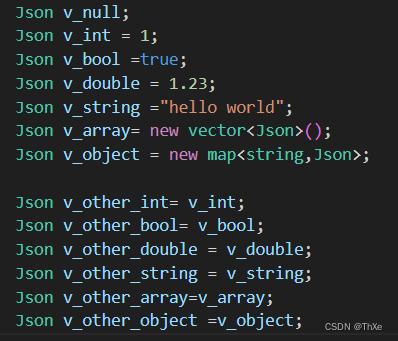
简单来说Json就是一种数据表达格式,采用key-value的存储形式。支持常见的数据类型,如null、bool、int、double、string.不仅如此Json还支持数组,以及Json对象嵌套,Json对象以{}包裹,数组以[]包裹,下列数据中subJson为一个Json对象,array为一个Json数组。
{
"nullkey": null,
"boolean": false,
"int": 10,
"double": 1.23,
"string": "abc",
"subJson": {
"math": 99
},
"array": [
"I'm the first one.",
2,
{
"sb2": 222
}
]
}
Json主要用于数据交互,比如我们想要做个天气预报的系统,这时候我们需要一些天气相关的数据,可以访问一些免费的API,通过http中的get请求,就可以获得一个Json格式的字符串。那么我们就可以通过解析这个字符串获取相关信息。
{
"city":"北京","city_en":"beijing",
"date_y":"2012年2月16日", "date":"", "week":"星期四", "fchh":11, "gotowalk":"false",
"subJson": {
"hot": 99.9
}
}
我们希望能够将Json字符串转换为变成语言中的对象,这样我们就能很方便的来处理这些数据,如上面的一个Json数据,可以在C++中表示成一个类。
class infomation
{
string city;
string city_en;
string date_y;
string week;
int fchh;
bool gotowalk;
double hot;
}该项目期望可以如下将Json字符串给对象赋值
infomation inf = new infomation();
string JsonStr = http.get(http:/m.weather.com.cn/data/101010100.html);//某个API返回一个Json字符串
Json changer ;
changer.prase(JsonStr);//解析Json
inf.city=changer["city"];
inf.fchh=changer["fchh"];
inf.hot=changer["subJson"]["hot"];本项目希望给一些刚入门的小白降低一些门槛,也为了说明该项目从无到有的构建过程,将整个项目分为6个Task branch,每一个Task branch都在上一个Task的基础上增添代码,相应的代码可以见branch
通过枚举表示Json的数据type,根据type不同来使用构造函数,给 m_value实际的值
class Json
{
public :
enum Type
{
json_null=0,
json_bool,
json_int,
json_double,
json_string,
json_array,
json_object
};
Json();
Json(bool value);
Json(int value);
Json(double value);
Json(const char * value);
Json(string value);
Json(Type type);
Json(const Json &other);
private:
union Value
{
bool m_bool;
int m_int;
double m_double;
std::string *m_string;
std::vector<Json> * m_vector;
std::map<string,Json>* m_object;
};
Value m_value;
Type m_type;
};实现逆向赋值
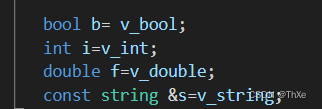
重载一下基本类型运算符
operator bool();
operator int ();
operator double();
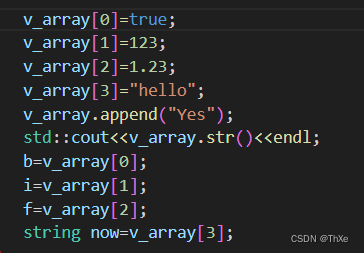
operator string();实现数组相关API
output:[true,123,1.23,"hello","Yes"]重载[],str使用递归来将对象解析为字符串
Json &operator [](int index);
void append(const Json &other);
string str ()const;
实现object相关API,并注意内存泄漏的问题
v_object["bool"]=true;
v_object["int"]=123;
v_object["double"]=1.23;
v_object["str"]="hello word";
std::cout<< v_object.str()<<endl;重载运算符
Json &operator [](const char *key);
Json &operator [](const string & key);
void copy(const Json & other);
void clear();实现如下常用接口
/*迭代器*/
typedef std::vector<Json>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin();
iterator end();
/*是否为某类型*/
bool isNull() const ;
bool isBoll()const;
bool isInt()const ;
bool isDouble()const;
bool isString()const;
bool isArray()const;
bool isObject()const;
/*返回具体的值*/
bool asBool()const;
int asInt()const;
double sDouble()const;
string asString()const;
/*判定是否存在某索引*/
bool has(int index);
bool has(const string key);
bool has(const char*key);
/*删除某元素*/
void remove(int index);
void remove(const string key);
void remove(const char*key);
1:完成基本数据类型的解析:NULL,int,double,string 2:完成符合类型解析:array,object
string str="null";
Json v;
v.parse(str);
cout<<v.str()<<endl;
str="true";
v.parse(str);
cout<<v.str()<<endl;
str="false";
v.parse(str);
cout<<v.str()<<endl;
str="123";
v.parse(str);
cout<<v.str()<<endl;
str="1.23";
v.parse(str);
cout<<v.str()<<endl;
str="-1.23";
v.parse(str);
cout<<v.str()<<endl;
str="\"hello\"";
v.parse(str);
cout<<v.str()<<endl;
str="[1,2]";
v.parse(str);
cout<<v.str()<<endl;
str="[1, 2,3 ,\"true\",true, false,1.23,-100,-0]";
v.parse(str);
cout<<v.str()<<endl;
// str="{\"name\":Alic,\"age\":18}";
str="{\"a\": 1,\"b\":\"2\"}";
v.parse(str);
cout<<v.str()<<endl;
str="{\"name\":\"Alice\",\"age\": 18}";
v.parse(str);
cout<<v.str()<<endl;