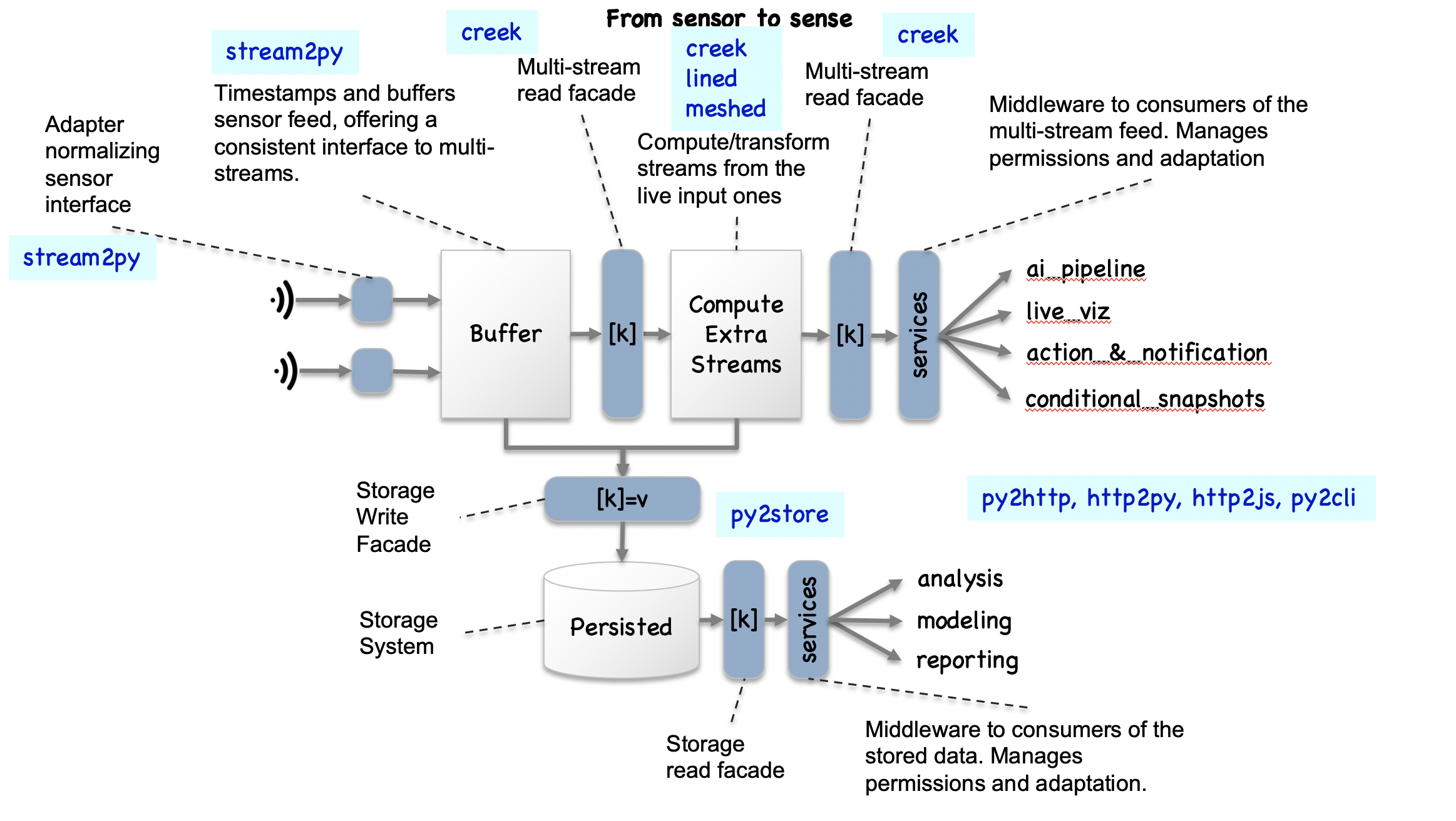
Build live stream tools
To install: pip install know
The tools are made to be able to create live streams of data (e.g. from sensors) and funnel them into proceses with a consistent interfaces. One important process being the process that will store all or part of the data, through a simple storage-system-agnositic facade.
proc = LiveProc(
source=Sources( # make a multi-source object (which will manage buffering and timing)
audio=AudioSource(...),
plc=PlcSource(...),
video=VideoSource(...),
),
services=Services( # make a multi-data service (and/or writer/transformer) object
storage=Store(...),
notifications=Notif(...),
live_viz=LiveViz(...),
),
... # other settings for the process (logging, etc.)
)
proc() # run the processWith a variety of sources, target storage systems, etc.
from know.audio_to_store import *
wfs = demo_live_data_acquisition(chk_size=100_000, end_idx=300_000, logger=print)
print(f"{len(wfs)=}")The end_idx=300_000 is there to automatically stop the demo after 300 thousand bytes are acquired
(at the default rates that's about 1.5 seconds).
If you specify end_idx=None, the process will run until you interrupt it.
Here's what's actually being fed to the demo when you don't specify any explicit live_source or store.
You can use this to try different combinations of specs out:
from know.audio_to_store import *
wfs = demo_live_data_acquisition(
live_source=LiveWf(
input_device_index=None, # if None, will try to guess the device index
sr=44100,
sample_width=2,
chk_size=4096,
stream_buffer_size_s=60,
),
store=mk_session_block_wf_store(
rootdir=None, # will choose one for you
# template examples: '{session}_{block}.wav' '{session}/d/{block}.pcm', '{session}/{block}', 'demo/s_{session}/blocks/{block}.wav'
template='{session}/d/{block}.pcm', #
pattern=r'\d+',
value_trans=int
),
chk_size=100_000,
end_idx=300_000,
logger=print
)
print(f"{len(wfs)=}")What you want to see above, is how you can easily change the folder/file template you use to store data.
Below, we'll also show how you can change the data storage system backend completely, using a mongo database instead!
Here, see how you can use MongoDB to store your data.
For this, you'll need to have a mongoDB server running locally,
and mongodol installed (pip install mongodol).
from know.audio_to_store import mk_mongo_single_data
def _cast_data_field_to_json_list(d):
return list(map(int, d))
play_nice_with_json = wrap_kvs(data_of_obj=_cast_data_field_to_json_list)
mongo_store = play_nice_with_json(
mk_mongo_single_data(
mgc='mongodol/test', # enter here, the `db_name/collection_name` you want to use (uses local mongo client)
key_fields=('session', 'block'),
data_field='data'
)
)
wfs = demo_live_data_acquisition(
live_source=LiveWf(
input_device_index=None, # if None, will try to guess the device index
sr=44100,
sample_width=2,
chk_size=4096,
stream_buffer_size_s=60,
),
store=mongo_store,
chk_size=100_000,
end_idx=300_000,
logger=print
)
print(f"{len(wfs)=}")