Project about sorting algorithms and Big O (200%) One of the bests project that I made! If you love algorithms and computer science! I should recommend to consider do it!
- At least four different sorting algorithms
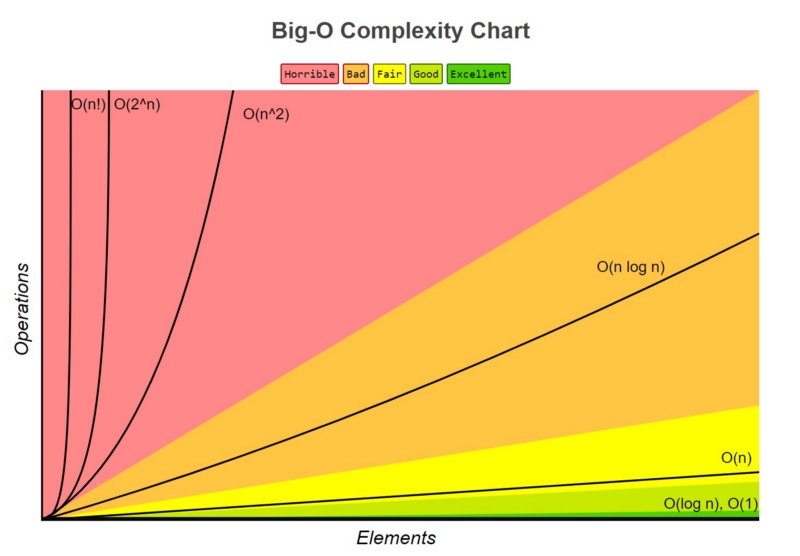
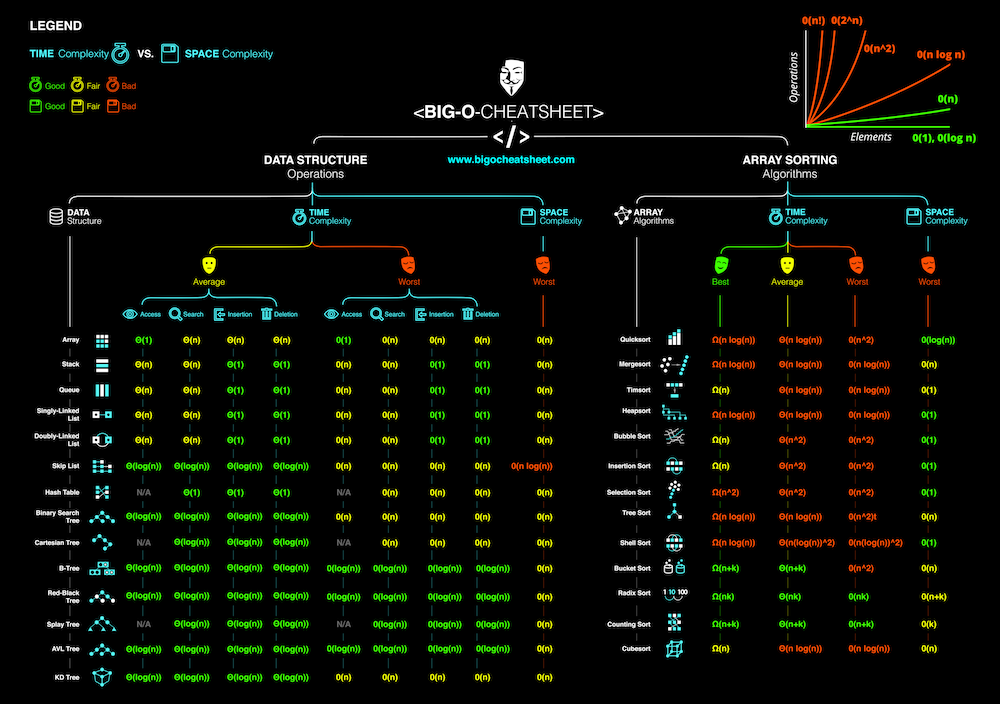
- What is the Big O notation, and how to evaluate the time complexity of an algorithm
- How to select the best sorting algorithm for a given input
- What is a stable sorting algorithm
- Sorting algorithm
- Big O notation
- Sorting algorithms animations
- 15 sorting algorithms in 6 minutes (WARNING: The following video can trigger seizure/epilepsy. It is not required for the project, as it is only a funny visualization of different sorting algorithms)
Before do it, I recommend you first design the algorithm in a whiteboard and take and consider:
- Behaviour when there equals value
- when is sorted
- when the pivot is not is not in the middle
This is important to calculate the Big O in the best, worst and avarage case The result og Big O calculation in the next exercises will be in this order:
- in the best case
- in the average case
- in the worst case
| ## | Sorting Algorithm | BigO of algorithm | Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Bubble sort | BigO for Bubble Sort | Prototype: void bubble_sort(int *array, size_t size). You’re expected to print the array after each time you swap two elements (See example below) |
| 1 | Insertion sort | BigO for Insertion Sort | Prototype: void insertion_sort_list(listint_t **list); You are not allowed to modify the integer n of a node. You have to swap the nodes themselves; You’re expected to print the list after each time you swap two elements (See example below) |
| 2 | Selection sort | BigO for Selection Sort | Prototype: void selection_sort(int *array, size_t size); You’re expected to print the array after each time you swap two elements (See example below) |
| 3 | Quick sort | BigO for Quick Sort | Prototype: void quick_sort(int *array, size_t size); You must implement the Lomuto partition scheme. The pivot should always be the last element of the partition being sorted. You’re expected to print the array after each time you swap two elements (See example below) |
| 4 | Shell sort - Knuth Sequence | Prototype: void shell_sort(int *array, size_t size); You must use the following sequence of intervals (a.k.a the Knuth sequence): n+1 = n * 3 + 1 = 1, 4, 13, 40, 121, ... ; You’re expected to print the array each time you decrease the interval (See example below). | |
