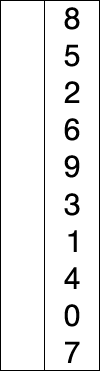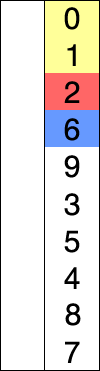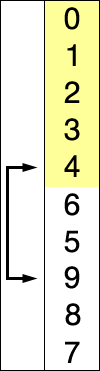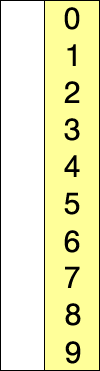
As of now in the latest browser or node, typing class would yield:
> class
SyntaxError: Unexpected reserved wordThis repo is a WIP that should slowly grow into a collection of implementation of letious algorithms with JS using ES6 constructs!
Let's start with Sorting Algorithms!
Before we create classes of each of the sorting algorithms, let's create a base class named Sorter
class Sorter {
constructor(nums) {
this.nums = nums;
}
}#Bubble Sort
PesudoCode:
repeat
hasChanged := false
decrement itemCount
repeat with index from 1 to itemCount
if (item at index) > (item at (index + 1))
swap (item at index) with (item at (index + 1))
hasChanged := true
until hasChanged = false
Worst case complexity is O(n^2)
class BubbleSort extends Sorter {
constructor(nums) {
super(nums);
}
sort() {
let length = this.nums.length;
do {
let swapped = false;
for(let i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
if (this.nums[i] > this.nums[i+1]) {
[this.nums[i],this.nums[i+1]] = [this.nums[i+1], this.nums[i]];
swapped = true;
}
}
} while(swapped == true);
return this.nums;
}
}let bubble = new BubbleSort([-1,0,-11,42,32,3]);
console.log(bubble.sort()); // [-11,-1,0,3,32,42]
#Insertion Sort
PesudoCode:
function insertionSort(array A)
for i from 1 to length[A]-1 do
value := A[i]
j := i-1
while j >= 0 and A[j] > value do
A[j+1] := A[j]
j := j-1
done
A[j+1] = value
done
class InsertionSort extends Sorter {
constructor(nums){
super(nums)
}
sort() {
for(let i = 1; i < this.nums.length; i++){
let value = this.nums[i];
let j = i - 1;
while(j >= 0 && this.nums[j] > value){
this.nums[j + 1] = this.nums[j];
j = j - 1;
}
this.nums[j + 1] = value;
}
return this.nums;
}
}let insertion = new InsertionSort([3,4,1,2,0]);
console.log(insertion.sort()); // 0,1,2,3,4
#Selection Sort
PesudoCode:
for i = 0 to numItems - 1
for j = i+1 to numItems
if A[i] > A[j]
A[i] <-> A[j]
End If
Next j
Next i
class SelectionSort extends Sorter {
constructor(nums){
super(nums);
}
sort(){
let len = this.nums.length,
min,i,j;
for (i=0; i < len; i++){
min = i;
for (j=i+1; j < len; j++){
if (this.nums[j] < this.nums[min]){
min = j;
}
}
if (i != min){
[this.nums[i],this.nums[min]] = [this.nums[min],this.nums[i]];
}
}
return this.nums;
}
}let selection = SelectionSort([1,2,-1,0,4,5]);
console.log(selection.sort()); // -1,0,1,2,4,5#Count Sort
class CountSort extends Sorter {
constructor(nums) {
super(nums);
}
sort() {
let i, x = 0, count = [];
for (i = this.min; i <= this.max; i++) {
count[i] = 0;
}
for (i=0; i < this.nums.length; i++) {
count[this.nums[i]]++;
}
for (i = this.min; i <= this.max; i++) {
while (count[i]-- > 0) {
this.nums[x++] = i;
}
}
return this.nums;
}
}