High performance CSV encoder and decoder with retained types and nullability.
This package is intended to quickly encode and decode csv while keeping all type information.
Compared to JSON, CSV is a much more compact format that is also readable without having to "beautify" it.
Instead of supporting the entire CSV specification, this package uses a more strict format that is optimized for performance.
The following data types are preserved: String, int, double, bool, null.
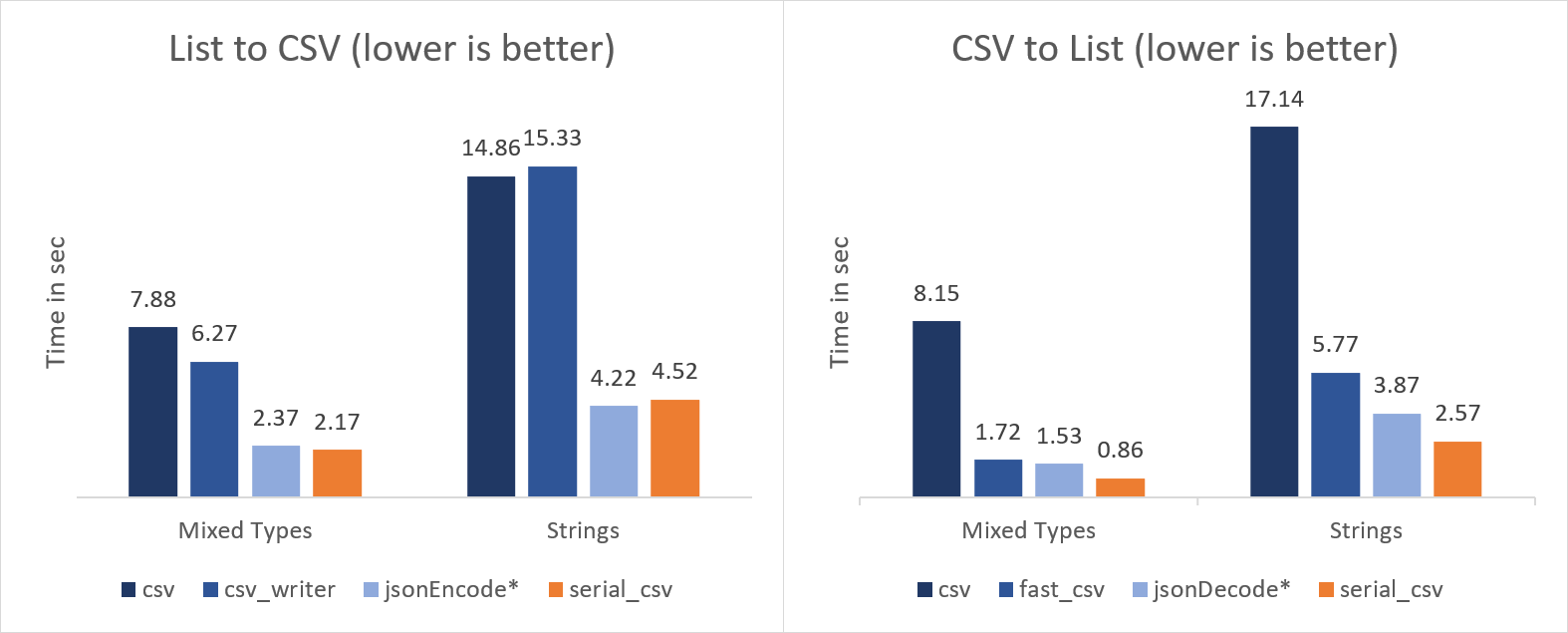
The benchmark consists of 30 billion cells (5000 rows x 3000 columns x 2000 iterations) running on a Ryzen 5 5600X.
For comparison, the packages csv (v5.0.2), fast_csv (v0.1.44), and csvwriter (v1.3.0) were used.
* jsonEncode and jsonDecode are using an equivalent data representation.
You can run the benchmark yourself with this code example.
This library uses a more strict CSV format to achieve high performance.
- string cells are always double-quoted
- numeric and boolean cells are not double-quoted
- null cells are encoded as empty cells
- double-quotes within cells are escaped with another double-quote
- cells are separated by commas
- every row must be terminated with
\n(LF) - the last row must be terminated with
\n(LF) - no comments (
#) are allowed
There is no "vendor lock-in" as the CSV is still valid CSV. You can use any other CSV library to read the CSV.
Just be careful not to modify the CSV with other tools as you might break the strict format.
Use SerialCsv.encode and SerialCsv.decode to encode and decode CSV.
"a","b","c"
1,2.3,"3"
4,,true
String encoded = SerialCsv.encode([
['a', 'b', 'c'],
[1, 2.3, '3'],
['4', null, true],
]);
List<List<dynamic>> decoded = SerialCsv.decode(encoded);
// The type information is retained.
String s = decoded[0][0]; // 'a'
int i = decoded[1][0]; // 1
double d = decoded[1][1]; // 2.3
bool b = decoded[2][2]; // true
Object? n = decoded[2][1]; // nullEncode and decode a list of rows with only string cells. No null is allowed.
const rows = [
['a', 'b', 'c'],
['1', '2', '3'],
['4', '5', 'true'],
];
String encoded = SerialCsv.encodeStrings(rows);
List<List<String>> decoded = SerialCsv.decodeStrings(encoded);Encode and decode a non-nested map. Keys must be strings. Values can be any supported type.
const map = {
'a': '1',
'b': 2,
'c': 3.4,
'd': true,
'e': null,
};
String encoded = SerialCsv.encodeMap(map);
Map<String, dynamic> decoded = SerialCsv.decodeMap(encoded);
// The type information is retained.
String s = decoded['a']; // '1'
int i = decoded['b']; // 2
double d = decoded['c']; // 3.4
bool b = decoded['d']; // true
Object? n = decoded['e']; // null