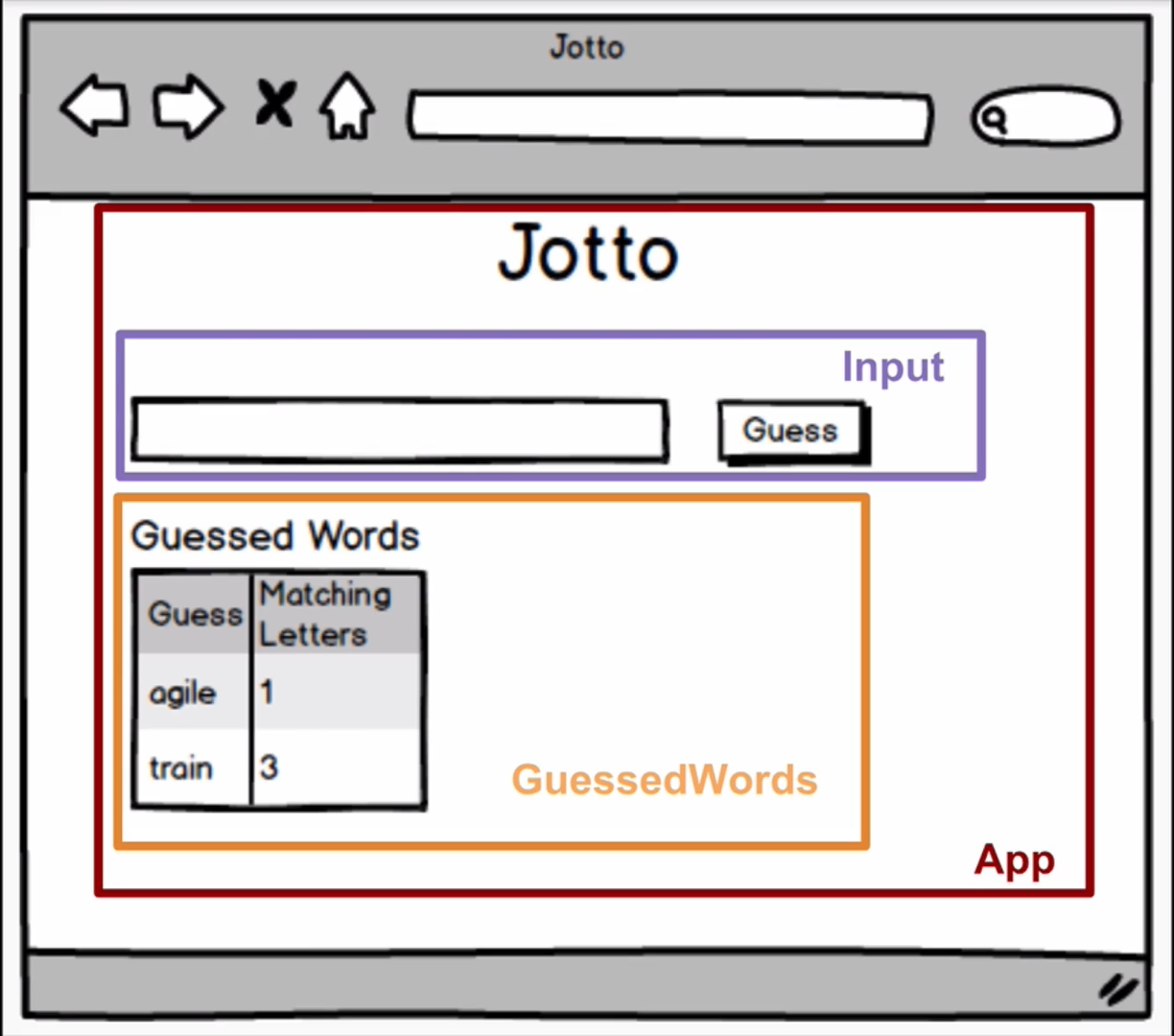
Basic React App game where user guesses random 5 letter word supplied by a server - used to demonstrate TDD and Enzyme+Jest testing
-
main- has base code for basic function and mock testsredux-testing- has code for Redux testingcontext-testing- has code for React Context testing
-
based on React Testing course by Bonnie Schulkin
-
https://www.udemy.com/course/react-testing-with-jest-and-enzyme/
- Jest in "Watch Mode" will only test files that have been updated since the last commit
-
Testing with props
- Hand down state from parents
- Don't need Redux or Context API
-
Set up common tools
- define functions in helper file
- Set up Enzyme for every file via Jest config
-
Use a localhost server to generate random 5 letter words for user to guess
- Will test server calls
-
Input: state-controlled field
- useState hook test
-
App: get secret word on mount
- useEffect hook test
-
Enzyme
-
Ezyme-React-Adapter-17
- npm install --save-dev enzyme @wojtekmaj/enzyme-adapter-react-17
-
Testing Prop Types
-
Runtime type checking for React props and similar objects.
