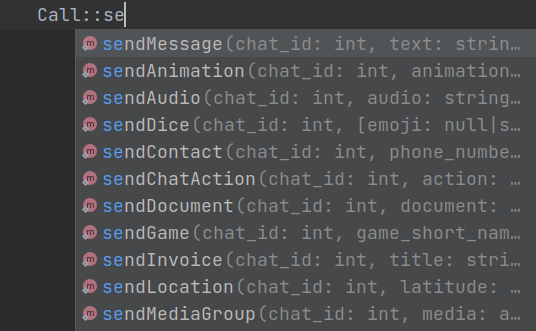
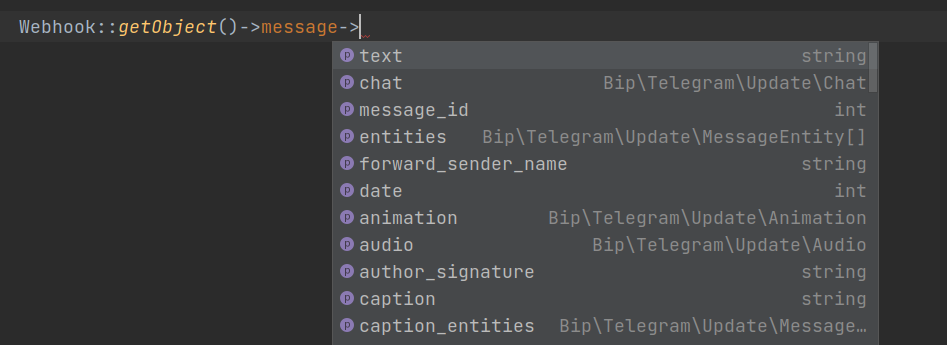
Bip (bot in php) is an open source library for creating stage base and powerful telegram bots. It is written in PHP and uses Telegram Bot API to communicate with Telegram servers.
Bip uses stages to implement the bots. Each stage is a class that contains Nodes, Node is a method of stage that do actions. These Nodes are handled by the Routing System. You can use Helpers to make your code more readable and easy to use. And use Call for calling telegram bot API methods with IDE Autocomplete.
For getting started, you need to get bip library and install it on your server.
It is recommended to use composer to install the Bip :
composer require biplib/bipin bots/NotePad of Bip library, There is a sample Notepad bot that you can run it and see how it works.
For running this bot, you need to edit bots/NotePad/config.php and set your bot token that you get from Bot Father.
Then copy URL of bots/NotePad/index.php and set it as webhook URL by calling this URL in your browser (replace <YOUR_BOT_TOKEN> with your bot token and <YOUR_SERVER_URL> with your server URL) :
https://api.telegram.org/bot<YOUR_BOT_TOKEN>/setWebhook?url=<YOUR_SERVER_URL>/bip/bots/NotePad/index.php
Note Telegram needs ssl certificate for webhook url, so you need to use https url. if you want only test Bip use telegram-bot-api for testing your bot on local machine.
if you get {"ok":true,"result":true,"description":"Webhook was set"} as response, your bot is ready to use. go to telegram and start your bot and enjoy it.
For creating your own Bots, you need to create a directory for each bot in bots directory.
Name of directory is the name of your bot must be PascalCase for example NotePad or MyBot for PSR-4 autoload compatibility.
Then create a index.php file for start point of bot in bot directory and add this code to it :
<?php
require __DIR__."/../../vendor/autoload.php"; #load autoloader
require 'config.php'; #load config file
use Bip\Bot; #use Bot class
use Bots\<BOT_DIRECTORY>\Stages\StartStage; #use StartStage class replace <BOT_DIRECTORY> with your bot directory
Bot::init(new StartStage()); #init bot with StartStage
Bot::run(); #run botThen create a config.php file in bot directory and add this code to it :
<?php
use Bip\App\Config;
use Bip\Database\LazyJsonDatabase;
Config::add([
'token' => '<YOUR_BOT_TOKEN>', #set your bot token
'admins' => [12345678,123456789],#set admins id
'database' => new LazyJsonDatabase('database.json.db'), #set database LazyJsonDatabase is simple file-based database
]);Now you can create stages for your bot in Stages directory of your bot.
For example, create StartStage.php in Stages directory and add this code to it :
<?php
namespace Bots\<BOT_DIRECTORY>\Stages; #replace <BOT_DIRECTORY> with your bot directory.
use Bip\App\Stage;
class StartStage extends Stage
{
public function controller()
{
route('welcome')->onMessageText('/start');
}
public function welcome()
{
msg('Hello World');
closeNode();
}
}controller method is called when bot is started, and it is used for routing. In this example, we route /start command to welcome method. Overriding controller method is required for each stage.
