This is an Adroid infrared application which use irblaster to sends custom crafted commands over IR , default rc6_6a_32
RC6all modes, includingRC6 6A,RC6 mode 6 submode 6A 32bitorRC6_mode_6protocol
Was tested on a Xiaomi Redmi note 7 and it is able to send all possible IR commands for any device which use this IR protocol.
This source code is licensed under GNU GPLv3
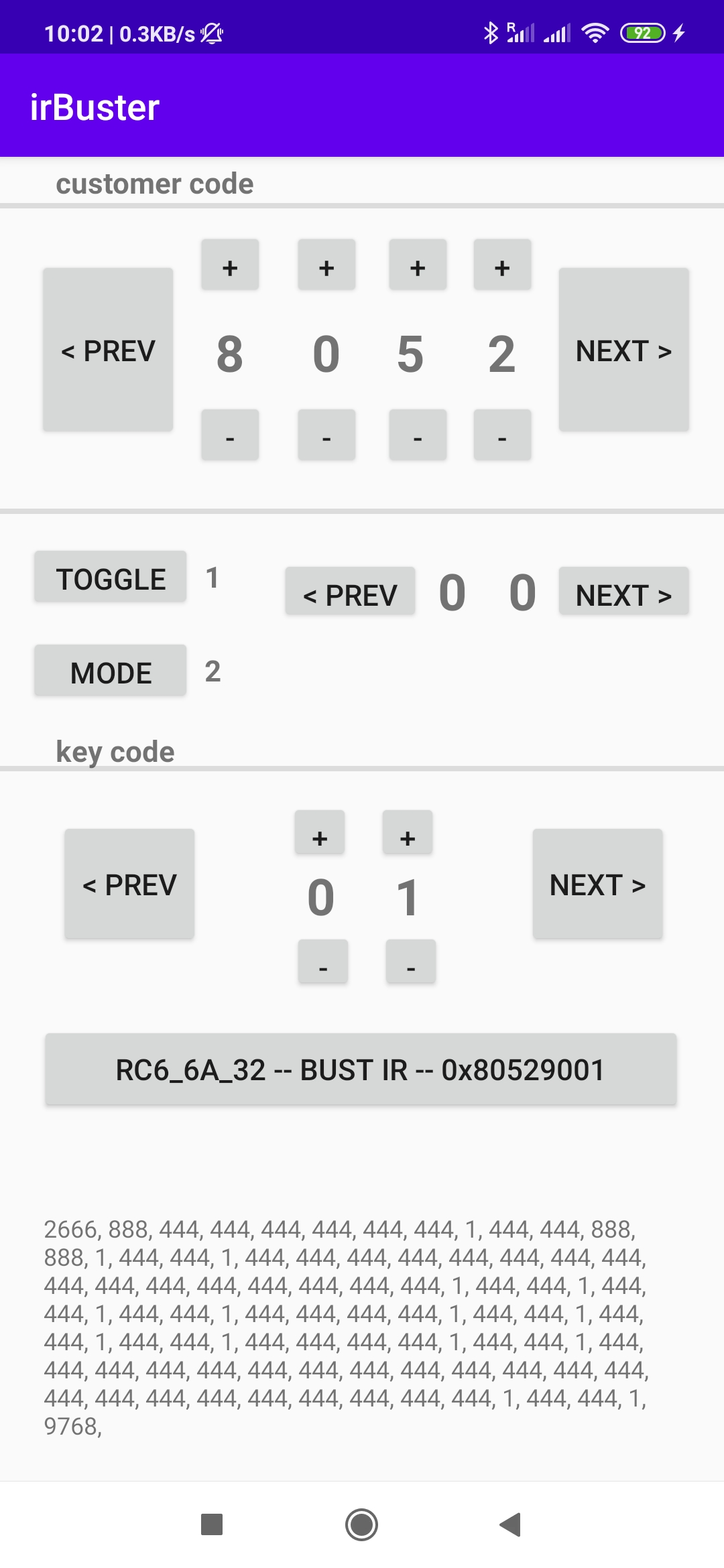
- prev/next buttons send the previous or next IR command preset-ed between them without to flip the toggle bit
- BUST IR button send command flipping the toggle bit each time is pressed
- +/- button increase or decrease value of their respective nibbles
- toggle button flip the toggle bit
- mode button change between all four modes of the Vu+ universal remote control
- in the footer of the screen you can see the actual command as IR values in usec
Working to port an emulator to my Vu+ Solo4K STB receiver i noticed that the kernel proprietary module allow a lot of other keys to be sent over IR than the actual remote control has. Just to have an idea the original RC has 43 working buttons but the kernel driver accept 91 keys, almost a full QWERTY. So, why not build an android IR keyboard? But how to find all codes to be sent over IR, well... here comes the irBuster
I had laying around an RTL-SDR usb dvb-t dongle and it has a raw IR port which helped me a lot in the development stage.