-
You can use prop-types to document the intended types of properties passed to components. React (and potentially other libraries—see the checkPropTypes() reference below) will check props passed to your components against those definitions, and warn in development if they don’t match.
-
npm install --save prop-types
-
-
Check Prop Types
-
Manually check PropTypes-compatible proptypes, returning any errors instead of logging them to console.error.
-
This function is more suitable for checking propTypes in unit tests than mocking console.error, avoiding some serious problems with that approach.
-
npm install --save-dev check-prop-types
-
Example: test('does not throw warning with expected props', () => { const expectedProps = {successState: false}; const propError = checkPropTypes(Congrats.propTypes, expectedProps, 'prop', Congrats.name); expect(propError).toBeUndefined(); })
-
-
- Test user flow - testing what the app does, not how
- Independent of code implementation
- Can be used for Redux or Context
- Initial state: props to send to components:
successStatesecretWordguessedWords
-
-
Jest methods on
testanddescribe -
.only: only run test/describe in this file with.onlyspecified -
.skip: don't run any test/describe in this file with.skipspecified- Good for isolating tests - such as when we have a particularly tricky code impl to test and we just want to isolate that one test until we get it passing
- or skipping tests when we may not have that part of the code or app functionality ready to test yet but we know the expected behavior to test for (and thus, can write tests to be skipped)
-
.todois for test to remind yourself to write laterdescribe('invalid word guessed', () => { test.todo('guessedWords table does not get another row'); });
-
-
-
npm install axios
-
getSecretWordin both Context and Redux Implementations- Actual function slightly different
- In Redux we're adding that secret word to the global state
- in Context we're setting the App level state
- Both functions will call
axios
- Actual function slightly different
-
Test code using
moxiosis the same for both
-
-
-
npm install --save-dev moxios
-
Random word server is necessary for actual app, but we don't want to test the server when testing the app
-
Using Moxios lets us test just the app and mock axios calls
-
How Moxios works
- Test installs Moxios
- Axios will now send requests to Moxios instead of HTTP
- Test specifies Moxios response to return to Axios to return to our app
- Test installs Moxios
-
Moxios Syntax
-
Test calls
moxios.install()- Sets moxios as the axios adapter
- Routes axios calls to moxios instead of http
-
Can pass axios Instance to
moxios.install()- Use your configured settings
- If not instance, leave param blank for default settings
-
Call
moxios.wait()during test-
watches for axios calls
-
Sends response using the callback passed to
.wait()moxios.wait(() => { const request = moxios.requests.mostRecent(); request.respondWith({ status: 200 response: secretWord }); });
-
-
-
-
getSecretWordreturns a promise from Axios- Put assertion in
.then()callback after runninggetSecretWord()- Assertion will run after promise resolves
- So Much Asynchronicity!
moxios.wait()is also asynchronous- More important than ever, when testing asychronous functions, to see our tests fail
- It is very easy to make a mistake such that a test completes before async resolves
- Leaving the impression that the test passed when really the async function never even resolved!
- Tests can and do pass even though assertions fail!
