#####What is MoodLocator? MoodLocator is a demo application created for Bluemix. It combines the API economy and Bluemix, which is a Platform as a Service, provided by IBM. This description explains how to easily upload an alone standing application to the Bluemix Cloud and to add Bluemix Services with it.
#####What it does. MoodLocator uses Google Maps and Twitter to display the current Twitter Messages (Tweets) on a map. This has a city name as defined search criteria and therefore also defines the border area to collect the tweets. Bluemix provides the cloud platform where this app runs and even though one of the Bluemix services called Watson User Modeling will be chosen to combine.The Watson User Modeling service collects the City Tweets and uses linguistic analytics to extract a spectrum of cognitive and social characteristics of them.
#####What are you looking for? If you didn't test my application already, you can test it on MoodLocator. If you just want to get a quick overview over my bluemix demo, take a look over my Slideshare presentation. Here on GitHub you will find two kinds of descriptions. One called Presentation and the other one called Technical. Presentation is to understand, what you need to run the application and present it. Technical is to fully understand my code, so that you can use the User Modeling Service in your own application.
#Technical
It is very important that the technical part is always up to date. When something changes, please contact me. I will change the code as quick as possible.
Welcome to the technical view of my Bluemix demo application. Here you will find everything you need to understand my code. I recommend to check out my [Slide share] presentation to get a quick overview what is happening behind my application.
This is what you need to understand my code:
- Basic knowledge of Bluemix
- HTML
- CSS
- JavaScript
- Node.js
Do not be afraid when you are not a pro in programming, I'm neither. When you do not know how to use Bluemix or how to create an application in Bluemix, than take a look in the Presentation section.
If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact me!

####Overview
- Directories and Files
- Basic Bluemix Node.js application
- Download Starter Application
- Prepare Starter Application
- The core of the application
- What is app.js
- Start the application
- The user visit the website (1)
- Skeleton of the website
- Style
- Map
- Searchfield
- Server reaction
- Socket.IO
- Coordinates
- Watson
- The user visit the website (2)
- Marker
- Menu buttons
- Progress bar
#####1. Directories and Files Here are the directories and files you will find when you clone / download the application from GitHub and open the section node. Just take a quick look, we will go deeper into it at a later point of this documentation. When you get lost you can always come back here and get an overview where we are in the application.
#####2. Basic Bluemix Node.js application
My documentation will be like a tutorial, that means, we start at the very basic (Starter Application) and I add my code to it and describe what it does.
I think it is better to understand the chronicle order of the code, so I will jump between server-sided code and client-sided code.

######Download Starter Application There are two ways to follow up with my code: When you are a starter in Node.js and Bluemix, I recommend to add the code with me and build the application together. When you understand how Node.js works, just clone / download my git repository and take a look in my code every time I add something.
We start with the basic Starter Application, which you can download from Bluemix.
Go to the Bluemix Website and log in with your Bluemix account.
Create a new application and open it afterwards.
Click on "Start Coding" it is in the Overview Section on the left side.
Click on big blue button "Download Starter Code" and it will start downloading.
You downloaded the Starter Application from Bluemix and the files should look like that
######Prepare Starter Application
Open the Starter Application in a basic text editor
I recommend Sublime or Notepad++
When you take a look at the directory views. You will see, that we are using jade as a templating language instead of plain HTML. In case of understanding issues I will use ejs as a templating language. It adds a bit of Javascript to plain HTML, it is easier to understand for everyone. In the next step we will change jade to ejs.
Open package.json
The file package.json is required by the Node.js environment. It specifies the Node.js project name, dependencies, and other configurations of your Node.js application. As you can see we are requiring two dependencies, express version 3.4.7 and jade version 1.1.4 lets change that to ejs.
In "dependencies" set jade to ejs with version ^1.1.0
In order to use ejs we have to update express to version ^4.6.1
In "dependencies" set the version of express to ^4.6.1
Now we have to delete our jade files and create an ejs file.
Open the directory "views" and delete every ".jade" file.
After that make a new empty file in "views" and name it "index.ejs"
In the next step we have to tell our application to use them.
Open app.js
The app.js file is the core file, which is the server side JavaScript for your application written using the Node.js API. We changed our dependencies and now we have to tell our server which one he should use. Express 4.x is a little bit different to express 3.x so we have to delete some of the middleware.
