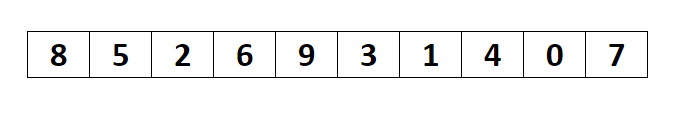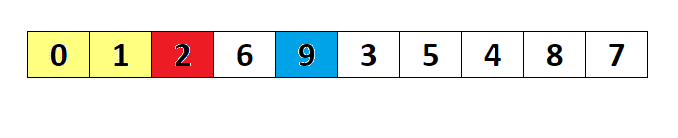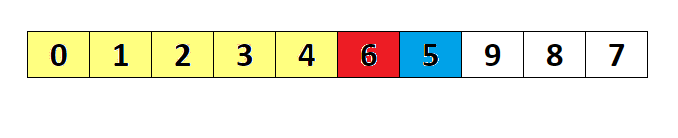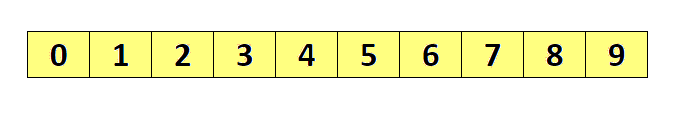What you should learn from this project:
- At least four different sorting algorithms
- What is the Big O notation, and how to evaluate the time complexity of an algorithm
- How to select the best sorting algorithm for a given input
- What is a stable sorting algorithm
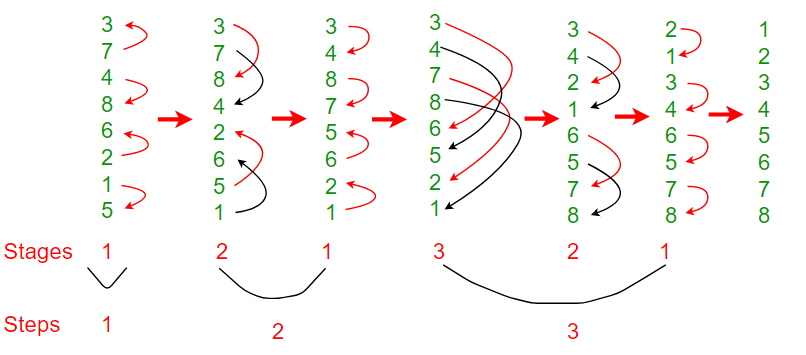
- Bubble Sort is the simplest sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they are in wrong order.
- Insertion sort is the sorting mechanism where the sorted array is built having one item at a time. The array elements are compared with each other sequentially and then arranged simultaneously in some particular order. The analogy can be understood from the style we arrange a deck of cards.
- The selection sort algorithm sorts an array by repeatedly finding the minimum element (considering ascending order) from unsorted part and putting it at the beginning. The algorithm maintains two subarrays in a given array.
- The subarray which is already sorted.
- Remaining subarray which is unsorted. In every iteration of selection sort, the minimum element (considering ascending order) from the unsorted subarray is picked and moved to the sorted subarray.
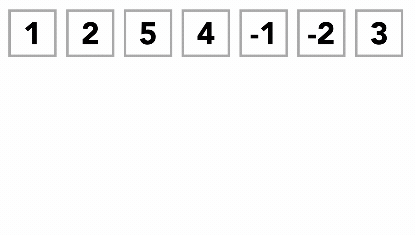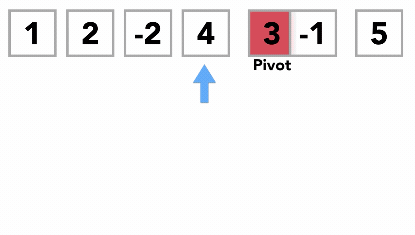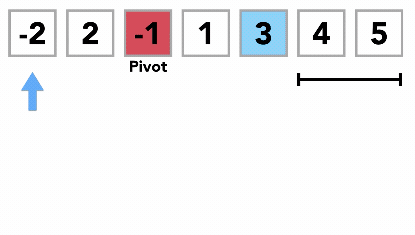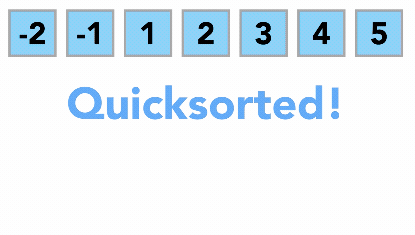
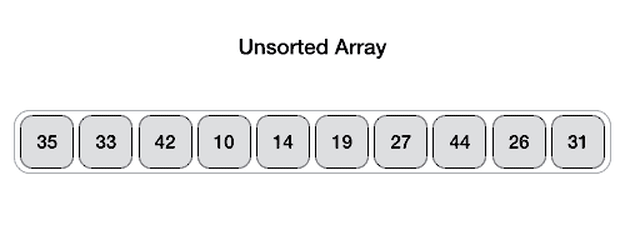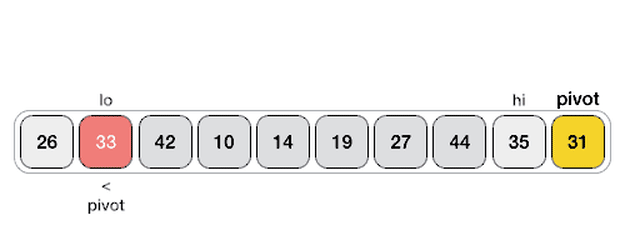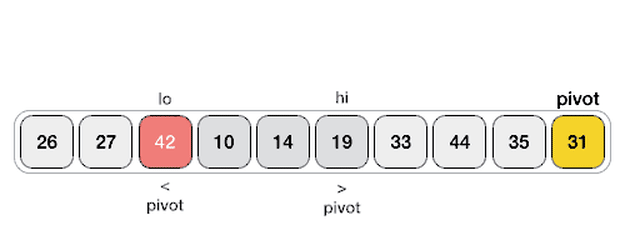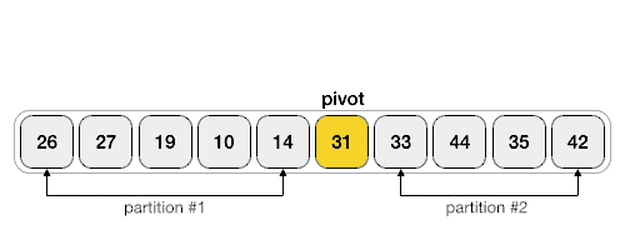
- Like Merge Sort, QuickSort is a Divide and Conquer algorithm. It picks an element as pivot and partitions the given array around the picked pivot. There are many different versions of quickSort that pick pivot in different ways.
- Always pick first element as pivot.
- Always pick last element as pivot (implemented below)
- Pick a random element as pivot.
- Pick median as pivot.
- ShellSort is mainly a variation of Insertion Sort. In insertion sort, we move elements only one position ahead. When an element has to be moved far ahead, many movements are involved. The idea of shellSort is to allow exchange of far items. In shellSort, we make the array h-sorted for a large value of h. We keep reducing the value of h until it becomes 1. An array is said to be h-sorted if all sublists of every h’th element is sorted.