- If you're not careful, the test can exist before the promise resolves
- Since the test function is a regular JS function, when it calls the async call, the test function may finish without error before the async call
- This is why it's important to see your async tests fail
- If you can see the test fail, you know the assertion is being run before the test function completes, and thus the async call is resolving
- Make sure to return your function call
getSecretWord()in the test- this way we know the test won't finish before async promise resolves
- Make sure to call assertion in the
.then()callback from your function call- Can also use async and await
- won't run until
getSecretWord()async promise resolves
- Make sure you can see the tests fail
-
-
Before, we mocked pieces of or methods of modules individually:
React.useState()by overriding the useState method -
That was done test-file by test-file
- reasonable: sometimes we wanted to mock, sometimes we didn't
-
We are going to want to mock the
getSecretWordaction everywhere- never want to go across the network except maybe for End-to-End testing
-
For this: mock the module globally so it will automatically be mocked for all of our files
-
- Global mock file can be used by any test file
- Located in folder with special name:
__mocks__ - Useful if you want to mock every time ( or almost every time)
- Test files import from
__mocks__code instead of actual module code
-
-
For any node module
- At same level as the
node_modulesfolder- jotto-redux/
- mocks
- react.js
- node_modules
- src
- mocks
- jotto-redux/
- At same level as the
-
For project modules
- At the same level as the module
- src
- App.js
- App.test.js
- mocks
- helpers.js
- helpers.js
- src
- At the same level as the module
-
-
__mocks__file that provides mocks- mocking a node module (ex. 'react')
- mocks automatically unless you explicitly unmock at the top of the test file
- mocking a project module
- will not mock unless you explicitly mock at the top of the test file
- mocking a node module (ex. 'react')
-
- Issue with location of node modules
__mocks__folder needs to be at top level ofsrc, not same level asnode_modules- link to issue: facebook/create-react-app#7539
- Mocks reset automatically before each test
- This is a problem if you've specified return value
- Issue with location of node modules
-
- React hook that runs function on component reload, every reload
- or specify to re-run only when certain values change
- "re-run when an empty array changes" = run only on mount
- equivalent of
componentDidMount - example - we wouldn't want to
secretWordto change every time the player guessed a word! No one would play that game
- equivalent of
- use Enzyme
mountnotshallowforuseEffectuseEffectnot called onshallow- enzymejs/enzyme#2086
- Mock module containing
getSecretWord- set up global mock to avoid network calls in tests
- Clear mock using
.clearMock()after each test so we know that we dont have any side effects from any previous tests- mock tracks calls cumulatively until reset
secretWordshould not update on App update- evil game - word changes every guess
- Notes: we are not testing that React's useEffect hook works properly
- That's React's job
- We are testing that our code is using the hook properly
- Will trigger update with Enzyme
setProps()update()doesnt triggeruseEffect()- issue enzymejs/enzyme#2254
- React hook that runs function on component reload, every reload
-
-
- Shared State is used for props needed by lots of components
- Global settings (language, visual theme, user properties)
- Deeply nested components that need access to certain props that their ancestors don't
- Redux vs Context API
- Simple apps: Context works great
- Sophisticated apps: Redux has better tools
- optimization for high frequency updates or state changes
- rich ecosystem for developers
- tools for debugging
- middleware for automatic code upon any action
- for example, logging events to analytics pipelines
- Shared State is used for props needed by lots of components
- npm install --save redux react-redux
ToBe() vs toStrictEqual()
-
If you're testing immutable types like an object or an array use expect(object).toStrictEqual() instead of toBe()
-
If you're testing mutable types like a number or a String, toBe() will work fine
- Also
toStrictEqual()is a deep equal so it will not only compare the top level properties of an object but also any values contained within
- Also
-
- Reducer is a function (previousState, action) => newState
- Undefined state
- return expected initial state (success =
false)
- return expected initial state (success =
- Unknown action
- return whatever state was passed in as an argument
CORRECT_GUESSaction type- return
true
- return
-
-
get
successpiece of state- whether or not to display input box and button
- passed as a prop when creating Input component
-
Refactor Input component to receive
successviauseSelector -
Also will need to call action creator when a word is guessed (set)
- that will come in with Redux Thunk
-
- useSelector is a way to access state using a functional component
- no need to use class-based components or
connectto higher order component (HOC)
- no need to use class-based components or
- useSelector takes a function as an argument, transforms the state and then returns only the piece of state we need
- For Input, we want the success piece of state
state=>state.success
- useSelector is a way to access state using a functional component
-
- Two choices for testing state accessed with
useSelector:- wrap component in
Providerand usemountmount(<Provider> <Input /> </Provider>)- Pros: closer to actual code, cleaner, more readable
- Cons: less isolated, slower if many children -
<Provider>requires a store and a store requires a test store factory (see testUtils.js)
- mock
useSelector- Pros: isolated, faster if many children
- Cons: farther from actual code, need to duplicate selector function, can be messy, confusing leading to testing errors
- wrap component in
- Two choices for testing state accessed with
-
- npm install redux-thunk
- More flexibility for action creators
- Return function instead of an action
- Thunk = function that returns a function
- Can dispatch multiple actions
- Can access current state
- Perfect for our
guessWordaction creator- It will always dispatch
GUESS_WORDwith every user guess - If guessed word is correct, it will also dispatch
CORRECT_GUESS - Lets us access
successpiece of state - For determining whether or not to dispatch
CORRECT_GUESS
- It will always dispatch
-
store.dispatch()- Takes an action creator
store.getState()- Return state object
- Useful for assertions
-
- Create a store with initial state
- Will contain
secretWord
- Will contain
- Dispatch action creator
store.dispatch(guessWord())
- Check state
- Use Jest's
.toEqual()to test state object as a whole - Inside our test, we'll make an object of the state as we think it should be and compare it to the actual state from the store
- Use Jest's
- Create a store with initial state
-
- Because we are testing action creators and reducers together
- Where to put the tests?
