2014/09/28 - EuroBSDcon2014 Slides
The use of large frames makes network communication much less demanding for the CPU. Yet, backward compatibility and slow links requires the use of 1500 byte or smaller frames. Modern NICs with hardware TCP segmentation offloading (TSO) address this problem. However, a generic software version (GSO) provided by the OS has reason to exist, for use on paths with no suitable hardware, such as between virtual machines or with older or buggy NICs.
Much of the advantage of TSO comes from crossing the network stack only once per (large) segment instead of once per 1500-byte frame. GSO does the same both for segmentation (TCP) and fragmentation (UDP) by doing these operations as late as possible. Ideally, this could be done within the device driver, but that would require modifications to all drivers. A more convenient, similarly effective approach is to segment just before the packet is passed to the driver (in ether_output())
Our preliminary implementation supports TCP and UDP on IPv4/IPv6; it only intercepts packets large than the MTU (others are left unchanged), and only when GSO is marked as enabled for the interface.
Segments larger than the MTU are not split in tcp_output(), udp_output(), or ip_output(), but marked with a flag (contained in m_pkthdr.csum_flags), which is processed by ether_output() just before calling the device driver.
ether_output(), through gso_dispatch(), splits the large frame as needed, creating headers and possibly doing checksums if not supported by the hardware.
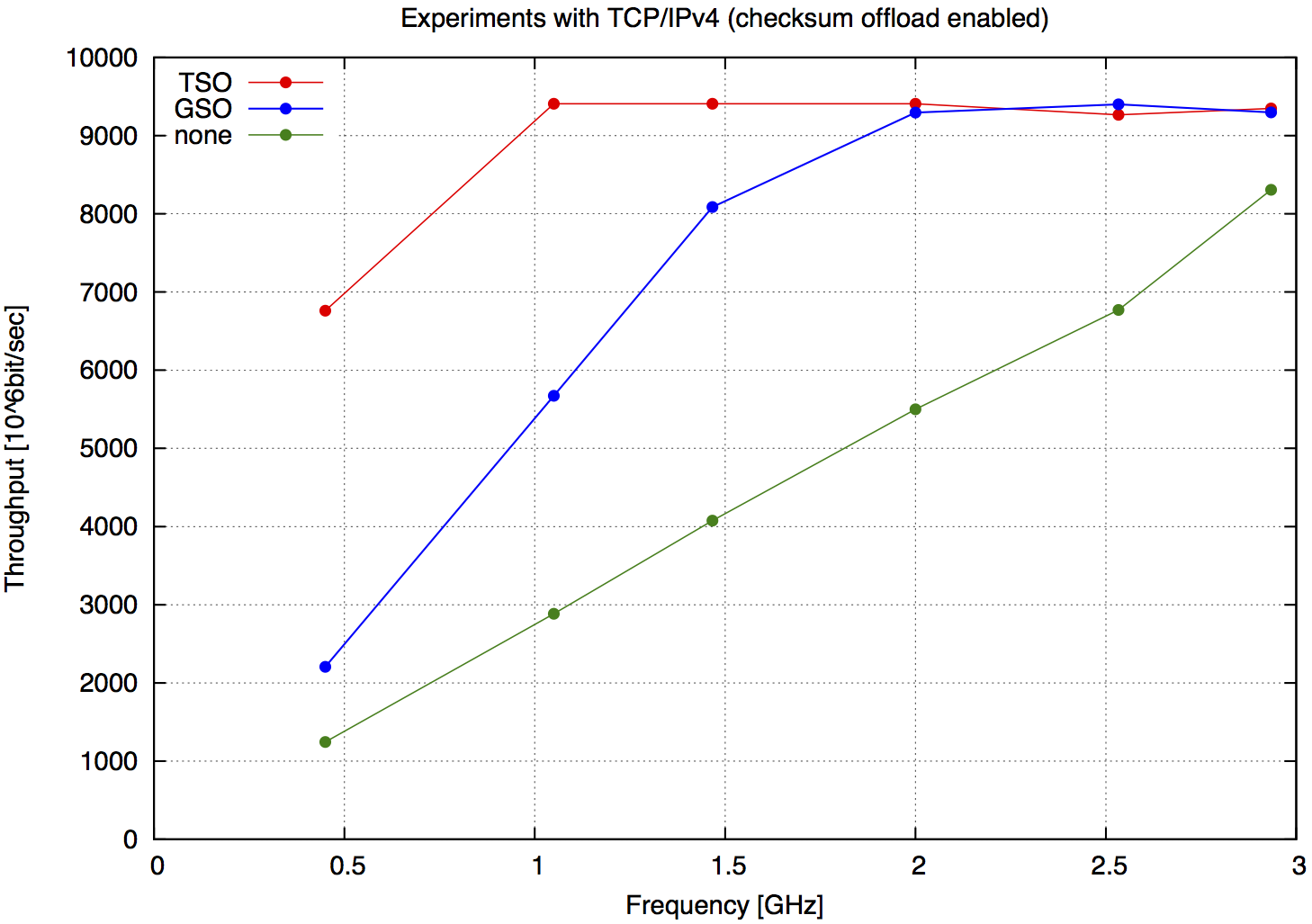
Our preliminary implementation, depending on CPU speed, shows up to 95% speedup compared to segmentation done in the TCP/IPv4 stack, saturating a 10 Gbit link at 2 GHz with checksum offloading [Tab. 1].
