Python package for concise, transparent, and accurate predictive modeling. All sklearn-compatible and easily customizable.
docs • imodels overview • demo notebooks
Modern machine-learning models are increasingly complex, often making them difficult to interpret. This package provides a simple interface for fitting and using state-of-the-art interpretable models, all compatible with scikit-learn. These models can often replace black-box models (e.g. random forests) with simpler models (e.g. rule lists) while improving interpretability and computational efficiency, all without sacrificing predictive accuracy! Simply import a classifier or regressor and use the fit and predict methods, same as standard scikit-learn models.
from imodels import BayesianRuleListClassifier, GreedyRuleListClassifier, SkopeRulesClassifier # see more models below
from imodels import SLIMRegressor, RuleFitRegressor
model = BayesianRuleListClassifier() # initialize a model
model.fit(X_train, y_train) # fit model
preds = model.predict(X_test) # discrete predictions: shape is (n_test, 1)
preds_proba = model.predict_proba(X_test) # predicted probabilities: shape is (n_test, n_classes)
print(model) # print the rule-based model
-----------------------------
# the model consists of the following 3 rules
# if X1 > 5: then 80.5% risk
# else if X2 > 5: then 40% risk
# else: 10% riskInstall with pip install imodels (see here for help).
| Model | Reference | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Rulefit rule set | 🗂️, 🔗, 📄 | Extracts rules from a decision tree then builds a sparse linear model with them |
