MySQL is a popular relational database management system that is widely used in web applications, data analytics, and other industries. It supports transactions, ACID compliance, and is known for its high performance and scalability. It also provides support for a wide range of data types, including integers, decimals, strings, and date/time values. MySQL is often used for applications that require high concurrency, such as e-commerce sites, banking systems, and social media platforms.
##SQLite
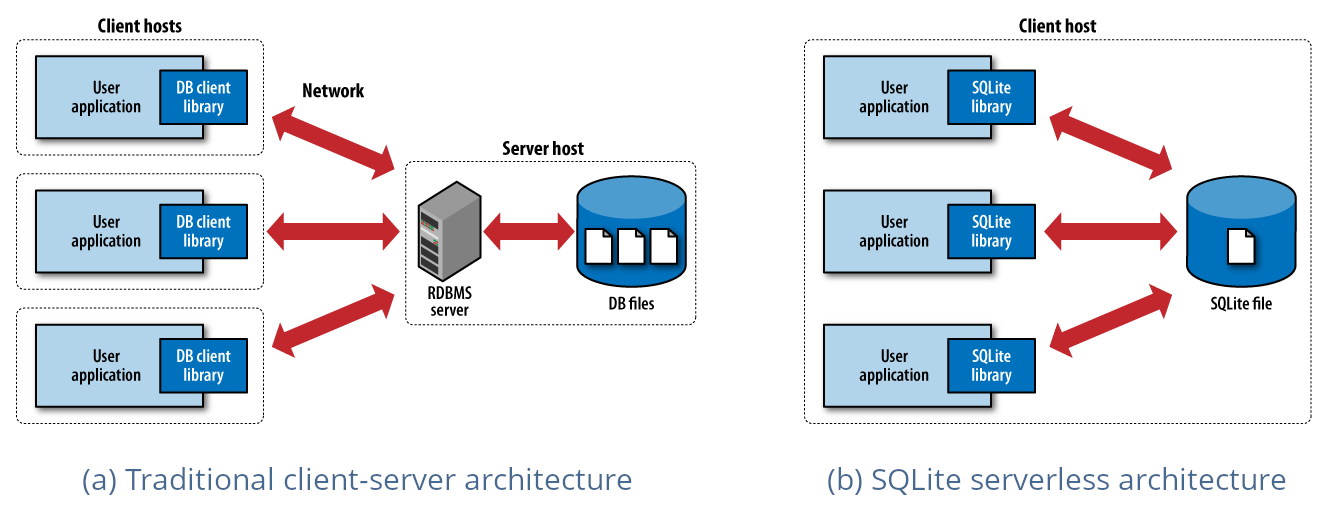
On the other hand, SQLite is a lightweight, file-based relational database that is often used for smaller projects or applications that do not require the full functionality of a traditional database management system. It has a very small footprint and does not require a separate server process or installation, making it easy to set up and use. SQLite is often used in mobile applications, embedded systems, and small-scale desktop applications.
MongoDB is a popular NoSQL document-oriented database that is designed for scalability, flexibility, and performance. Unlike relational databases like MySQL and SQLite, which store data in tables, MongoDB stores data in flexible, JSON-like documents that can be easily manipulated and queried. MongoDB is often used in modern web applications, content management systems, and other applications that require fast read/write performance and the ability to handle large amounts of unstructured or semi-structured data.
In summary, while MySQL is ideal for large-scale, high-performance applications, SQLite is better suited for smaller projects or applications that require a lightweight, file-based database. Meanwhile, MongoDB is designed for handling unstructured or semi-structured data and providing scalability and performance for modern web applications