##Patches & utilities
In this repo you can find:
- kernel patches for
- FreeBSD-current
- FreeBSD 10-stable
- FreeBSD 9-stable
- simple application that prints the GSO statistics:
- picobsd images:
- PicoBSD-current
- PicoBSD 10-stable
- PicoBSD 9-stable
At https://github.com/stefano-garzarella/freebsd you can get the FreeBSD source with GSO support [various branch for FreeBSD current (gso-master), 10-stable (gso-10), 9-stable (gso-9)].
##How to use GSO
-
Apply the right kernel patch.
- FreeBSD-current
- FreeBSD 10-stable
- FreeBSD 9-stable
-
To compile the GSO support add 'options GSO' to your kernel config file and rebuild a kernel.
-
To manage the GSO parameters there are some sysctls:
-
net.inet.tcp.gso - GSO enable on TCP communications (!=0)
-
net.inet.udp.gso - GSO enable on UDP communications (!=0)
-
for each interface:
- net.gso.dev."ifname”.max_burst - GSO burst length limit [default: IP_MAXPACKET=65535]
- net.gso.dev."ifname”.enable_gso - GSO enable on “ifname” interface (!=0)
-
-
To show statistics:
- make sure that the GSO_STATS macro is defined in sys/net/gso.h
- use the simple gso-stat.c application to access the sysctl net.gso.stats that contains the address of the gsostats structure (defined in gso.h) which records the statistics. (compile with -I/path/to/kernel/src/patched/)
##How to use PicoBSD image with GSO
- Real Machine
- Copy the PicoBSD image on a usb-stick
- sudo dd if=picobsd.bin of=/dev/rdisk1 bs=1m
- Plug the usb-stick into a real machine
- Turn it on
- Copy the PicoBSD image on a usb-stick
- Virtual Machine
##Experiments In experiments agains an LRO-enabled receiver (otherwise TSO/GSO are ineffective) we have seen the following performance, taken at different clock speeds (because at top speeds the 10G link becomes the bottleneck).
- Test Date: Sep 9, 2014
- Transmitter: FreeBSD 11-CURRENT - CPU i7-870 at 2.93 GHz + Turboboost, Intel 10 Gbit NIC.
- Receiver: Linux 3.12.8 - CPU i7-3770K at 3.50GHz + Turboboost, Intel 10 Gbit NIC.
