IdParser.Core can be used to parse AAMVA-compliant driver's licenses and ID cards into objects that you can
work with. More information on the versions of the AAMVA standard can be found here.
More information on the D20 Data Dictionary can be found here.
- Include the using
using IdParser.Core;- Then you're off to the races!
var parseResult = Barcode.Parse(barcode);
Console.WriteLine(parseResult.Card.StreetLine1.Value); // "123 NORTH STATE ST."
Console.WriteLine(parseResult.Card.IssuerIdentificationNumber.Value.GetDescriptionOrDefault()); // "New York"
if (parseResult.Card is DriversLicense license)
{
Console.WriteLine(license.Jurisdiction.VehicleClass.Value); // "C"
}If a field fails to parse, you can inspect the field's raw value:
if (parseResult.Card.FirstName.HasError)
{
Console.WriteLine(parseResult.Card.FirstName.Error); // The error message, if any.
Console.WriteLine(parseResult.Card.FirstName.RawValue); // The raw value from the scanned ID text.
}You can iterate through all errors that occurred:
if (parseResult.Errors.Count > 0)
{
foreach (var error in parseResult.Errors)
{
// All errors have a Message describing what went wrong.
Console.WriteLine($"Error: {error.Message}");
// Element-level errors will have an Element ID and the element's raw value.
Console.WriteLine($"Element ID: {error.ElementId}");
Console.WriteLine($"Raw Value: {error.RawValue}");
}
}You can also check to see whether a field was present in the scanned ID text:
Console.WriteLine($"First Name present? {parseResult.Card.FirstName.Present}");Take a look at the unit test project for more examples and usage.
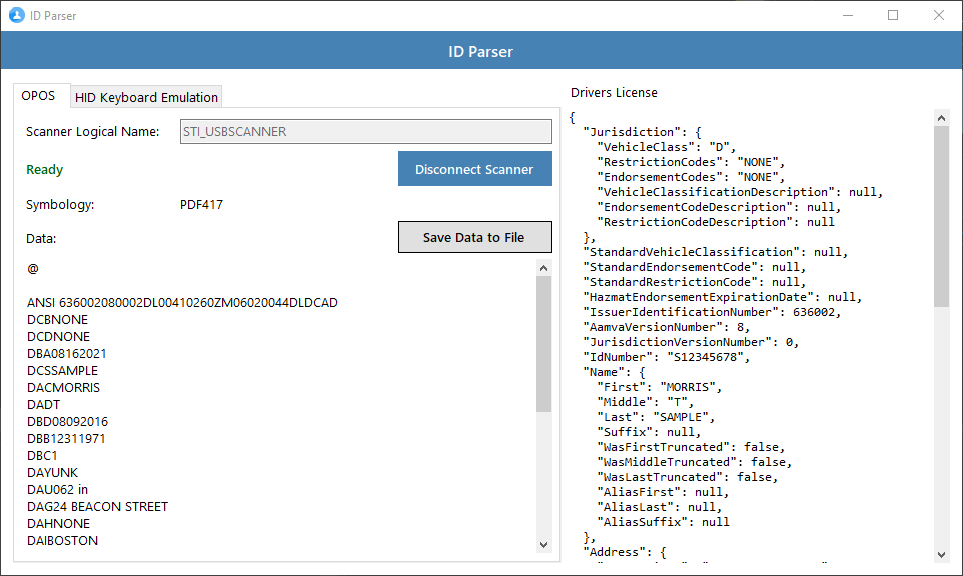
The IdParser.Core.Client project is a handy GUI application to help test and verify that an ID
will be parsed correctly. The app works with both OPOS and HID keyboard emulation scanners.
This is a fork of Connor O'Shea's IdParser library. Big thanks to him for all of his work.
The main changes I made for v1.0.0 of IdParser.Core are:
- Dropped support for
.NET Framework. If you need that, please use the originalIdParser. - Supports only
.NET 6and above. If you need support for earlier versions of.NET/.NET Core, please use the originalIdParser. - The parser classes are now static and no longer instantiated by
Activator.CreateInstance. This reduced memory allocations per call considerably, and also sped things up. - The
Abbreviation,Country, andDescriptionattribute values are now cached so that we don't have to repeatedly use reflection to get their values. - Unhandled parsing exceptions are now rethrown, regardless of what the caller passes for the validation level (
NoneorStrict). - Where possible, modernized the code base to use newer framework and language features, such as
Span<T>. - The return value of
Parseis now an object that returns both the ID card and a collection of any unknown element Ids. Parsenow accepts an optionalMicrosoft.Extensions.Logging.ILoggerFactoryparameter. When not null, the library will log to an instance ofILogger.