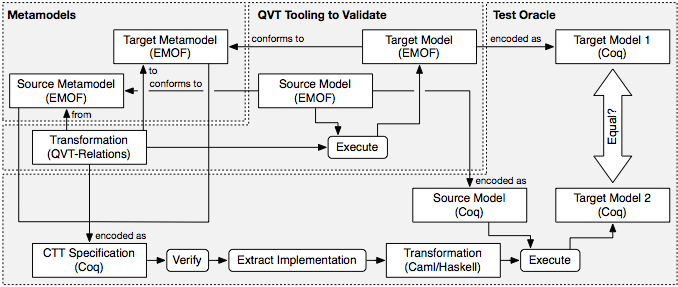
QVTr2Coq is a systematic embedding of the QVT Relations (QVT-R) transformation language in Constructive Type Theory (CTT) as implemented by the Coq proof assistant. The framework allows to manually construct and verify implementations of QVT-R transformation programs in Coq. Verified transformations can be used as a test oracle, i.e., for testing existing QVT-R transformation tools if they are in compliance with standardised semantics.
QVT-R semantics are complex and not well understood. At the present time, QVT-R semantics are implicitly modeled in tooling, but we cannot be sure if interpreters do what we expect the QVT-R specification to do.
One solution to this problem is to build a test oracle that can be utilised to semi-automatically construct reference implementations of individual transformations to test QVT-R execution engines. Because of the problem-oriented nature of the QVT-R language, there is a gap between specification and the actual interpretation of QVT-R programs. To ensure that a model transformation specified in QVT-R results in the intended behaviour, it must be tested.
For demonstration, we used the framework to generate a CTT specification from the well-known UML2RDBMS example transformation. The specification is then verified in a manual step and an implementation is extracted.
The project consists of three Xtend-based model transformations for encoding QVT-R in Coq,
- QVTr2Coq translates QVT-R programs (parsed with QVTd) to Coq specifications;
- Ecore2Coq translates Ecore metamodels to Coq specifications;
- XMI2Coq translates Ecore instances to Coq specifications.
Additionally, we provide a verified implementation of UML2RDBMS as an example use case. We made a case study that compares the behavior of ModelMorf against our own language specification with respect to the UML2RDBMS transformation. This involves:
- UMLinstantiator generates a defined number of randomly generated UML model instances.
- UML2RDBMS contains a Haskell implementation with a thin XML wrapper around the UML2RDBMS implementation extracted from the proof.
- RDBMScomparator compares the output of the ModelMorf engine against the output of our own Haskell implementation.
The study demonstrates that all 100 randomly generated model instances result in RDBMS model instances equal on ModelMorf and our verified implementation. It is possible to verify additional QVT-R execution engines, like Eclipse QVTd or qvtMedini. Results can be found in folder CaseStudy.
QVTr2Coq runs on the Eclipse Modeling Tools. The following steps assume a fresh installation of Eclipse.
-
Download Eclipse Modeling Tools 4.3 (Kepler) (Kepler) and launch it;
-
Install through menu Help > Install Modeling Components... Eclipse Xtext 2.5+ of the Model Development Tools (MDT) project;
-
Choose Help > Install New Software... to install Eclipse QVTd 0.10+ of the Model to Model Transformation (MMT) project, update site;
-
Download QVTr2Coq and import contained projects through File > Import > Existing Projects into Workspace… into your Eclipse workspace.
You are ready to use the code generator to produce Coq specifications from QVT-R programs, Ecore metamodels and instances thereof. To do so, use the run configuration Generate Coq Code. The transformation searches in subfolder model for files ending with .qvtr, .ecore, and .xmi. Resulting Coq specifications (.v files) are placed into src-gen.
To run a proof on generated Coq files, you need to install the Coq proof assistant, version 8.4 or higher. We recommend to download Coq bundled with CoqIDE.
Folder model already contains QVT-R implementations together with their Ecore metamodels. One of them is the example transformation UML2RDBMS that maps UML to RDBMS models. It is the same version as that provided by the Eclipse QVTd project.
In folder proof you will find the generated Coq specification of UML2RDBMS, complemented by an example proof and a Haskell program, UML2RDBMS.hs, which has been extracted from the proof. Several of the lemmas are general enough to be used in your own proofs, these are contained in ListHelpers.v.
- A. Rentschler, J. Terrell, S. Zschaler, L. Happe, R. Reussner. Testing QVT-R Transformation Tools with Coq-Verified Implementations. Submitted to the 7th International Conference on Model Transformation (ICMT'14).
- [Andreas Rentschler] (http://sdq.ipd.kit.edu/people/andreas_rentschler/) from Karlsruhe Institute of Technology
- [Jeffrey Terrell] (http://www.inf.kcl.ac.uk/pg/terrellj/) from King's College, London
- [Steffen Zschaler] (https://kclpure.kcl.ac.uk/portal/steffen.zschaler.html) from King's College, London
This research is a cooperation between King's College London (KCL) and Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT). Work has partly been funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) under grant No. RE 1674/5-1: Model-Driven Methods and Tools for Performance Prediction and Capacity Planning of Component-Based Software Systems (codenamed FERDINAND project) and the Priority Programme SPP 1593: Design For Future – Managed Software Evolution (more specifically, the ADVERT project).