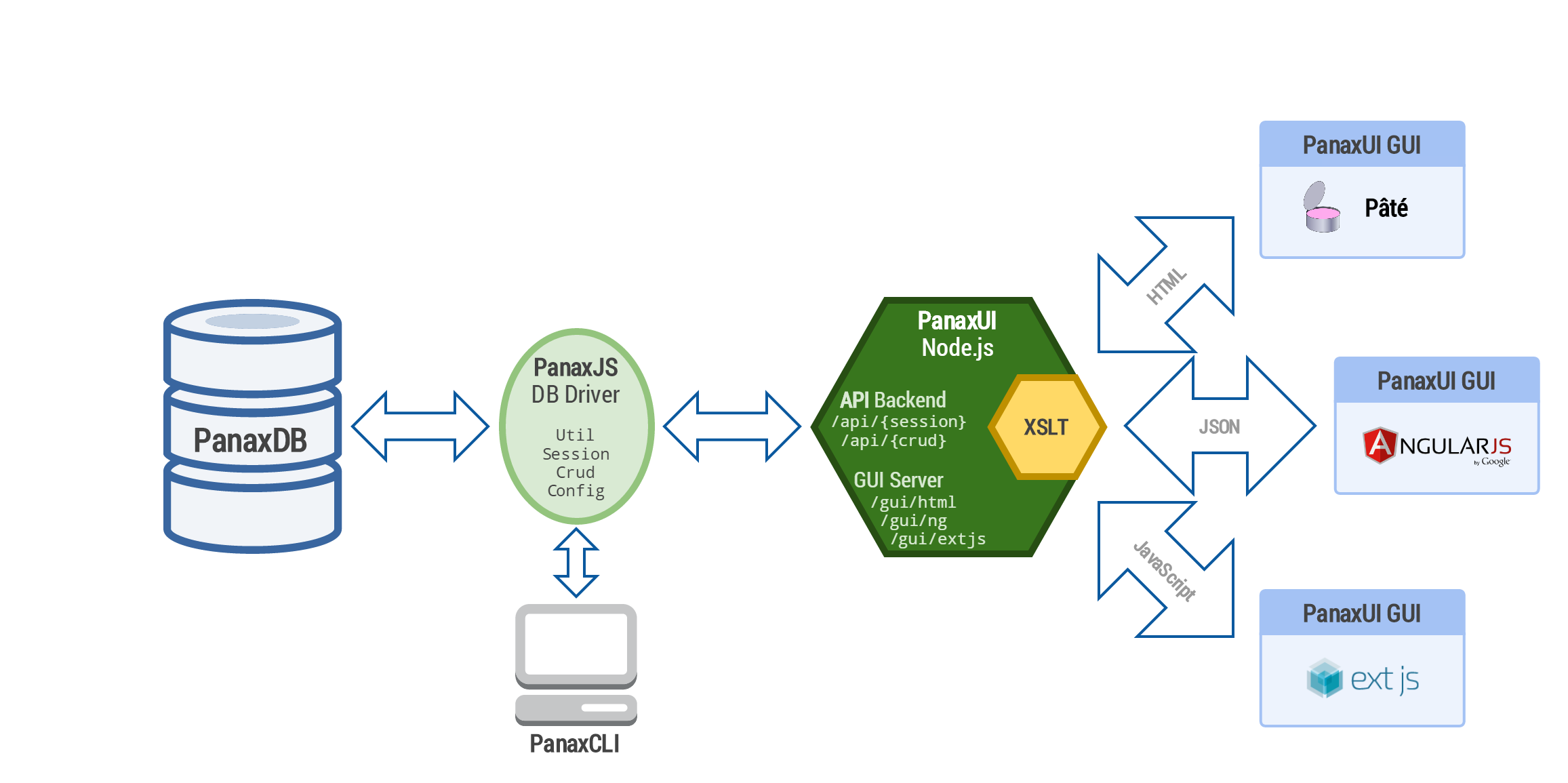
Panax is a framework for generation of business applications based on solid relational data models.
A detailed configuration-driven approach allows a high customization level and complex business-rules.
