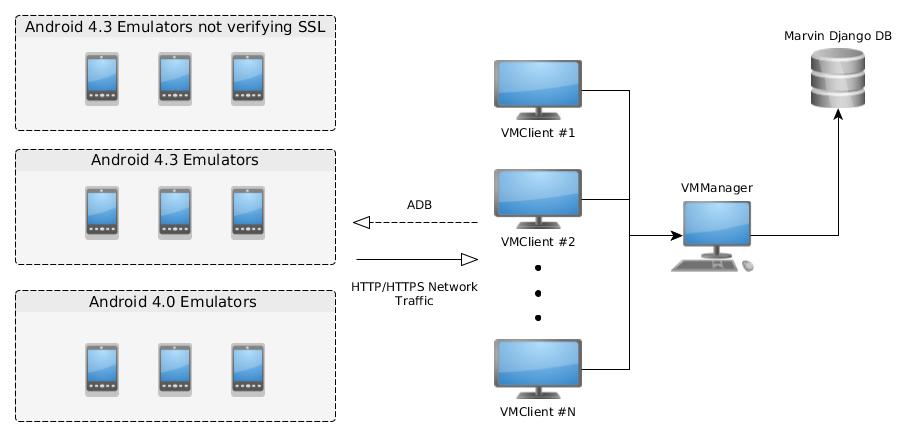
Dynamic android vulnerability scanner using OpenNebula and Android-x86 emulators.
Version: 0.01
Vulnerabilities analyzed dynamically are:
- JAVASCRIPT_INTERFACE
- PHONEGAP_JS_INJECTION
- PHONEGAP_CVE_3500_URL
- SSL_CUSTOM_TRUSTMANAGER
- SSL_CUSTOM_HOSTNAMEVERIFIER
- SSL_ALLOWALL_HOSTNAMEVERIFIER
- SSL_INSECURE_SOCKET_FACTORY
- SSL_WEBVIEW_ERROR
- WEBVIEW_FILE_SCHEME
Also it checks for new vulnerabilities that might be found while searching for others:
- ZIP_PATH_TRAVERSAL
- INSECURE_TRANSMISSION
- INSECURE_STORAGE
VMManager is in charge of searching new vulnerabilities to be analyzed in Marvin's Django database.
VMClients receive the app and type of vulnerability to analyze and emulator to use from VMManager. It uses ADB to connect to the emulator and start the analysis. It also configures the emulator to act as its gateway to intercept HTTP/HTTPS requests.
VMClients uses a custom fuzzer MarvinToqueton developed for interacting with the application to try triggering the vulnerabilities.
The emulators are running Android 4.3 x86 because of Cydia Substrate support. The project is using Android-x86 images.
There are 3 types of emulator:
- Emulators with no SSL verification
- Emulators with normal SSL verification (They are used to check if an application does proper SSL verification)
- Emulators running ICS 4.0 (Used for exploiting Javascript Interface vulnerability)
VMManager configurations are in settings.py:
NET_ID = 1 #ID used for OpenNebula virtual network
#credentials for RPC
ONE_IP = "http://IP:2633/RPC2"
ONE_CREDS = "" #OpenNebula xml RPC credentials
ELASTIC_SEARCH_SERVER = "ELASTIC_SEARCH_IP_ADDRESS"
DOWNLOAD_APK_SITE = "http://FRONTEND_IP_ADDRESS/frontpage/"
ANDROID_VM_POOL = {"NONSSL":{"NON_SSL_EMULATOR_IP"},"SSL":{"EMULATOR_IP"},"JAVASCRIPTINTERFACE":{"ICS_EMULATOR_IP"}}
IMPORTANT: Under the django_support directory, also configure the settings.py file with the corresponding SECRET_KEY, database password and BungieSearch URL from Marvin-frontend configuration.
VMClient configurations are also in the settings.py file:
VM_MANAGER_IP = 'VMMANAGER_IP_ADDRESS:8082'
REPORTER_IP = 'localhost:8081'
DEBUG_MODE = False
#Some fuzzer configurations that can be modified in Marvin-toqueton project.
