Model — View — ViewModel (MVVM)
The separate code layers of MVVM are:
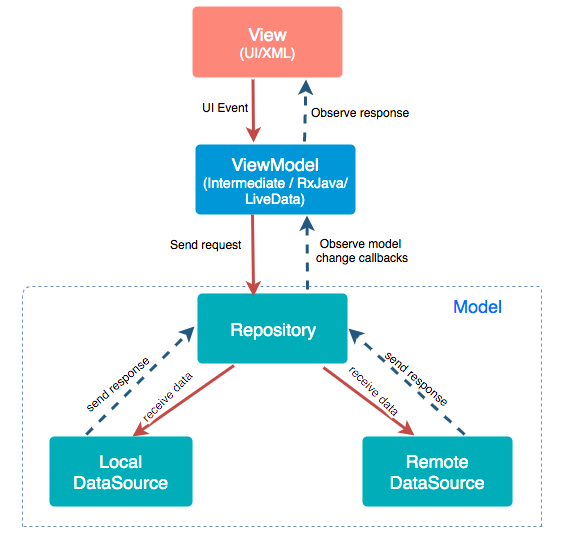
Model: This layer is responsible for the abstraction of the data sources. Model and ViewModel work together to get and save the data.
View: The purpose of this layer is to inform the ViewModel about the user’s action. This layer observes the ViewModel and does not contain any kind of application logic.
ViewModel: It exposes those data streams which are relevant to the View. Moreover, it servers as a link between the Model and the View.
MVVM pattern has some similarities with the MVP(Model — View — Presenter) design pattern as the Presenter role is played by ViewModel. However, the drawbacks of the MVP pattern has been solved by MVVM in the following ways:
1.ViewModel does not hold any kind of reference to the View.
2.Many to 1 relationship exist between View and ViewModel.
3.No triggering methods to update the View.
Ways to Implement MVVM in the Project
There are 2 ways to implement MVVM design pattern in Android projects:
1.Using the DataBinding library released by Google
2.Using any tool like RxJava for DataBinding.