- new file: src/integration.test.js
- would separate into many test files for a larger app
-
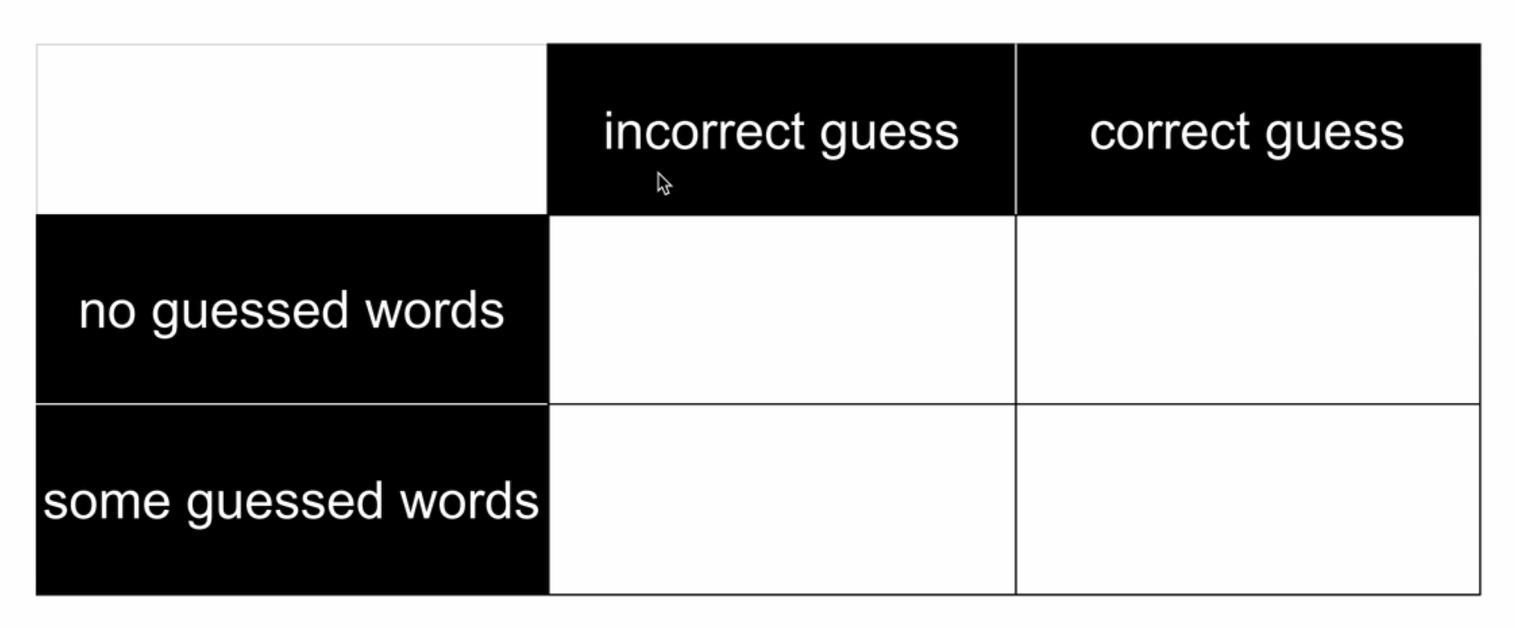
- This matrix shows each of the code scenarios we want to test
- incorrect guess with no guessed words
- incorrect guess with some guessed words
- correct guess with no guessed words
- correct guess with some guessed words
- We can use this matrix to help us set up our tests
- This matrix shows each of the code scenarios we want to test
-
-
-
- Functional "guess word" tests
- We need to:
- adapt
setupfunction- use
storeFactoryto create store from initial state - Wrap App in Provider with store as a prop
- use
- Add
guessWordaction dispatcher to Input component- use Redux
useDispatch()hook
- use Redux
- Update
Appcomponent to getguessedWordsfrom state
- adapt
-