This repository contains the open-sourced codes and datasets from the below paper published in the IEEE IOT Journal.
If you use this work, please cite our paper: Latif E, Parasuraman R. Instantaneous Wireless Robotic Node Localization Using Collaborative Direction of Arrival. IEEE Internet of Things Journal. 2023 Jul 18.
IEEE Published version: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10185556 Preprint available at: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2307.01956
This repository contains the datasets and scripts used in the experimentation for localization algorithm using Wireless signal Collaborative Direction of Arrival (CDOA) estimated using a mobile robot - -wireless sensor network (WSN) cooperation mechanism in real-time. Three sets of experimentational content is provided in this repository: 1. Simulation (Datasets and Codes), 2. Real-world public datasets from the literature (Dataset1 [1] and Dataset2 [2]), 4. Real Robot Hardware (ROS package and its Dataset). Each content is enclosed in a separate folder with the respective name. Simulation scripts generate data internally. However, real-world experimentation requires data files to be included in the respective folder in the repository.
The proposed localization framework can be visualized as:
On the Left, the Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) anchor nodes are placed at the corners, and the Mobile Robot can be localized within the WSN's boundary polygon.
On the Right, the Access Points (AP) are placed at the corners, and the mobile robot can be localized within the AP boundaries.
Although we present the experimental results for the WSN nodes/AP anchors in a specific square/triangular shape, the approach can be generalized to other configurations as long as all the nodes are not colinear.
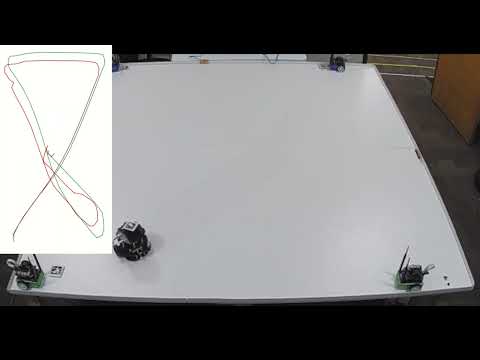
A hardware demonstration experiment setup is shown below using the configuration of WSN anchor nodes.
Below, we present different datasets and associated robot localization trajectories or information.
Simulation experimentations taken place for 6 x 6 meter of bounded region where Access Point is placed on the top of the moving robot and wireless sensor nodes places at the fixed positions (corners) which are (0,0), (0,6), (6,0), and (6,6) respectively. The robot followed three different trajectories: Inside, Boundary, and Diagonal. For each of the trajectories, we predicted the position using multiple localization techniques and proposed an approach as well.
In the Simulation folder, there is a separate Python script file for each localization technique.
To execute the script, run: $ python3 <script_file>
It contains script files, same as the simulation, to run algorithms on data available in CSV files.
To execute the script run: $ python3 <script_file> <dataset file>
Experimentation Testbed and data points can be visualized as:
The reference at [1] provides details of the dataset completely.
It contains script files same as simulation to run algorithms on data available in csv files.
To execute the script run: $ python3 <script_file> <dataset file>
Experimenatation Testbed and datapoints can be visualized as:
The reference at [2] povides details of the dataset completely.
This folder uses a ROS package (ros_network_analysis) which consists of wireless publisher node scripts along with the server subscriber script. For latest source code on this package, please download the ros_network_analysis package from its source code following the instructions at https://github.com/herolab-uga/ros-network-analysis
To launch the network_analysis run: $ roslaunch network_analysis wireless_quality.launch <node_id>
Another ROS package named "ros_rssi_collaboration" needs to be installed to run the RSSI node collaboration algorithm and receive rssi from each node in a synchronous way.
To launch the rssi_collaboration run: $ roslaunch rssi_collaboration rssi_collaboration.launch
Furthemore, a folder contains dataset in the form of rosbags, one can easily extract data rosbags. However, we also have provided dataset int he form of .csv for convinience in the respective folders. It also contains script files to run algorithms on data available in CSV files.
To run localization over recorded Odom and RSSI, execute the script run: $ python3 <script_file> <dataset file>
ROS package named "ros_pf_doa_localization" needs to be installed to run the online localization over received RSSI through node collaboration in a synchronous fashion.
To launch the ros_pf_doa_localization run: $ roslaunch ros_pf_doa_localization ros_pf_doa_localization.launch
It will launch online localization script which receives RSSI from connected nodes and provide real-time pose estimation along with the ground truth.
Experimentation Testbed and data points can be visualized as:
[1] Pachos et al. "Rssi dataset for indoor localization fingerprinting." [Online]. Available: https://github.com/pspachos/RSSI-Dataset-for-Indoor-Localization-Fingerprinting.git
[2] P. Szeli ́nski and M. Nikodem, "Multi-channel BLE RSSI measurements for indoor localization," 2021. [Online]. Available: https://dx.doi.org/10.21227/hc74-3s30
-
Ehsan Latif - PhD Candidate
-
Dr. Ramviyas Parasuraman - Principal Investigator
Heterogeneous Robotics Lab (HeRoLab), School of Computing, University of Georgia.
For further information, contact Prof. Ramviyas Parasuraman ramviyas @ uga.edu