ROS (Kinetic and Melodic) packages developed at the VisioTec research group, CTI Renato Archer, Brazil. Further information about this group can be found here.
Click on the thumbnails to watch the videos on YouTube.
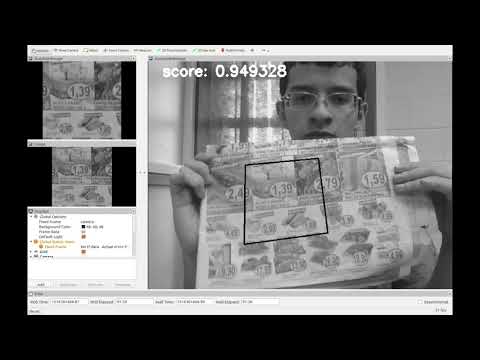
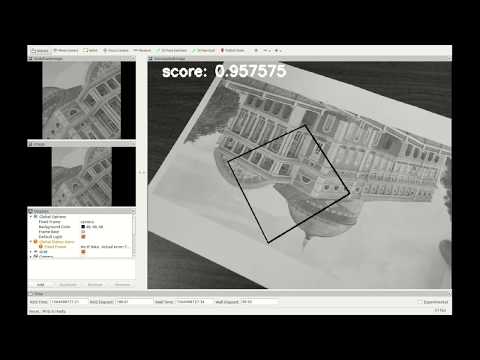
- Intensity-based visual tracking with full 8-DoF homography
- Robust intensity-based visual tracking with full 8-DoF homography and occlusion handling
- Unified intensity- and feature-based visual tracking with full 8-DoF homography
If you use this work, please cite this paper:
@inproceedings{Nogueira2020TowardsAU,
title={Towards a Unified Approach to Homography Estimation Using Image Features and Pixel Intensities},
author={Lucas Nogueira and Ely Carneiro de Paiva and Geraldo F. Silveira},
booktitle={International Conference on Autonomic and Autonomous Systems},
pages={110-115},
year={2020}
}
There is a technical report available here describes the underlying algorithm and its working principles.
@TechReport{nogueira2019,
author = {Lucas Nogueira and Ely de Paiva and Geraldo Silveira},
title = {Visio{T}ec robust intensity-based homography optimization software},
number = {CTI-VTEC-TR-01-19},
institution = {CTI},
year = {2019},
address = {Brazil}
}
These packages were tested on:
- version (tag) 2.1 - ROS Neotic with Ubuntu 20.04 and OpenCV 4.2
- version (tag) 2.0 - ROS Melodic with Ubuntu 18.04.
- version (tag) 1 - ROS Kinetic with Ubuntu 16.04
This package depends on the OpenCV module xfeatures2d. It is necessary to install OpenCV from source, and configure its compilation to include it, because this module is not compiled by default or included in the opencv packages from the Ubuntu distribution.
(Exception: in ROS Kinetic/Ubuntu 16.04, this module is installed by default with the ROS packages, and therefore no further steps are needed.)
Here there are instructions about OpenCV instalation, for ROS Melodic:
- https://answers.ros.org/question/312669/ros-melodic-opencv-xfeatures2d/
- https://linuxize.com/post/how-to-install-opencv-on-ubuntu-18-04/
To simplify, here are direct URLs for the 4.2 versions of opencv and opencv_contrib repos: https://github.com/opencv/opencv/archive/refs/tags/4.2.0.tar.gz https://github.com/opencv/opencv_contrib/archive/refs/tags/4.2.0.tar.gz
and this is the cmake command used to compile opencv (the ENABLE_NONFREE option enables compiling the feature detectors; and the path on the EXTRA_MODULES_PATH option must point to your opencv_contrib directory.
cmake -D CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=RELEASE
-D CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local
-D INSTALL_C_EXAMPLES=ON
-D INSTALL_PYTHON_EXAMPLES=ON
-D OPENCV_GENERATE_PKGCONFIG=ON
-D OPENCV_EXTRA_MODULES_PATH=~/opencv_build/opencv_contrib-4.2.0/modules
-D OPENCV_ENABLE_NONFREE=ON ..
-D BUILD_EXAMPLES=ON ..
The dependency on xfeatures2d is necessary because of the Feature detection algorithm. If you just want to use the intensity-based algorithms, you may use the v1 version of this repo, although it is dated.
Install the usb_cam driver from ROS repositories.
sudo apt-get install ros-[kinetic|melodic]-usb-cam
Setup a ROS workspace.
mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src
Install the VisioTec Library. It is a standalone cpp library, non-ROS.
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/visiotec/vtec.git
cd vtec
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
Install the ROS packages
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/visiotec/vtec_ros.git
cd ~/catkin_ws
catkin_make
source devel/setup.bash
Tracks a planar object in an image sequence. This uses a pure intensity-based homography estimation algorithm.
-
camera/image(sensor_msgs/Image)The incoming image stream from the camera.
-
annotated_image(sensor_msgs/Image)The image stream annotaded with the tracked image region and the score.
-
stabilized_image(sensor_msgs/Image)The warped image patch from the image stream, that tries to match to the reference image patch.
-
reference_image(sensor_msgs/Image)The reference template extracted from the reference image file.
-
tracking(vtec_tracker/TrackingResult)Information about the tracking, including the estimated homography and the quality score.
-
image_topic(string, default: "usb_cam/image_raw")The name of the image input topic.