Without comments it will look like that
1 var express = require('express');
2
3 var app = express();
4 app.use(app.router);
5 app.use(express.errorHandler());
6 app.use(express.static(__dirname + '/public'));
7 app.set('view engine', 'jade');
8 app.set('views', __dirname + '/views');
9
10 app.get('/', function(req, res){
11 res.render('index');
12 });
13
14 var appInfo = JSON.parse(process.env.VCAP_APPLICATION || "{}");
15 var services = JSON.parse(process.env.VCAP_SERVICES || "{}");
16
17 var host = (process.env.VCAP_APP_HOST || 'localhost');
18 var port = (process.env.VCAP_APP_PORT || 3000);
19
20 app.listen(port, host);
21 console.log('App started on port ' + port);4 Delete this line
5 Delete this line
7 Change the view-engine from jade to ejs
1 var express = require('express');
2
3 var app = express();
4 app.use(express.static(__dirname + '/public'));
5 app.set('view engine', 'ejs');
6 app.set('views', __dirname + '/views');
7
8 app.get('/', function(req, res){
9 res.render('index');
10 });
11
12 var appInfo = JSON.parse(process.env.VCAP_APPLICATION || "{}");
13 var services = JSON.parse(process.env.VCAP_SERVICES || "{}");
14
15 var host = (process.env.VCAP_APP_HOST || 'localhost');
16 var port = (process.env.VCAP_APP_PORT || 3000);
17
18 app.listen(port, host);
19 console.log('App started on port ' + port);Now we prepared our application and can start building it. Here you will find the difference between ejs and jade. In order to run the application local you have to install the node modules express and ejs.

#####3. The core of the application
We take a look in the core of the Starter Application, which we will find it in app.js. I decided to split app.js in several sections, so we can pick one part finish it and go over to the next one.

######What is app.js Easy spoken our server is defined in app.js, everything what we are doing there has influence on our server. I copied our prepared application and added some comments and sections to it.
######Start the application When we start our application the server sided code will run and trigger everything. We take a look in every section, I describe what is happening and after that we will flow with the code and add code to each section when it is necessary.
