Video of the effects: https://youtu.be/N9-BhrHccWc
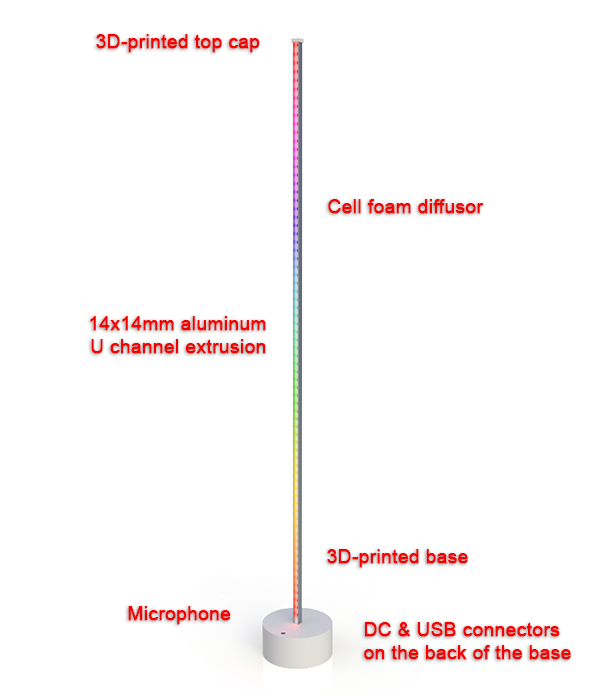
Control an addressable LED strip with an ESP8266 via a web browser or a microphone.
- Turn the LED-strip on and off
- Adjust the brightness
- Adjust the speed
- Change the color pattern manually or randomly after selected time period
- Change the color palette manually or randomly after selected time period
- Layered effects: Glitter & Strobe
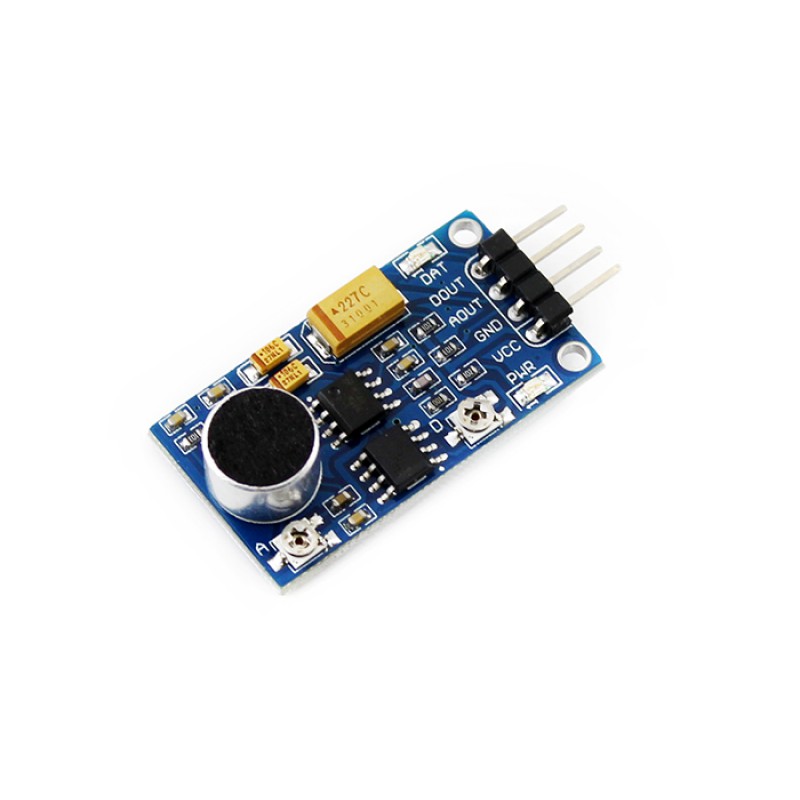
- Sound reactive color patterns (possibility to use without microphone using generated signal)
- Single solid color option
- User interface cleaned from all the excess, using now only one single page
- Code cleaned
- All the patterns now use color pattern
- Microphone support & sound reactive patterns added (https://github.com/atuline/FastLED-SoundReactive)
- All but sound reactive patterns now react to speed change
- A lot of new color patterns and palettes added
Recommended by Adafruit NeoPixel "Best Practices" to help protect LEDs from current onrush:
The web app is stored in SPIFFS (on-board flash memory).
The web app is a single page app that uses jQuery and Bootstrap. It has buttons for On/Off, a slider for brightness, a pattern selector, and a color picker (using jQuery MiniColors). Event handlers for the controls are wired up, so you don't have to click a 'Send' button after making changes. The brightness slider and the color picker use a delayed event handler, to prevent from flooding the ESP8266 web server with too many requests too quickly.
The app is installed via the Arduino IDE which can be downloaded here. The ESP8266 boards will need to be added to the Arduino IDE which is achieved as follows. Click File > Preferences and copy and paste the URL "http://arduino.esp8266.com/stable/package_esp8266com_index.json" into the Additional Boards Manager URLs field. Click OK. Click Tools > Boards: ... > Boards Manager. Find and click on ESP8266 (using the Search function may expedite this). Click on Install. After installation, click on Close and then select your ESP8266 board from the Tools > Board: ... menu.
The app depends on the following libraries. They must either be downloaded from GitHub and placed in the Arduino 'libraries' folder, or installed as described here by using the Arduino library manager.
Download the app code from GitHub using the green Clone or Download button from the GitHub project main page and click Download ZIP. Decompress the ZIP file in your Arduino sketch folder.
The web app needs to be uploaded to the ESP8266's SPIFFS. You can do this within the Arduino IDE after installing the Arduino ESP8266FS tool.
With ESP8266FS installed upload the web app using ESP8266 Sketch Data Upload command in the Arduino Tools menu.
Then enter your wi-fi network SSID and password in the Secrets.h file, and upload the sketch using the Upload button.
The web app files can be gzip compressed before uploading to SPIFFS by running the following command:
gzip -r data/
The ESP8266WebServer will automatically serve any .gz file. The file index.htm.gz will get served as index.htm, with the content-encoding header set to gzip, so the browser knows to decompress it. The ESP8266WebServer doesn't seem to like the Glyphicon fonts gzipped, though, so I decompress them with this command:
gunzip -r data/fonts/
The firmware implements basic RESTful web services using the ESP8266WebServer library. Current values are requested with HTTP GETs, and values are set with POSTs using query string parameters. It can run in connected or standalone access point modes.