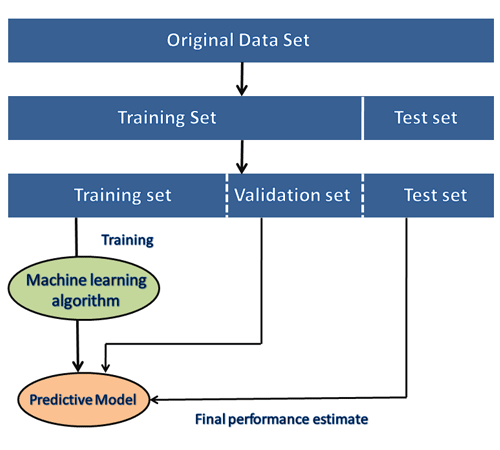
During the development of the ML project, the developers completely rely on the datasets. In building ML applications, datasets are divided into two parts:
- Training dataset:
- Test Dataset
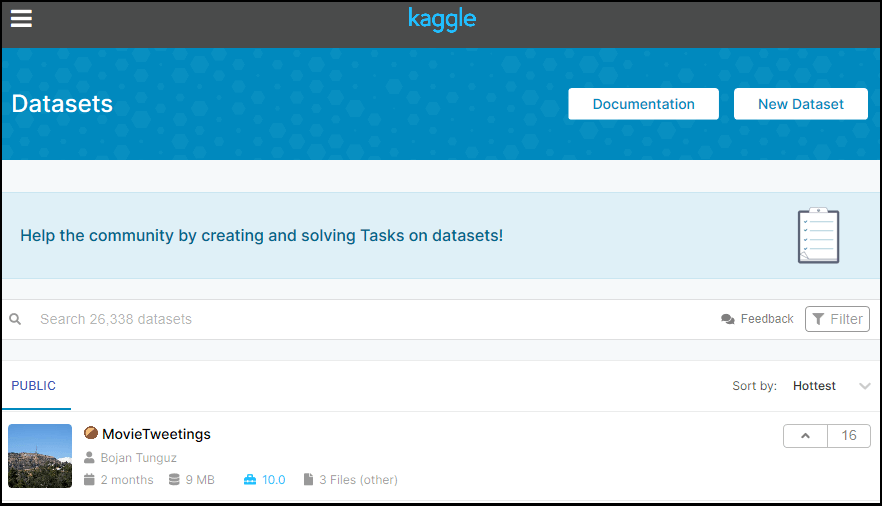
Kaggle is one of the best sources for providing datasets for Data Scientists and Machine Learners. It allows users to find, download, and publish datasets in an easy way. It also provides the opportunity to work with other machine learning engineers and solve difficult Data Science related tasks.
Kaggle provides a high-quality dataset in different formats that we can easily find and download.
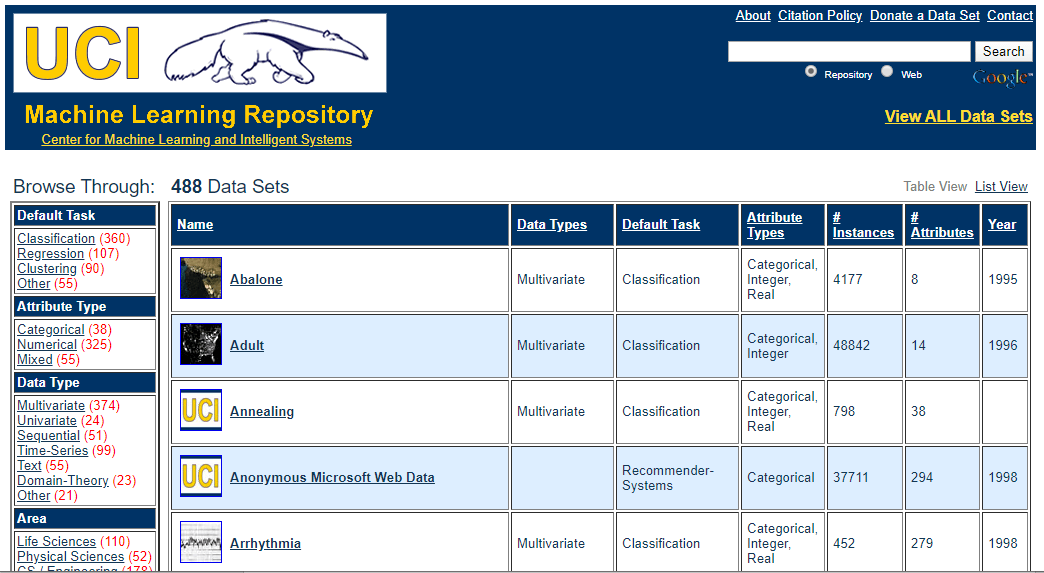
UCI Machine learning repository is one of the great sources of machine learning datasets. This repository contains databases, domain theories, and data generators that are widely used by the machine learning community for the analysis of ML algorithms.
It classifies the datasets as per the problems and tasks of machine learning such as Regression, Classification, Clustering, etc. It also contains some of the popular datasets such as the Iris dataset, Car Evaluation dataset, Poker Hand dataset, etc.