- Cocktail Sort is a variation of Bubble sort. The Bubble sort algorithm always traverses elements from left and moves the largest element to its correct position in first iteration and second largest in second iteration and so on. Cocktail Sort traverses through a given array in both directions alternatively.
- Counting sort is a sorting technique based on keys between a specific range. It works by counting the number of objects having distinct key values (kind of hashing). Then doing some arithmetic to calculate the position of each object in the output sequence.
- The merge sort algorithm is a stable external sort algorithm based on the divide and rule technique. The idea of the merge-sort algorithms is to divide the array in half over and over again until each piece is only one element long. Then those elements are put back together (shuffled) in sort order.
- Heap sort is a comparison-based sorting technique based on Binary Heap data structure. It is similar to selection sort where we first find the minimum element and place the minimum element at the beginning. We repeat the same process for the remaining elements.
- Radix sort is a sorting algorithm that sorts the elements by first grouping the individual digits of the same place value. Then, sort the elements according to their increasing/decreasing order.
- Bitonic sort is parallel sorting algorithm that performs comparisons. Number of comparisons done by Bitonic sort are more compared to other popular sorting algorithms. This sort is better for parallel implementation as user always compares the elements in a predefined sequence and this sequence of comparison does not actually depend upon data. And hence this bitonic sort is basically suitable for hardware implementations.
- Hoare's Partition Scheme works by initializing two indexes that start at two ends, the two indexes move toward each other until an inversion is (A smaller value on the left side and greater value on the right side) found. When an inversion is found, two values are swapped and the process is repeated.
- Big O Notation is a way to measure an algorithm’s efficiency. It measures the time it takes to run your function as the input grows. Or in other words, how well does the function scale.
- Diana Carhuamanta - CarolinaDCode # sorting_algorithms