| 5 | Cocktail shaker sort | BigO for cocktail sort | Prototype: void cocktail_sort_list(listint_t **list); You are not allowed to modify the integer n of a node. You have to swap the nodes themselves. You’re expected to print the list after each time you swap two elements (See example below) |
| 6 | Counting sort | BigO for counting sort | Prototype: void counting_sort(int *array, size_t size); You can assume that array will contain only numbers >= 0; You are allowed to use malloc and free for this task; You’re expected to print your counting array once it is set up (See example below); This array is of size k + 1 where k is the largest number in array |
| 7 | Merge sort | BigO for merge sort | Prototype: void merge_sort(int *array, size_t size); You must implement the top-down merge sort algorithm; When you divide an array into two sub-arrays, the size of the left array should always be <= the size of the right array. i.e. {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} -> {1, 2}, {3, 4, 5} ; Sort the left array before the right array ; You are allowed to use printf ; You are allowed to use malloc and free only once (only one call) |
| 8 | Heap sort | BigO for heap sort | Prototype: void heap_sort(int *array, size_t size); You must implement the sift-down heap sort algorithm ; You’re expected to print the array after each time you swap two elements (See example below) |
| 9 | Radix sort | Prototype: void radix_sort(int *array, size_t size); You must implement the LSD radix sort algorithm ; You can assume that array will contain only numbers >= 0; You are allowed to use malloc and free for this task ; You’re expected to print the array each time you increase your significant digit | |
| 10 | Bitonic sort | BigO for Bitonic Sort | Prototype: void bitonic_sort(int *array, size_t size); You can assume that size will be equal to 2^k, where k >= 0 (when array is not NULL …) ; You are allowed to use printf ; You’re expected to print the array each time you swap two elements (See example below) ; Output: see example |
| 11 | Quick Sort - Hoare Partition scheme | BigO | Prototype: void quick_sort_hoare(int *array, size_t size); You must implement the Hoare partition scheme. ; The pivot should always be the last element of the partition being sorted. ; You’re expected to print the array after each time you swap two elements |
| 12 | Dealer - Sort a deck of cards, deck.h | Write a function that sorts a deck of cards. Prototype: void sort_deck(deck_node_t **deck); You are allowed to use the C standard library function qsort or any other sorting algorithm, I use cocktail algorithm to implement the solution in this problem! |