| Skope rule set | 🗂️, 🔗 | Extracts rules from gradient-boosted trees, deduplicates them, then forms a linear combination of them based on their OOB precision |
| Boosted rule set | 🗂️, 🔗, 📄 | Uses Adaboost or SLIPPER to sequentially learn a set of rules |
| Bayesian rule list | 🗂️, 🔗, 📄 | Learns a compact rule list by sampling rule lists (rather than using a greedy heuristic) |
| Greedy rule list | 🗂️, 🔗 | Uses CART to learn a list (only a single path), rather than a decision tree |
| OneR rule list | 🗂️, 📄 | Learns rule list restricted to only one feature |
| Optimal rule tree | 🗂️, 🔗, 📄 | (In progress) Learns succinct trees using global optimization rather than greedy heuristics |
| Iterative random forest | 🗂️, 🔗, 📄 | (In progress) Repeatedly fit random forest, giving features with high importance a higher chance of being selected. |
| Sparse integer linear model | 🗂️, 📄 | Forces coefficients to be integers |
| Rule sets | ⌛ | (Coming soon!) Many popular rule sets including Lightweight Rule Induction, MLRules |
Docs 🗂️, Reference code implementation 🔗, Research paper 📄
See also our fast and effective discretizers for data preprocessing.
The final form of the above models takes one of the following forms, which aim to be simultaneously simple to understand and highly predictive:
| Rule set | Rule list | Rule tree | Algebraic models |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
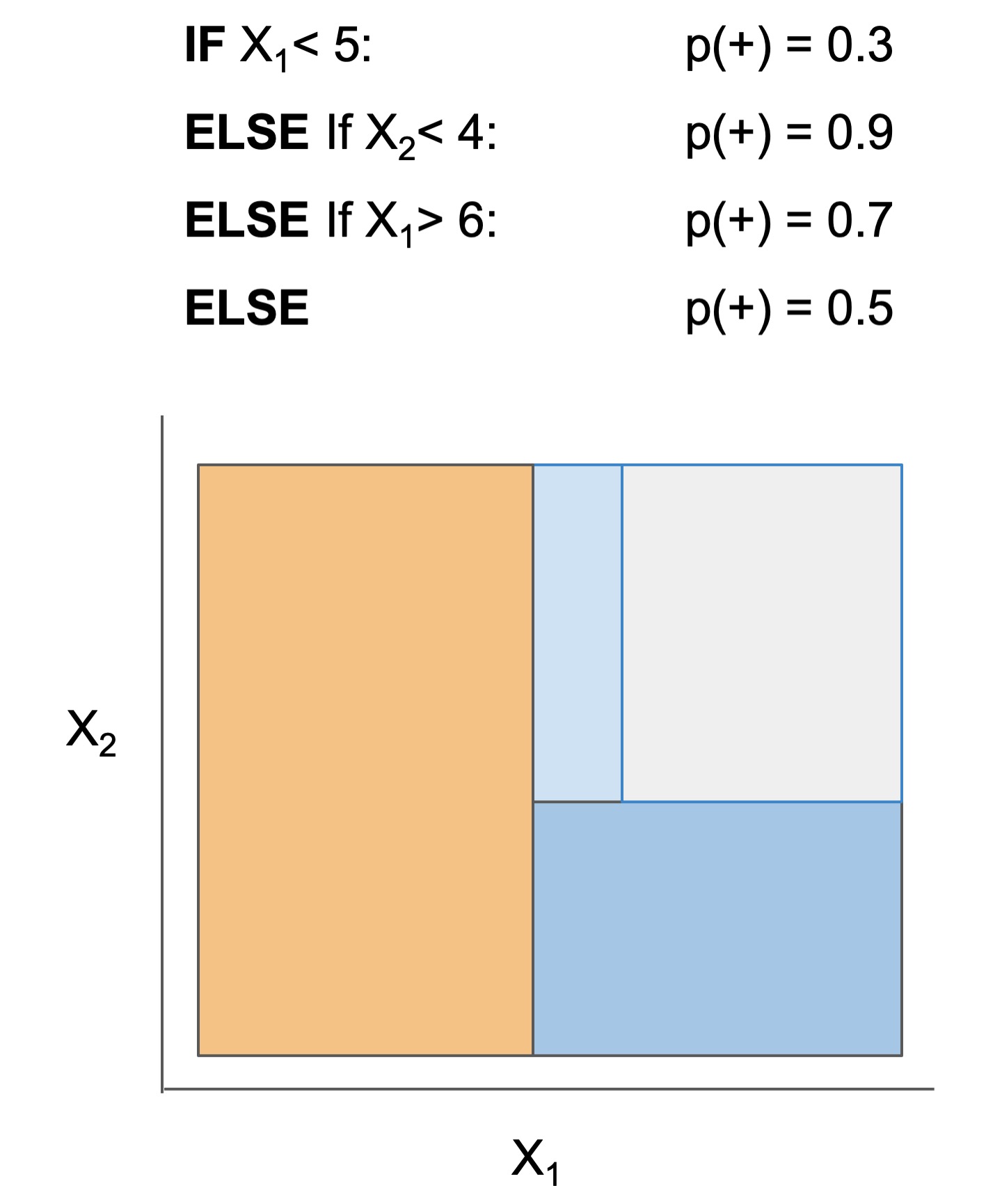 |
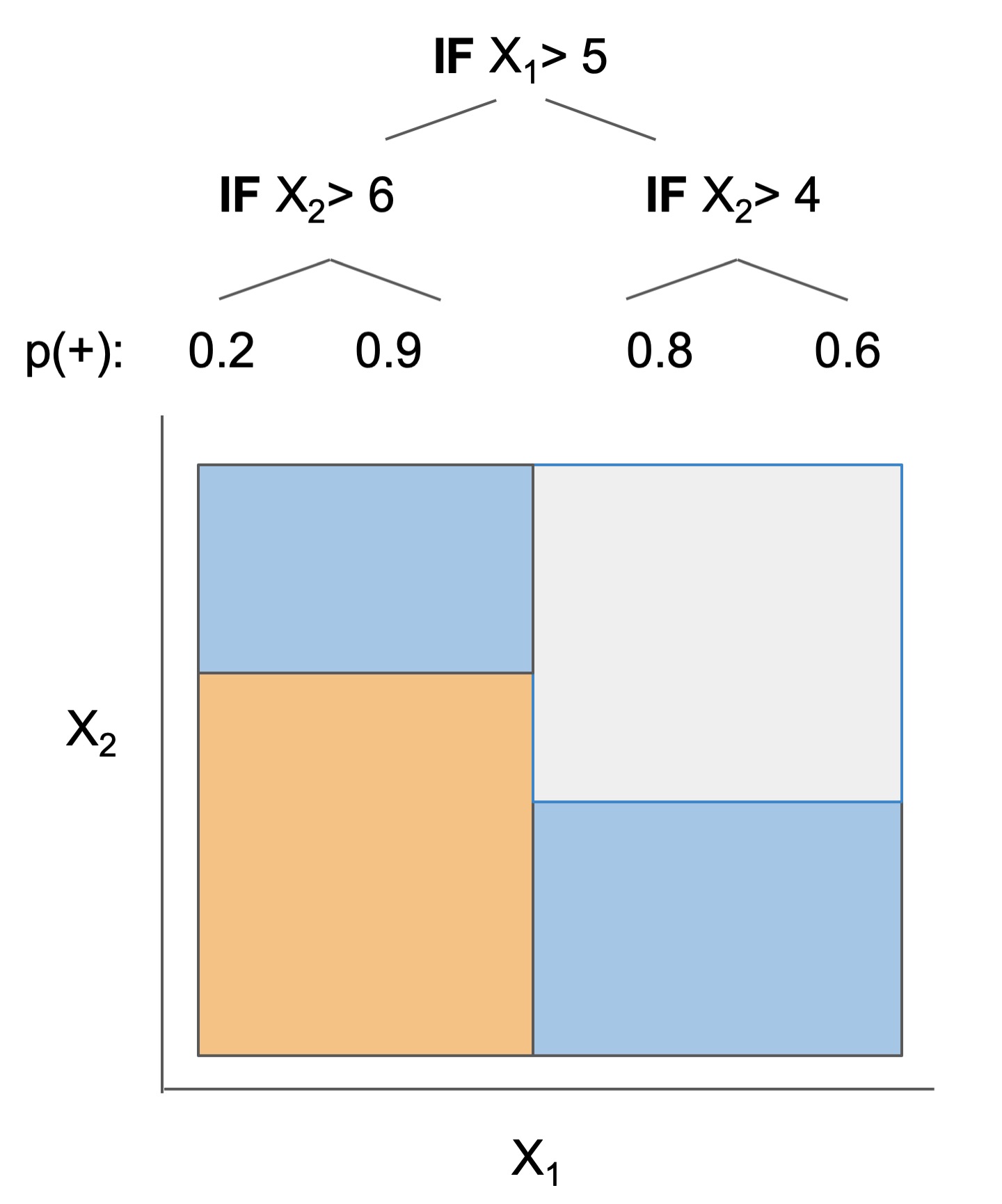 |
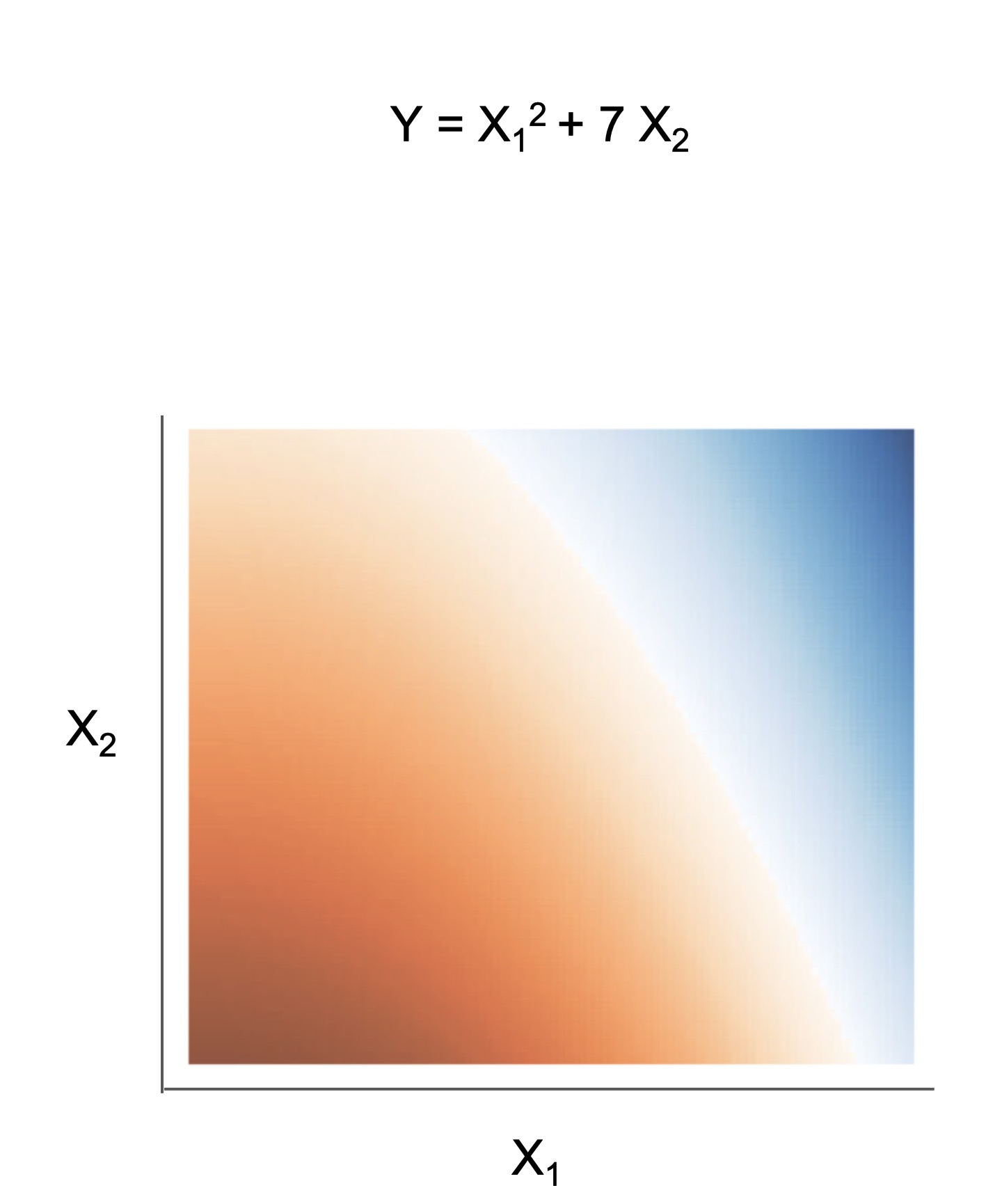 |
Different models and algorithms vary not only in their final form but also in different choices made during modeling. In particular, many models differ in the 3 steps given by the table below.
ex. RuleFit and SkopeRules