I. As you know node.js has something called modules. Modules are like libraries, packages of code that you can implement at the start of your application. We require the module express, but what is Express? Express is a minimal and flexible Node.js web application framework that provides a robust set of features for web and mobile applications. Later we will come back here and add more modules to our application.
II. We setup our middleware and create an instance "app" from express. Then we tell this instance, which directories it should use and set our "view engine" to "ejs".
III. When our instance get an request on the path '/', easy spoken when a user visit our website "ourwebsite.com/", it will render the index.ejs for the client.
IV. If we push our application to Bluemix, Bluemix will add a file, which contains our application information and service information. If our application is running inside of Bluemix, it will get "VCAP_APPLICATION", which is in JSON format an parse the information into a string and save it to "appInfo", else it will give back a empty JSON object "{}". The same process is happening for "VCAP_SERVICES".
V. It is similar to section 4, when we are connected to Bluemix it will add a file. This file will tell us which port and host we should use. If we are running the application outside of Bluemix it uses our "localhost" on port "3000". When our application decided where it is, outside or inside of Bluemix, the server will start on the given port and host.
#####4. The user visit the website Now we will look through the user perspective and add everything we need. As we can see in section III, when the user is visiting our website on the path '/' he will render "index.ejs".
Open the "index.ejs" file you created earlier you will find it in "views"
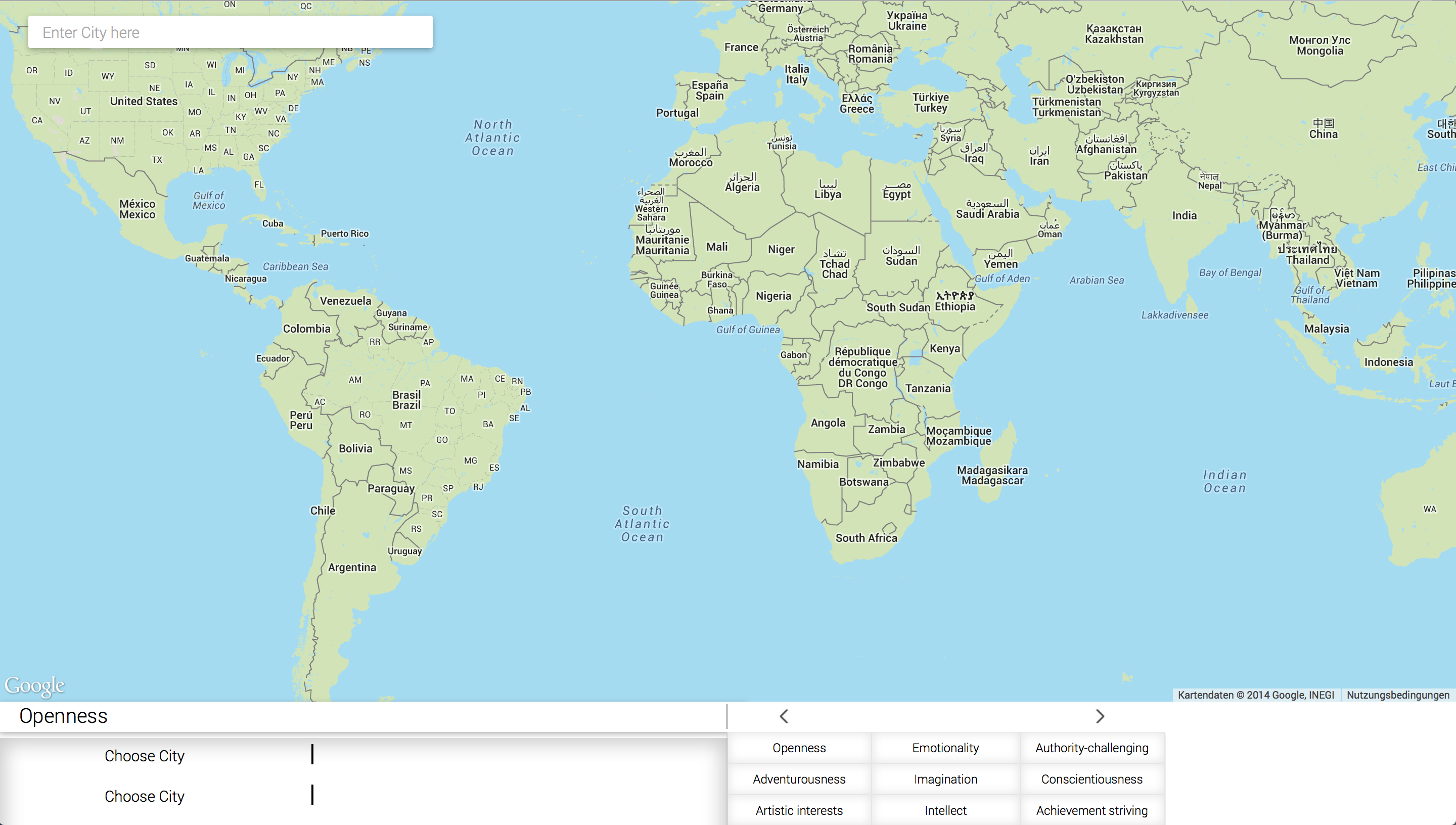
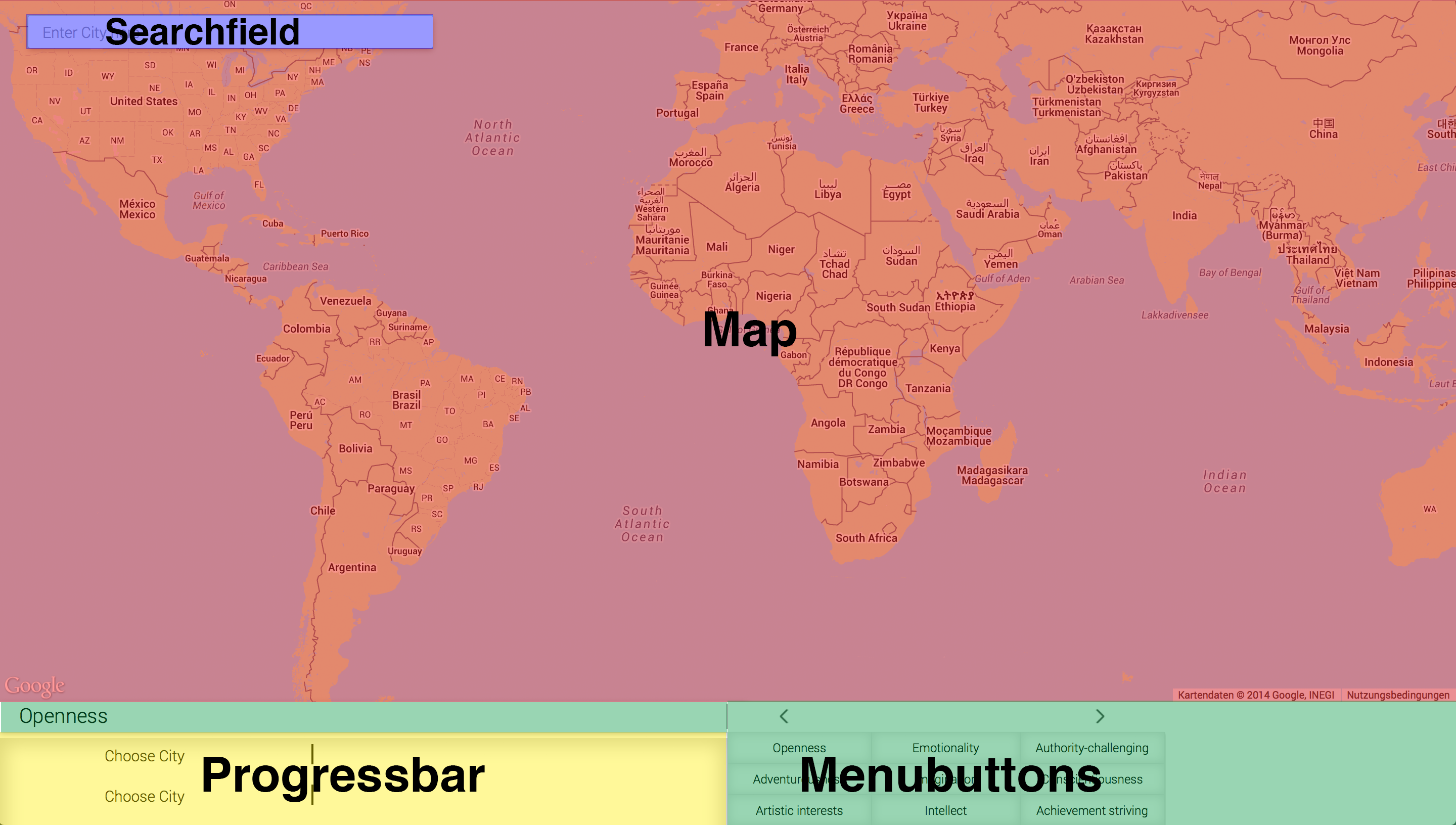
######Skeleton of the website If you want to understand this section you should know what we need for our application. If you do not know what this application does, check out my [Slide share] presentation. What elements we are going to need for our website:
(blue) Searchfield to search a city.
(red) Map to display the city and the tweets.
(green) Menu buttons to select the User Modeling parameters.
(yellow) Progress bar to show the value for the selected parameter.
######Style My documentation wont cover styling the html elements with css. In order to get the application running, you have to use my stylesheets or create your own stylesheets. You will find them by downloading my GitHub repository.
Open the directory node
