Fitting Differential Equations to Time Series Data (deFit).
Use numerical optimization to fit ordinary differential equations (ODEs) to time series data to examine the dynamic relationships between variables or the characteristics of a dynamical system. It can now be used to estimate the parameters of ODEs up to second order.
- Fit ordinary differential equation models to time series data
- Report model parameter estimations, standard errors, R-squared, and root mean standard error
- Plot raw data points and fitted lines
- Support ordinary differential equation models up to second order
- deFit can run in Python and R environments
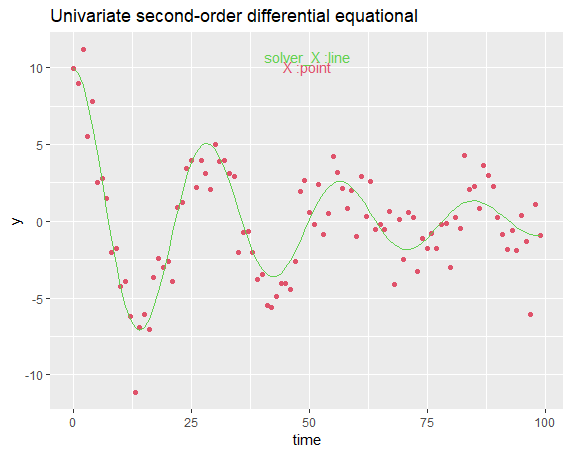
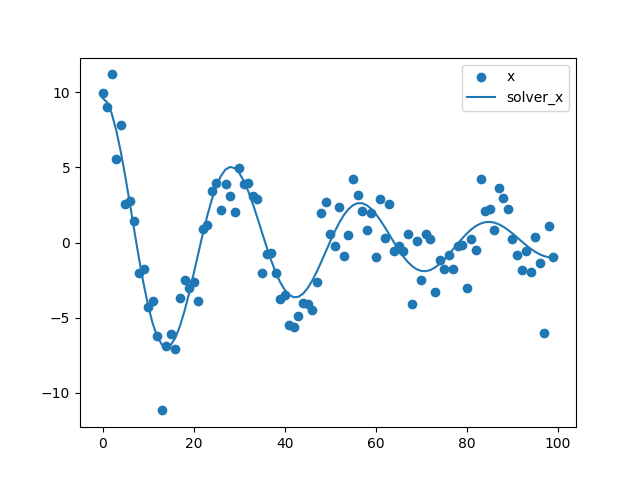
To get a first impression of how deFit works in simulation, consider the following example of a differential equational model. The figure below contains a graphical representation of the model that we want to fit.
library(deFit)
data('example1')
model1 <- '
X =~ myX
time =~ myTime
X(2) ~ X(1) + X
'
result1 <- defit(data = example1, model = model1)To get a first impression of how deFit works in simulation, consider the following example of a differential equational model. The figure below contains a graphical representation of the model that we want to fit.
import defit
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.read_csv('defit/data/example1.csv')
model1 = '''
x =~ myX
time =~ myTime
x(2) ~ x + x(1)
'''
result1 = defit.defit(data=df1,model=model1)