- Benchmark tool: netperf 2.6.0
| Freq. | TSO | GSO | none | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [GHz] | [Gbps] | [Gbps] | [Gbps] | GSO-none |
| 2.93 | 9347 | 9298 | 8308 | 11.92 % |
| 2.53 | 9266 | 9401 | 6771 | 38.84 % |
| 2.00 | 9408 | 9294 | 5499 | 69.01 % |
| 1.46 | 9408 | 8087 | 4075 | 98.45 % |
| 1.05 | 9408 | 5673 | 2884 | 96.71 % |
| 0.45 | 6760 | 2206 | 1244 | 77.33 % |
| Tab.1 TCP/IPv4 packets (checksum offloading enabled) |
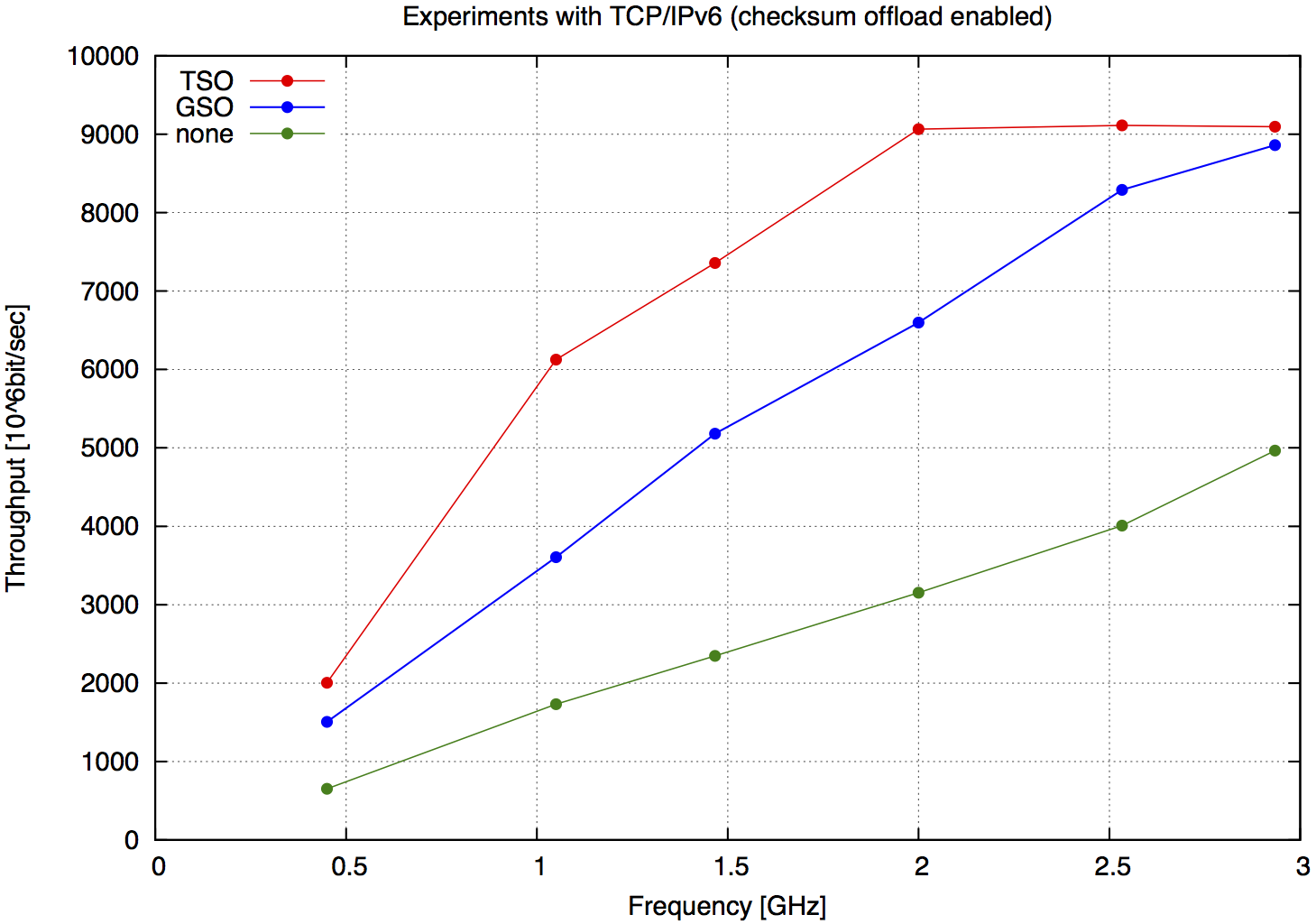