Start the server with:
python VMManager.py
And VMClients with:
./client.sh
Marvin dynamic analyzer obtains the next app to analyze from the pool of unverified vulnerabilities on Marvin's database. If you want to run an analysis on a single app you can change the variable DEBUG_MODE to True in settings.py of the client. Then you can run an analysis with:
python VMClient.py [VULNERABILITY_ID] [PACKAGE-NAME/FILE-NAME] '''{"emulator":"EMULATOR_IP_ADDRESS","count":0}'''
In the case of PHONEGAP_CVE_3500_URL, you must also include the parameter "activity" with a reference to the initial application activity. If you only want to run checks against vulnerabilities not found statically such as ZIP path traversal, insecure storage and insecure transmission use "dummy" as the vulnerability ID.
IMPORTANT: The filename of the APK must be the same as the package name.
VMManager and VMClient can use any Linux virtual machine hosted in OpenNebula. Authors used ttylinux - kvm from OpenNebula Marketstore as template.
Run to install dependencies:
pip install bungiesearch
sudo apt-get install python-mysqldb
apt-get install default-jre
apt-get install python-django
Run to install dependencies:
apt-get install mitmproxy
Download from the Android-x86 site the ISO for 4.3 or 4.0 release. Install it in a disk with your favorite virtualization tool. Authors used VirtualBox.
Convert the installed image to KVM qemu's format in order to support OpenNebula's snapshot feature. You can use the following command:
qemu-img convert -O qcow2 original-image image-converted.qcow
Upload the image to OpenNebula and create a new template for the emulator.
Example of template:
CONTEXT=[NETWORK="YES",SSH_PUBLIC_KEY="$USER[SSH_PUBLIC_KEY]"]
CPU="2"
DISK=[DRIVER="qcow2",IMAGE="Image Name",IMAGE_UNAME="Your user"]
GRAPHICS=[LISTEN="0.0.0.0",TYPE="VNC"]
HYPERVISOR="kvm"
MEMORY="512"
NIC=[MODEL="pcnet",NETWORK="Your Virtual Network Name",NETWORK_UNAME="Your user"]
SUNSTONE_CAPACITY_SELECT="YES"
SUNSTONE_NETWORK_SELECT="YES"
IMPORTANT: Set QCOW2 as the image mapping driver for snapshot support.
IMPORTANT: When creating a ICS Android device, set the network interface driver to pcnet.
Create a VM using the previous template and boot the device.
IMPORTANT: Start the kernel in debug mode the first time and edit the file /mnt/grub/menu.lst. Add "quiet nomodeset vga=788" before the option video=-16 to kernel arguments.
So far there is no contextualization support for Android VMs running in OpenNebula so the network interfaces have to be configured manually. First to run commands as root run in Terminal application the following commands:
adb root
adb kill-server
adb start-server
adb shell
The following commands should work to set the network if run using the Terminal application as root.
ifconfig eth0 [IP] netmask [NETMASK]
busybox route add default gw [GATEWAY] dev eth0
Once the network configuration is set,exit the Terminal in root mode and use adb to allow remote debugging with:
adb tcpip 5556
Manually configure:
- Disable all sound in emulator (Settings->Sound)
- Unverify appplications with Settings->Security->Uncheck Verify Apps
Then run android_setup_client.sh in a host with the following parameters:
emulator_setup.sh {SSL/NOSSL} {EMULATOR-IP} {GATEWAY-IP-FOR-EMULATOR}
Choose {SSL/NOSSL} to emulator deploy type 1 or 2.
This script:
- Roots the emulator
- Adds network static configuration
- Installs SuperUser and CydiaSubstrate, links Substrate and allows it to run as root.
- If it's NOSSL type, install Android-SSL-TrustKiller to skip SSL verification
- Install the Marvin-toqueton fuzzer.
- Disables lockscreen and suspension
Lastly, create a snapshot of the VM running with any name you refer.
- Deployed Marvin-frontend
- Python 2.7.x (DO NOT USE Python 3.X)
- Send an email to stic at fundacionsadosky.org.ar