Don't forget to call closeNode() at the end of each node. If you don't call closeNode(), bot will not continue to next node and will be stuck in current node. With bindNode() you can bind a node to a method and call it later. For example :
...
class StartStage extends Stage
{
public string $name = 'none'; #public properties are automatically reassigned to the stage
public function controller() #controller is method that is called first.
{
route('setName')->onMessageText('/setName');
route('getName')->onMessageText('/getName');
}
public function setName() #this method is Node
{
msg('What is your name?');
bindNode('saveName');
}
public function saveName() #this method is Node
{
$this->name = Webhook::getObject()->message->text;
msg("You'd like me to call you by the name $this->name");
closeNode();
}
public function getName() #this method is Node
{
msg("Your name is $this->name");
closeNode();
}
private function isSepehr() #this method is not Node (because it is private)
{
return $this->name == 'Sepehr';
}
}Note Only public methods can be routed. And public properties automatically reassigned to the stage. If you don't want to automatically reassign a property, private it. And if your method is not Node, private it. For improving your database performance.
Bip has some components that you can use them in your bot. For example, you can use Logger to log your bot actions, or use Webhook to get webhook data with Autocomplete IDE.
Bot is the main class of Bip. It is used for initializing the bot and running it. You can use it like this :
<?php
...
use Bip\Bot;
Bot::init(new StartStage()); #init bot with StartStage
Bot::run(); #run botNote Bot is a singleton class. so you can use its methods without creating an instance of it.
Stage is a class that contains nodes, controller, default method and properties. That we will explain it in the following sections.
You can consider a stage is a specific part of your bot. Suppose you have a bot that has a specific part for shopping and another part for chatting, you can create ShopStage and ChatStage class and use them in your bot.
Stage classes should be in Stages/ directory of your bot.
For example, in Notepad bot, you can find StartStage classes in Stages/ directory.
in Stages/ (or anything else) directory of your project, create a PHP class file for your stage (file name should be PascalCase and The file name must be the same as the class name)
for example, we create MenuStage.php file in Stages/ directory and add this code to it :
<?php
namespace Bot\<STAGE_DIRECTORY>; #read following note for more information
use Bip\App\Stage;
class MenuStage extends Stage
{
public function controller()
{
route('menu')->onMessageText('/menu');
}
public function menu()
{
msg('This is menu');
closeNode();
}
}And extends your stage from Bip\App\Stage class.
Note For psr-4 autoload your stages you must add namespace for your stage classes. stage namespaces start with
namespace Bot\<STAGE_DIRECTORY>;that<STAGE_DIRECTORY>is the path of stage directory. for example in NotePad botbots/NotePad/Stages/StartStage.phpstage hasnamespace Bots\NotePad\Stages;.
Note
Botsnamespace point tobotsdirectory in Bip root directory. you can change it incomposer.jsonfile.
Nodes are public methods that are called when a specific event occurs. For example, when a user sends a message to your bot, a node is called. A node is the state of user, For example, We want to get two number from user and multiply them. We can create a node for getting first number and another node for getting second number and multiply them in a third node. For example :
...
class CalculatorStage extends Stage
{
#public properties are automatically reassigned to the stage
public int $firstNumber = 0;
public int $secondNumber = 0;
public function controller()
{
route('getFirstNumber')->onMessageText('/start');
}
#public methods are nodes
public function getFirstNumber()
{
msg('Enter first number');
bindNode('saveFirstNumber');
}
public function saveFirstNumber()
{
$this->firstNumber = Webhook::getObject()->message->text;
msg('Enter second number');
bindNode('saveSecondNumber');
}
public function saveSecondNumber()
{
$this->secondNumber = Webhook::getObject()->message->text;
msg("Result is : ".$this->firstNumber * $this->secondNumber);
closeNode();
}
}Note Only public methods can be routed. and public properties automatically reassigned to the stage. if you don't want to automatically reassign a property private it. and if your method is not Node private it. for improving your database performance.
controller is a public method that is called first of any node in each run.
