Somewhat useful python custom libraries
- Create Vectors and use operations in any way you want.
- Convenient, no dimensions limits, easily manipulated.
Use it as an object, list, dictionary, tuple, whatever, anything works.
from vectors import *
foo = Vector(5,7)
print(foo)>>> Vector2(5, 7)Or choose your own way to create a Vector
a = Vector([3,4,6])
b = Vector({'y':8, 'x':3})
c = Vector(1)
d = Vector()>>> Vector3(3, 4, 6)
>>> Vector2(3, 8)
>>> Vector1(1)
>>> Vector0()- Working operators:
bool abs sum ceil floor round invert str == -x and or % * + - / // ** [x] [x]=x len hash repr < > <= >= ~
Just think of them as normal numbers:
a = Vector(1,2)
b = Vector(3,4)
print(a+b)>>> Vector2(4, 6)Not the same dimension? Doesn't matter.
- 0 will be the default value for missing values
a = Vector(1,2,3)
b = Vector(5)
print(a-b)>>> Vector3(-4, 2, 3)- empty values will be ignored for divisions (no divisions by 0)
operators:///%
a = Vector(6,2,1,0)
b = Vector(2)
print(a/b) # a//b also works btw>>> Vector4(3.0, 2, 1, 0)Coordinates are saved in Vector.coords
foo = Vector(7,8,9)
print(foo.coords)>>> [7, 8, 9]However, that was the polically correct way, which is boring. Again, do it however you want:
foo = Vector(7,8,9)
for v in foo:
print(v)7 8 9Or unpacking the values
def bar(x,y,z):
print(x+y+z)
foo = Vector(7,8,9)
bar(*foo)24You get it at this point...
foo = Vector(7,8,9)
foo.coords[0] = 1
foo[1] = 2
foo.z = 3
print(foo)
print(foo.coords[0], foo[1], foo.z)Vector3(1, 2, 3)
1 2 3Operators such as == != are self-explanatory,
a = Vector(1,2,3)
b = Vector(3,3,3)
c = Vector(2,1,0)
print(a == b-c)>>> TrueBut some aren't really black and white:
- Ambigous operators:
bool(foo) will always return True
if (Vector(0)): True
This allows simpler boolean operations:
vec and "Correct" or "Incorrect"a>b will return sum(a)>sum(b) (sum of all coordinates)
Vector(-8,8) > Vector(1) = False
Vectors are compatible with the math lib
import math
foo = Vector(1.3, 2.8)
print(math.floor(foo))
print(math.ceil(foo))Vector2(1, 2)
Vector2(2, 3)It is also possible to use these methods without the library
print(foo.floor())
print(foo.ceil())Use either copy clone new
Or you can even use Vector(vec):
foo = Vector(1,2)
a = foo.copy()
b = foo.clone()
c = foo.new()
d = Vector(foo)
foo.x = 0
print(a,b,c,d)
print(foo)Vector2(1, 2) Vector2(1, 2) Vector2(1, 2) Vector2(1, 2)
Vector2(0, 2)Returns the minimum and maximum vectors of all given vectors:
-> (min: Vector, max: Vector)
a = Vector(1,2,3)
b = Vector(3,3,2)
c = Vector(2,1,0)
print(a.bounds(b,c)) # using self
print(Vector.bounds(a,b,c))>>> (Vector3(1, 1, 0), Vector3(3, 3, 3))
>>> (Vector3(1, 1, 0), Vector3(3, 3, 3))(<=> length of a vector)
Dot vectors of one or multiple vectors:
-> scalar: int
a = Vector(1,2,3)
b = Vector(3,3,2)
print(a.dot(b))>>> 15
⚠️ Only for Vector3
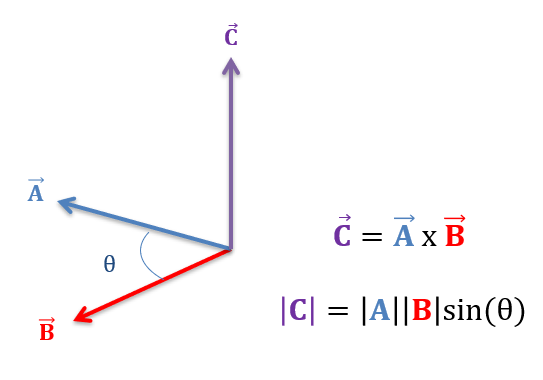
Cross product of 2 Vectors: -> crossed: Vector
```py a = Vector(1,2,3) b = Vector(3,3,2) print(a.cross(b)) ``` ```py >>> Vector3(-5, 7, -3) ```
⚠️ Only for Vector2
Returns the angle between 2 vectors:
-> radians: float
a = Vector(1,0)
b = Vector(0,1)
print(a.angle(b))>>> 1.571 # radians
⚠️ Only for Vector2
Returns True if both vectors are orthogonal:
(<=> vecA.dot(vecB) <= approx)
-> orthogonal: bool
a = Vector(1,0)
b = Vector(0,1)
print(a.orthogonal(b))>>> TrueReturns the linearly interpolated vector:
a = Vector(6,3)
b = Vector(10,1)
print(a.lerp(b, 0.5))>>> Vector2(8, 2)[Only supported in 2D for now]
An object with a Vector position and a rotation number
arrow = Pointer(Vector(0,0), 0, unit='deg') # radians by default
arrow.move(Vector(5,0))
arrow.rotate(45)
arrow.forward(5)