Using lirc drivers under Linux combining mode2 and ir-keytable commands you can easy identify all protocols /commands sent by any remote control around
- enable all protocols
ir-keytable -p unknown -p other -p lirc -p rc-5 -p jvc -p sony -p nec -p sanyo -p rc-6 -p sharp -p xmp -p mce-kbd - show rc key presses
ir-keytable -s rc0 -t
This is a sample output lirc protocol(rc6_6a_32): scancode = 0x80529001 pressing KEY_1 on Vu+ remote control, if you press again that key you will notice the toggle bit
0x80529001
0x80521001
So the toggle bit is in the msb nibble of the second lsb byte and the key itself is in the lsb byte, we can see this by pressing different keys
0x80529001
0x80521002
0x80529003
0x80529004
So far we found that the infrared protocol is RC6 mode 6 submode 6A which works on 36Khz and has a command on 32bit and the last two bytes contain toggle bit and the key command. Well, this mean that other two bytes contain the customer ID which a long customer id.
-
The android IR blaster can be driven directly with pulses in usec, so if know the exact order of pulses you can send them and the command is sent over IR, but how to find them? For this I used
mode2command -
The
mode2 --driver default --device /dev/lirc0command will have following output
space 5117600
pulse 2692
space 914
pulse 406
space 457
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 457
space 914
pulse 406
space 965
pulse 1320
space 914
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 406
space 457
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 406
space 508
pulse 406
space 457
pulse 914
space 914
pulse 863
space 914
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 914
space 914
pulse 863
space 914
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 914
space 914
pulse 406
space 457
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 406
space 457
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 457
space 457
pulse 406
space 508
pulse 406
space 457
pulse 914
pulse 9702
- If you remove first space line and copy comma separated all those numbers and send them to the IR blaster driver you will emit corresponding command regardless the knowledge of what is in this command.
`
- public final int[] KEY_1 = {2742, 914, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 914, 457, 914, 1371, 914, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 914, 914, 914, 914, 457, 457, 914, 914, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 914, 914, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 457, 914, 9702}; // 0x80521001
- ConsumerIrManager msCIB;
- msCIB = (ConsumerIrManager)getSystemService(Context.CONSUMER_IR_SERVICE);
- msCIB.transmit(36000, KEY_1); `
-
The above code will send the IR command, as simple as that :)
-
If this is not enough, let see what is going on
- First of all we need to understand the basics, an IR command is made from blinking an IR led, in our cases with a frequency of 36Khz or 36000Hz
- Then we need to acknowledge that ALWAYS first signal is ON and the last one is OFF, where ON is IR led emitting and then OFF not, basically a sequence of on/off patterns in usec
- With that sequence in mind we can easily see that the MSB of the command goes first in the "air" so in order to send a bit we need to understand how it is sent
- An encoded bit is a sequence of 444usec on and another 444usc off, this bit will be 1, if you inverse the order, first sequence is off and second on then the bit is 0 As following
+++++----++++----++++----
2472,914,457,457,457,457
Where + represent ON and - OFF, above we just sent the IR trailer and two bits with value 1 and 1
This is 1
++++---
457,457
And this is a 0 (zero)
----++++
457,457
So, if this is the situation, in order to send a zero after a one we need to change the pattern, how to to that, the original IR command use complicated patern so i found easier to change the pulse by adding a small value before the bit,
Basically if we want to send 0b101 binary value we will use following pulse line
+++++----++++----++----++++--++++----
2472,914,457,457,1,457,457,1,457,457
<-lead--><---1---><-----0----><-----1---->
As you can see the tiny usec (1) spent there change the pulse on or off as we need to set the values. This mean that we need to always know what was the last pulse value, high or low and REMEMBER that the last value 9702 is alwais zero
- The vusolo4k-keys.txt contain Vu+ Solo4K IR RC6 hex codes for
- The existing RC keys
- New keys discovered with irBuster which are not on the remote control and all new keys which remains to be discovered with irBuster
That's all folks!!!
I hope that will help in your future projects