You can use route method to route a node to a method. For example :
...
public function controller()
{
route('start')->onMessageText('/start');
route('welcome')->onMessageText('/menu');
route('profile')->onMessageText('Profile');
}
...Public properties in stage classes are automatically reassigned to the stage. It means that they are saved in database and in new requests they are reassigned to the stage. For example :
...
class CounterStage extends Stage
{
public int $counter = 0;
public function controller()
{
route('increment')->onMessageText('/increment');
}
public function increment()
{
$this->counter++;
msg("Counter is : $this->counter");
closeNode();
}
}
...CounterStage is a stage that has a counter property. When a user sends /increment command to bot, the counter property is incremented and reassigned to the stage. So when the user sends /increment command again, the counter property is incremented again and reassigned to the stage. And so on.
Note non-public properties are not reassigned to the stage.
Note highly recommended to use data type for properties. STM (Stage-Table Mapper) use data types for adding columns to the table. for example if you have a property that is
inttype, STM will add a column to the table withintdata type. if you don't use data type for properties, STM will add a column to the table withtextdata type.
default method is a method that is called when no node is routed. For example :
...
class CalculatorStage extends Stage
{
public function controller()
{
route('getFirstNumber')->onMessageText('/start');
}
public function getFirstNumber()
{
msg('Enter first number');
bindNode('saveFirstNumber');
}
public function saveFirstNumber()
{
$this->firstNumber = Webhook::getObject()->message->text;
msg('Enter second number');
bindNode('saveSecondNumber');
}
public function saveSecondNumber()
{
$this->secondNumber = Webhook::getObject()->message->text;
msg("Result is : ".$this->firstNumber * $this->secondNumber);
closeNode();
}
public function default()
{
msg('Invalid command');
}
}When a user sends a message that is not routed to any node, the default method is called. For example, if a user sends /start command to the bot, the getFirstNumber node is called. But if a user sends a message that is not routed to any node, the default method is called.
Bip has a Telegram Bot API wrapper for IDE Autocomplete. You can find it in Bip\Telegram\Call namespace. For example :
in the PHP version 8 and above you can pass named arguments to the method. For example :
...
public function test(){
Call::sendMessage(
chat_id: 123456789,
text: 'Hello World'
);
closeNode();
}
...Bip has a Webhook wrapper class that is used to get webhook data. you can find it in Bip\Telegram\Webhook namespace. for example :
Bip has some helpers that are used to make your code more readable. For example, msg(...) is a helper for sending message to user. You can find it in src/helpers.php.
msg helper is used to send message to user. It will send a message to current user. For example :
...
public function test(){
msg('Hello World');
closeNode();
}
...updateObj helper is used to get update object wrapper for IDE Autocomplete. It will return the update object. For example :
...
public function test(){
$text = updateObj()->message->text;
...
}
...update helper is used to get update object. it will return the update object same as updateObj() but without IDE Autocomplete for more speed running. for example :
...
public function test(){
$text = update()->message->text;
...
}
...bindNode helper is used to bind node to current stage. It will bind a node to the current stage. For example :
...
public function test(){
bindNode('nextNode');
}
public function nextNode(){
...
}
...closeNode helper is used to close the current node. If you don't close the current node, the node will be called again and again. For example, if you have a node that is called test and you don't close it, the test node will be called again and again. After closing the node, the default node will be bound to the stage. For example :
...
public function test(){
msg('Hello World');
}
...changeStage helper is used to change stage. It will change stage to the stage that is passed to it. For example :
...
public function test(){
changeStage(new AnotherStage());
}
...route helper is used to routing user to a node. It must be used in controller method. For example :
...
public function controller(){
route('nextData')->onMessageText('/next');
}
public function nextData(){
...
}
...dd helper is used to dump data to msg helper and die. For example :
...
public function test(){
dd('Hello World');
}
public function test2(){
dd(new TestClass());
}
public function test3(){
dd(['name' => 'Bip', 'version' => '1.0.0']);
}
...Bip has a global config class that is used to get config data. You can find it in Bip\Config namespace. You can use it in any part of your code for accessing config data. For example :
...
public function test(){
Config::add([
'token' => 'your api key'
]);
...
}
public function test(){
$token = Config::get('token');
...
}
...Bip has a database interface and classes that are used to connect to the database. You can find it in Bip\Database namespace. For example, LazyJsonDatabase class is a file based database that is used to store data in JSON file. It is lazy and does not be recommended for big data. LazyJsonDatabase is implemented from DatabaseInterface interface. You can implement your own database class from Database interface. You can implement your own database class from Database interface.
Bip has a logger class that is used to log data in JSON file. You can find it in Bip\Logger namespace. For example :
...
public function test(){
Logger::add('Start Node Called.');
...
}
...Note Logger is singleton, and you can use it in any part of your code.