RuleFit and SkopeRules differ only in the way they prune rules: RuleFit uses a linear model whereas SkopeRules heuristically deduplicates rules sharing overlap.ex. Bayesian rule lists and greedy rule lists
Bayesian rule lists and greedy rule lists differ in how they select rules; bayesian rule lists perform a global optimization over possible rule lists while Greedy rule lists pick splits sequentially to maximize a given criterion.ex. FPSkope and SkopeRules
FPSkope and SkopeRules differ only in the way they generate candidate rules: FPSkope uses FPgrowth whereas SkopeRules extracts rules from decision trees.See the docs for individual models for futher descriptions.
| Rule candidate generation | Rule selection | Rule pruning / combination |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
The code here contains many useful and customizable functions for rule-based learning in the util folder. This includes functions / classes for rule deduplication, rule screening, and converting between trees, rulesets, and neural networks.
Demos are contained in the notebooks folder.
imodels demo
Shows how to fit, predict, and visualize with different interpretable modelsimodels colab demo 
Shows how to fit, predict, and visualize with different interpretable models
clinical decision rule notebook
Shows an example of usingimodels for deriving a clinical decision rule
posthoc analysis
We also include some demos of posthoc analysis, which occurs after fitting models: posthoc.ipynb shows different simple analyses to interpret a trained model and uncertainty.ipynb contains basic code to get uncertainty estimates for a modelDifferent models support different machine-learning tasks. Current support for different models is given below:
| Model | Binary classification | Regression |
|---|---|---|
| Rulefit rule set | ✔️ | ✔️ |
| Skope rule set | ✔️ | |
| Boosted rule set | ✔️ | |
| Bayesian rule list | ✔️ | |
| Greedy rule list | ✔️ | |
| OneR rule list | ✔️ | |
| Optimal rule tree | ||
| Iterative random forest | ||
| Sparse integer linear model | ✔️ | ✔️ |
- Readings
- Reference implementations (also linked above): the code here heavily derives from the wonderful work of previous projects. We seek to to extract out, unify, and maintain key parts of these projects.
- sklearn-expertsys - by @tmadl and @kenben based on original code by Ben Letham
- rulefit - by @christophM
- skope-rules - by the skope-rules team (including @ngoix, @floriangardin, @datajms, Bibi Ndiaye, Ronan Gautier)
- Related packages
- Updates
- For updates, star the repo, see this related repo, or follow @csinva_
- Please make sure to give authors of original methods / base implementations appropriate credit!
- Contributing: pull requests very welcome!
If it's useful for you, please cite the package using the below, and make sure to give authors of original methods / base implementations credit:
@software{
imodels2021,
title = {{imodels: a python package for fitting interpretable models}},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software}
publisher = {The Open Journal},
year = {2021},
author = {Singh, Chandan and Nasseri, Keyan and Tan, Yan Shuo and Tang, Tiffany and Yu, Bin},
volume = {6},
number = {61},
pages = {3192},
doi = {10.21105/joss.03192},
url = {https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.03192},
}