| Freq. | TSO | GSO | none | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [GHz] | [Gbps] | [Gbps] | [Gbps] | GSO-none |
| 2.93 | 9097 | 8861 | 4966 | 78,43 % |
| 2.53 | 9113 | 8290 | 4008 | 106,84 % |
| 2.00 | 9066 | 6599 | 3152 | 109,36 % |
| 1.46 | 7357 | 5180 | 2348 | 120,61 % |
| 1.05 | 6125 | 3607 | 1732 | 108,26 % |
| 0.45 | 2005 | 1505 | 651 | 131,18 % |
| Tab.2 TCP/IPv6 packets (checksum offloading enabled) |
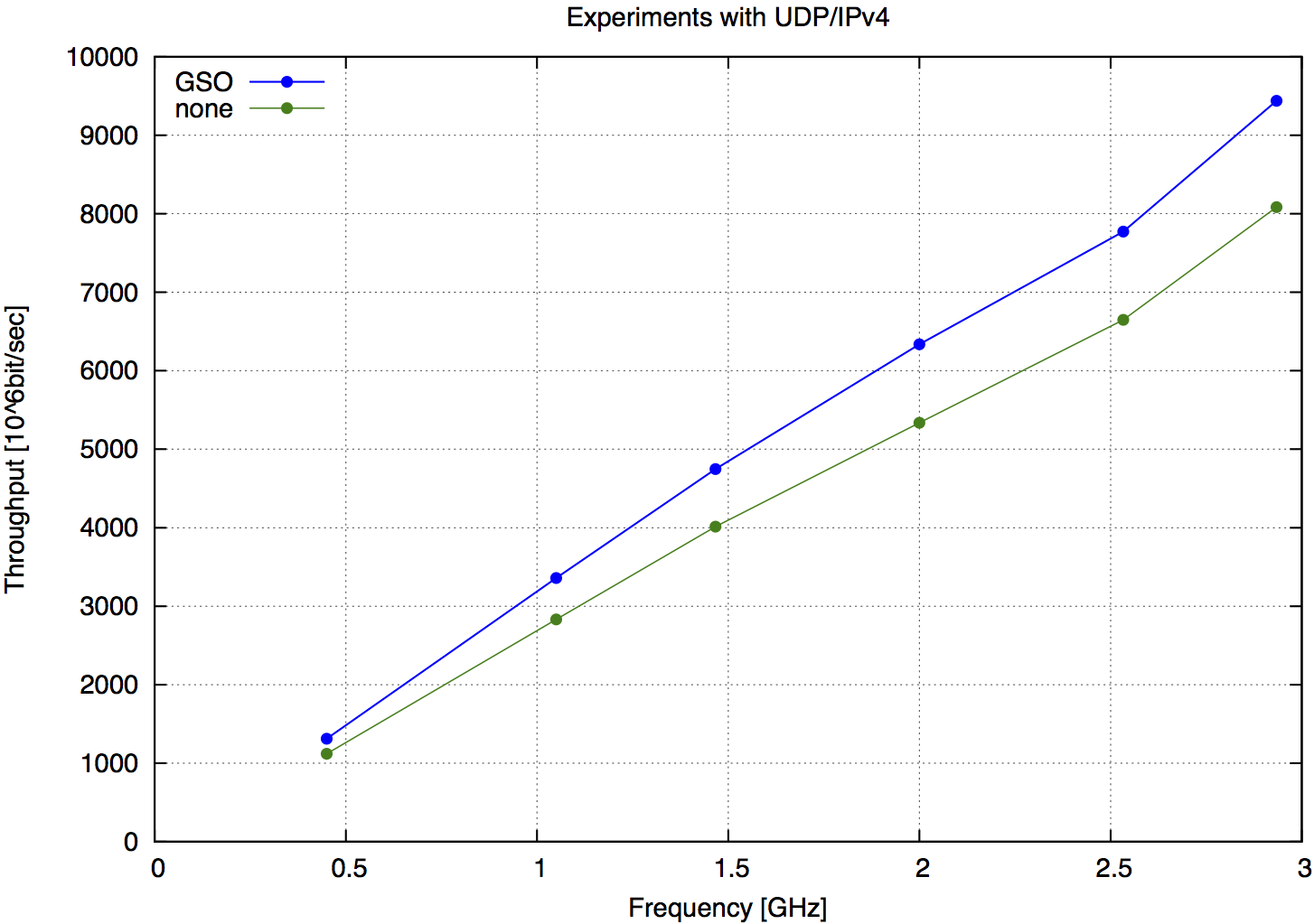
| Freq. | GSO | none | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|
| [GHz] | [Gbps] | [Gbps] | GSO-none |
| 2.93 | 9440 | 8084 | 16.77 % |
