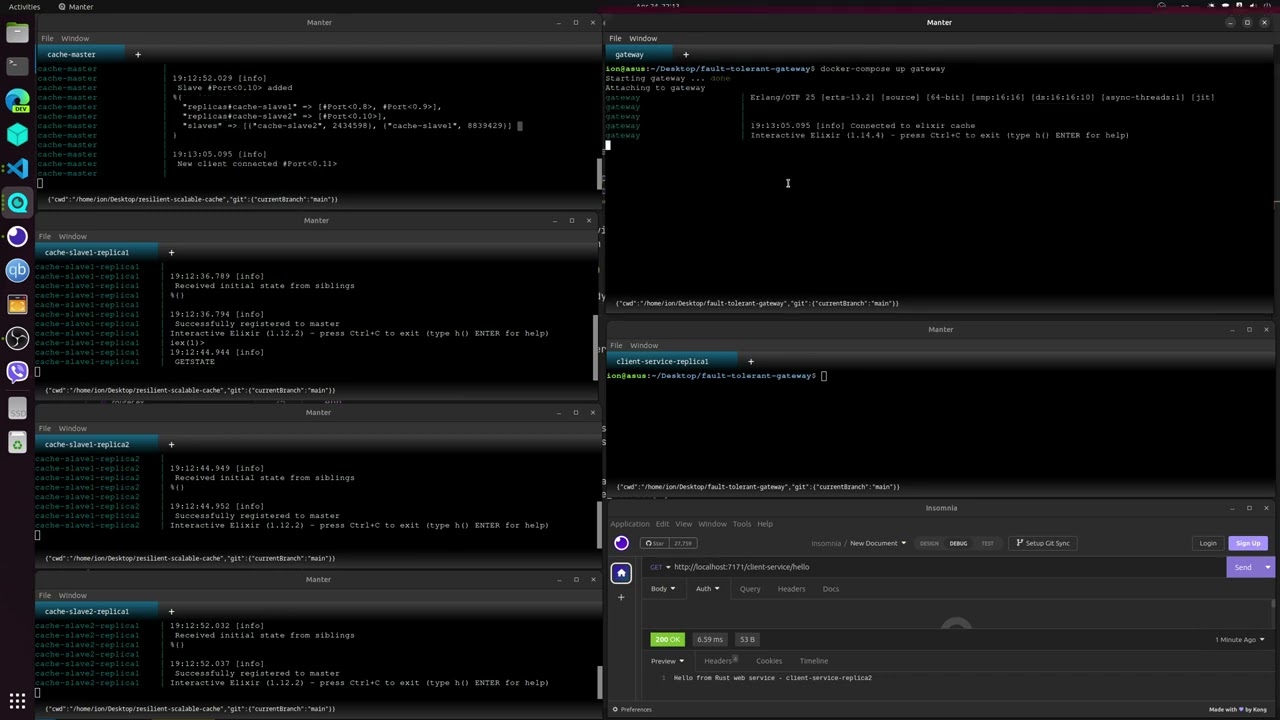
This project introduces a fault-tolerant gateway that functions as both a circuit breaker and a load balancer. It employs the resilient-scalable-cache as a key-value database.
The gateway is developed using the Elixir programming language, which inherently provides fault tolerance. Elixir allows developers to create applications that can automatically restart upon encountering errors, without losing their state and continuing to operate as if nothing happened. This resilience is due to Elixir's actor-based architecture.
The gateway maintains a Service Registry, which contains registered microservices responsible for executing business logic. Each microservice is required to register itself in the Gateway's Service Registry by calling the POST /register endpoint.
The Service Registry consists of keys stored in the resilient-scalable-cache, an alternative to Redis. The key name corresponds to the microservice name, and the values associated with the key are an array of references to the microservice replicas that the Gateway can use for redirecting requests.
For instance, consider a microservice named client-service. When a replica of this service starts, it sends a POST /register request to the Gateway, with the request body containing { "service": "client-service", "address": "the url to the replica" }. The Gateway then registers this microservice replica in the Service Registry by storing an array under the client-service key:
client-service: [{url to the replica, port, ...}]
The Gateway performs load balancing on replicas of the same microservice using the Service Registry. For example, when a call is made to the client-service through the Gateway, it employs the round-robin technique on the replicas stored under the client-service key.
Additionally, the Gateway serves as a circuit breaker. When forwarding a request to a microservice replica, if the Gateway detects a failed request, it records the failure in the cache. In the case of the client-service, when the Gateway detects a failed response from a replica, it creates a key called circuit-breaker#{the url to the replica} and sets its value to 1, indicating that one failure has occurred so far. After logging the failure, the Gateway proceeds to try the next replica until it finds a functional one. If a replica surpasses a predetermined failure threshold, it will be removed from the Service Registry.