Every change is reflected immediately in the resulting app, allowing agile prototyping.
Panax' aim is to be agnostic of database vendor, backend and user interface, exploiting state-of-the-art technologies, like Node.js and AngularJS, and allowing high extensibility.
See: Wiki:Panax' Dataflow
Full API documentation available in: http://panax.readme.io/
PanaxDB is the core technology of Panax, which is an enhancement layer (add-on) for your relational database.
It provides an API to interact with the database adding several super powers:
- Advanced scaffolding
- Metadata heuristics
- Automation capabilities
- Configuration over coding
- .. among others
More info: Wiki:PanaxDB
A Panax Entity consist of 3 parts:
- Fields: Contain all the columns' related metadata.
- Layout: UI representation: order, grouping, displaying, etc.
- Data: Data model itself.
Example call:
getXmlData @TableName='Employee', @ControlType=formView, @Mode=readonly,
@Filters='Id=377', @output='json', @getStructure=1, @getData=1
Example XML output:
<Employee ...>
<px:fields>
<Id fieldName="Id" Column_Name="Id" isPrimaryKey="1" isIdentity="1" dataType="int" length="10" isNullable="0" supportsInsert="1" supportsUpdate="1" headerText="Id" controlType="default" />
<Name fieldName="Name" Column_Name="Name" isPrimaryKey="0" isIdentity="0" dataType="nvarchar" length="30" isNullable="0" supportsInsert="1" supportsUpdate="1" headerText="Name" controlType="default" />
<Joined fieldName="Joined" Column_Name="Joined" isPrimaryKey="0" isIdentity="0" dataType="date" isNullable="0" supportsInsert="1" supportsUpdate="1" headerText="Join Date" controlType="date" />
</px:fields>
<px:layout>
<px:tabPanel>
<px:tab name="General">
<px:field fieldName="Name" />
</px:tab>
<px:tab name="Details">
<px:field fieldName="Joined" />
</px:tab>
</px:tabPanel>
</px:layout>
<px:data>
<px:dataRow>
<Id value="377" text="377" />
<Name value="John Doe" text="John Doe" />
<Joined value="2014-06-08 00:00:00" text="08/06/2014" />
</px:dataRow>
<px:dataRow>
<Id value="455" text="455" />
<Name value="Sarah Connor" text="Sarah Connor" />
<Joined value="2034-01-01 00:00:00" text="01/01/2034" />
</px:dataRow>
<px:dataRow>
...
</px:dataRow>
</px:data>
</Employee>
Example UI output with ExtJS:
[coming soon]
Example UI output with AngularJS:
[coming soon]
Data model has implicit business rules that can be defined with a combination of the following features:
- Relationships (1-1, 1-N, N-M)
- Data Types (str, int, custom made, etc)
- Properties (nullable, primary keys, unique keys, descriptions, extended, etc)
Panax' heuristics detect this metadata and adapts the entity model accordingly.
[coming soon]
Explicit business rules can be defined via:
- Panax Configurations applied to entities
- Programmability at database level (constraints, triggers, etc)
XPath-like configurations to change XML output
Examples:
> panax db config...........
JavaScript abstraction module used primarly by PanaxUI to communicate with PanaxDB
User interface modules for Panax
More info: Wiki:PanaxUI
[wip]
[wip]
Command-line interface
[wip]
See: Wiki: PanaxCLI Usage
| Old | New proposal | Description |
|---|---|---|
Field |
Database Column | |
Table |
Database Table | |
Schema |
Database Schema | |
Instance |
Database Instance | |
Catalog |
Entity |
A consumable database unit. Expressed as: [InstanceName.][SchemaName.]TableName |
Metadata |
Implicit and explicit information about an Entity | |
Fields |
Metadata form Entity' fields | |
Layout |
An ordered representation (ex. form, grid) from Entity' fields | |
Structure |
Combination of Entity' Fields + Layout | |
Data |
DataModel? |
Actual data from Entity' fields |
Mode |
A way to interact with a |
|
ControlType |
A representation (ex. graphical) of an |