-
bbox_pos_x(int, default: 200)The x coordinate of the upper left corner of the region of interest in the reference image.
-
bbox_pos_y(int, default: 150)The y coordinate of the upper left corner of the region of interest in the reference image.
-
bbox_size_x(int, default: 200)The length in pixels of the region of interest along the x direction.
-
bbox_size_x(int, default: 200)The length in pixels of the region of interest along the y direction.
-
max_nb_iter_per_level(int, default: 5)Maximum number of optimization iterations per pyramid level.
-
max_nb_pyr_level(int, default: 2)Maximum number of pyramids levels.
-
sampling_rate(double, default: 1.0)The sampling rate used to sample points used in the optimization process. 1.0 means 100% of the points are used.
-
homography_type(string, default: "full")Specifies the type of homography to be considered by the optimization algorithm. The options are: "full", "affine" and "stretch".
-
robust_flag(bool, default: "false")Set this to true to enable robust mode. This will try to detect partial occlusions on the current image and discard that information from the estimation procedure.
Tracks a planar object in an image sequence. Uses the Unified intensity- and feature-based homography estimation algorithm.
-
camera/image(sensor_msgs/Image)The incoming image stream from the camera.
-
annotated_image(sensor_msgs/Image)The image stream annotaded with the tracked image region and the score.
-
stabilized_image(sensor_msgs/Image)The warped image patch from the image stream, that tries to match to the reference image patch.
-
reference_image(sensor_msgs/Image)The reference template extracted from the reference image file.
-
tracking(vtec_tracker/TrackingResult)Information about the tracking, including the estimated homography and the quality score.
-
image_topic(string, default: "usb_cam/image_raw")The name of the image input topic.
-
bbox_pos_x(int, default: 200)The x coordinate of the upper left corner of the region of interest in the reference image.
-
bbox_pos_y(int, default: 150)The y coordinate of the upper left corner of the region of interest in the reference image.
-
bbox_size_x(int, default: 200)The length in pixels of the region of interest along the x direction.
-
bbox_size_x(int, default: 200)The length in pixels of the region of interest along the y direction.
-
max_nb_iter_per_level(int, default: 5)Maximum number of optimization iterations per pyramid level.
-
max_nb_pyr_level(int, default: 2)Maximum number of pyramids levels.
-
sampling_rate(double, default: 1.0)The sampling rate used to sample points used in the optimization process. 1.0 means 100% of the points are used.
-
fb_factor(double, default: 1.0)This factor impacts the weighting of the feature-based component in the optmization cost function. The FB weight is given by: 1-exp(-fb_factor*fb_cost). In summary, increasing this value will give a larger weight to the FB component.
Download the dataset from here: newspaper dataset
Open two terminal windows, and launch in the first one the tracker node with:
roslaunch vtec_tracker ibg_tracker.launch
In the other terminal, navigate to the directory where you downloaded the dataset, decompress and play the bagfile with:
rosbag decompress vtec_test_tracker.bag
rosbag play vtec_test_tracker.bag
Now you should see in RViz the tracking process using the default parameters from the launch file.
Download the dataset from here: theater dataset
Open two terminal windows, and launch in the first one the tracker node with:
roslaunch vtec_tracker ibg_tracker.launch config_file:=config_theater.yaml
In the other terminal, navigate to the directory where you downloaded the dataset, decompress and play the bagfile with:
rosbag decompress vtec_tracker_theater.bag
rosbag play vtec_tracker_theater.bag
Now you should see in RViz the tracking process using the default parameters from the launch file.
Download the dataset from here: occlusion dataset
Open two terminal windows, and launch in the first one the tracker node with:
roslaunch vtec_tracker ibg_tracker.launch config_file:=config_robust.yaml
In the other terminal, navigate to the directory where you downloaded the dataset, decompress and play the bagfile with:
rosbag decompress vtec_occlusion.bag
rosbag play vtec_occlusion.bag
Now you should see in RViz the tracking process using the parameters from the launch file.
Download the dataset from here: unified dataset
Open two terminal windows, and launch in the first one the tracker node with:
roslaunch vtec_tracker unified_tracker.launch
In the other terminal, navigate to the directory where you downloaded the dataset, decompress and play the bagfile with:
rosbag decompress vtec_unified.bag
rosbag play vtec_unified.bag
Now you should see in RViz the tracking process using the parameters from the launch file.
Open a terminal window and launch the tracker node:
roslaunch vtec_tracker tracker_live.launch
A Rviz window will pop-up with the camera images. In the terminal window where you issued the roslaunch command, press the S key to start tracking. This will select a bounding box in the current frame to be tracked. You can press S again anytime to restart the tracking process.
If you want to enable the robust to unknown occlusion mode, use the following command instead:
roslaunch vtec_tracker ibg_tracker_live_occlusion.launch
If you want to use the unified IB+FB algorithm, use the following command instead:
roslaunch vtec_tracker unified_tracker_live.launch
- IBGHO Technical Report: vtec_ibgho_TR.pdf
- VisioTec C++ Libraries: https://github.com/visiotec/vtec
- Geraldo Silveira's website: https://sites.google.com/site/geraldofsilveira/
This work was supported in part by the CAPES under Grant 88887.136349/2017-00, in part by the FAPESP under Grant 2017/22603-0, and in part by the InSAC (CNPq under Grant 465755/2014-3 and FAPESP under Grant 2014/50851-0).
Please report bugs and request features using the Issue Tracker.