| 2.53 | 7772 | 6649 | 16.89 % |
| 2.00 | 6336 | 5338 | 18.70 % |
| 1.46 | 4748 | 4014 | 18.29 % |
| 1.05 | 3359 | 2831 | 18.65 % |
| 0.45 | 1312 | 1120 | 17.14 % |
| Tab.3 UDP/IPv4 packets |
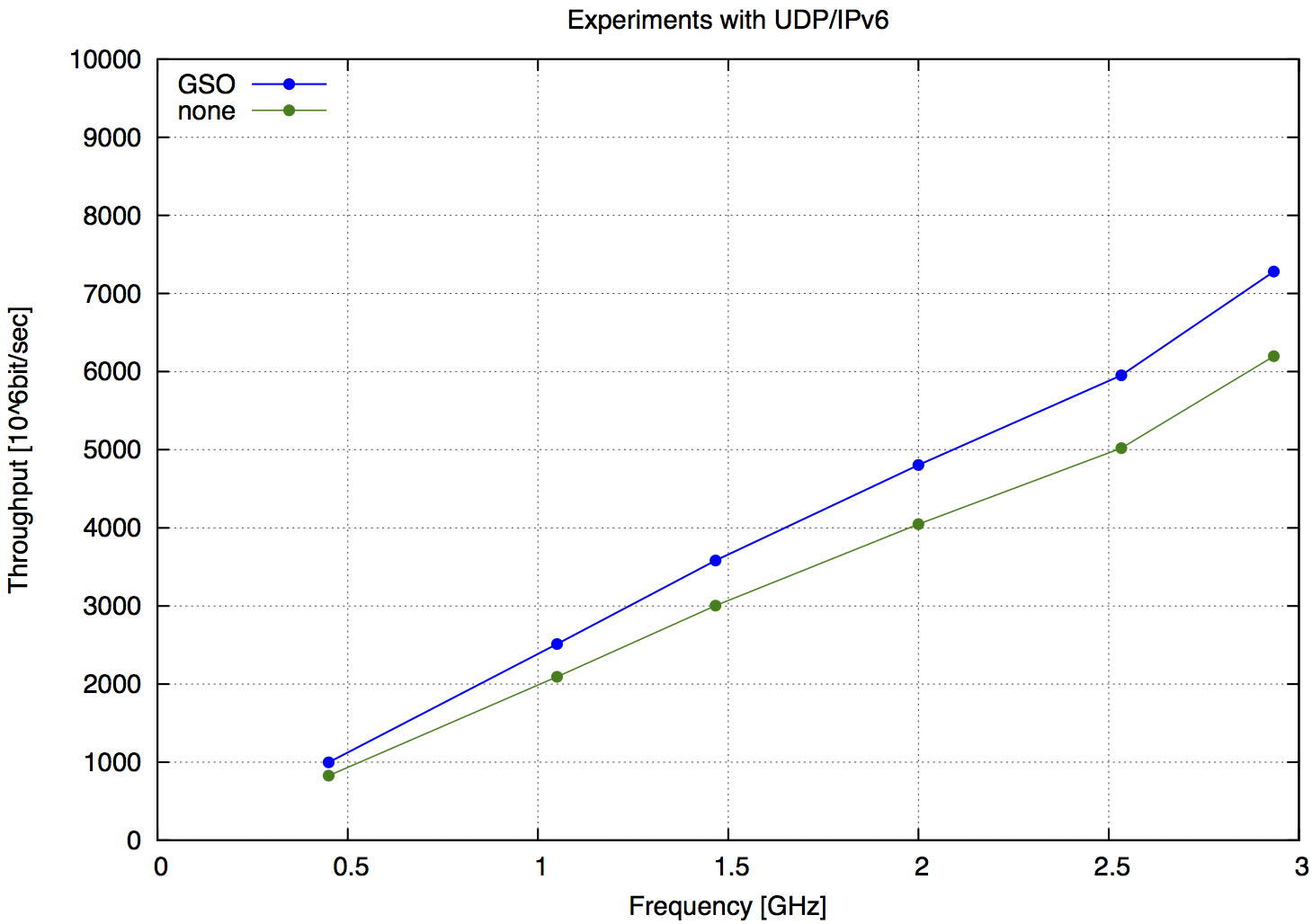
| Freq. | GSO | none | Speedup |
|---|---|---|---|
| [GHz] | [Gbps] | [Gbps] | GSO-none |
| 2.93 | 7281 | 6197 | 17.49 % |
| 2.53 | 5953 | 5020 | 18.59 % |
| 2.00 | 4804 | 4048 | 18.68 % |
| 1.46 | 3582 | 3004 | 19.24 % |
| 1.05 | 2512 | 2092 | 20.08 % |
| 0.45 | 998 | 826 | 20.82 % |
| Tab.4 UDP/IPv6 packets |