Simple GUI JoyStick using PySimpleGUI.
Make sure you have installed PySimpleGUI in your Python3.
To check, simply run python GUI_JoyStick.py
You will see this window;
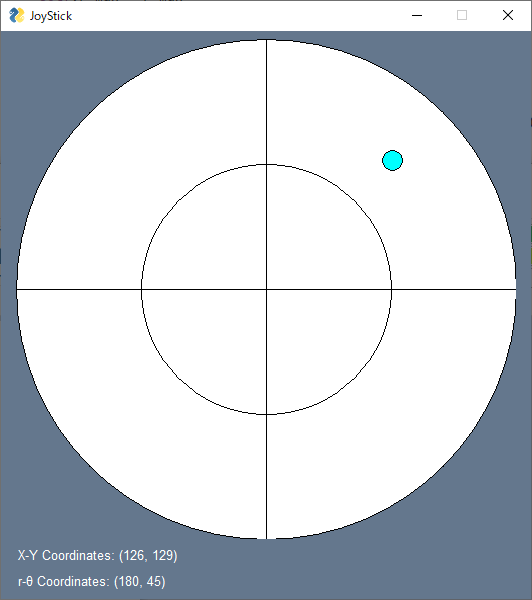
The JoyStick Pad, shown as cyan circle, will stick to your mouse pointer on left click-down,
and back to center on left click-up.
The coordinates at lower left side are written in (X [pxls], Y [pxls]) and (r [pxls], theta [deg]) formats.
To use coordinates in your own code, put GUI_JoyStick.py at the same directory located your code and do like following;
import GUI_JoyStick
js = GUI_JoyStick.JoyStick()
while True:
js.update()
print(js.xy_coordinates)
print(js.rt_coordinates)
if js.close:
break
In this case, js.xy_coordinates has (X [pxls], Y [pxls]) data, and js.rt_coordinates has (r [pxls], theta [rad]) data,
while GUI shows (X [pxls], Y [pxls]) and (r [pxls], theta [deg]).
It's possible to change circle size and pad size, on set js = GUI_JoyStick.JoyStick(r_max=[YourCircleSize], stick_size=[YourPadSize])
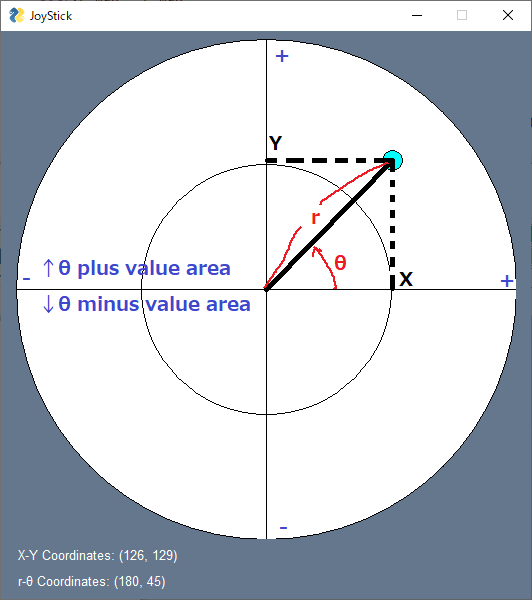
The origin to calculate coordinates are at the cross point of horizontal and vertical lines shown in UI.
The coordinates values are taken as shown in below;
This is an example to generate a cmd to control 2 wheels, left and right wheels, vehicle.
To do this, we need to tell directions and powers to apply for both wheels.
Copy GUI_JoyStick.py into ./example directory, and Run below to check how it works;
python ./example/ControlCrawlerMotor.py