Open the directory public
Open the directory stylesheets
Here you will find the "style.css" I used for my application.
Copy style.css
Open your application
Open the directory public
Open the directory stylesheets
Paste & replace style.css
######Map We need to display a map on our website, so what do we need? We need a map div element where the map will be shown. A connection to the Google Maps API where we get the map from. And a bit of Javascript Code to style and show the map on the screen. Lets start with the html code, we write it in "index.ejs".
1 <!DOCTYPE html>
2 <html>
3 <head>
4 <title> MoodLocator </title>
5 <!-- Use Stylesheet --> <link rel='stylesheet' href='/stylesheets/style.css'>
6 <!-- Use GoogleMapsAPI --> <script
7 type="text/javascript"
8 src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?sensor=false">
9 </script>
10 </head>
11
12 <body onload="initialize()">
13 <div id="map_canvas"></div>
14 <!-- Use MyScript --> <script
15 type="text/javascript"
16 src='/scripts/script.js'>
17 </script>
18 </body>
19 </html>-
Require "style.css" to style our website elements
-
Require the Google Maps API to get the current map and a lot of options for it
-
Set body and when our body is fully loaded call a client sided JavaScript function
-
Create an element "map_canvas" here the map gets displayed
-
Insert self written JavaScript, which reacts on user actions or element actions
In line 13 we call a JavaScript function "initialize( )" but what will happen when our body finished loading? We have to code what happens when that function gets called but first we have to create a script file.
Open the directory public
Create a directory called "scripts"
Create a file called "script.js"
Write the following Code there
1 function initialize() {
2
3
4 //MAP
5 //Settings for Goolge Map
6 var mapOptions = {
7 center: new google.maps.LatLng(0, 0),
8 mapTypeId: google.maps.MapTypeId.ROADMAP,
9 styles: styleMaps(),
10 disableDefaultUI: true,
11 scrollwheel: false,
12 draggable: false,
13 zoom: 3
14 };
15
16 //Crate Google Map with set parameters and link it to the UI DivElement
17 var map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById("map_canvas"), mapOptions);
18
19 //Client Sided Code goes here
20 }-
Set function "initialize()"
-
Set some options for our map
-
Set center of the map
-
Set map type to roadmap
-
Set a style to the map, you will find the style at the end of "script.js"
-
Disable UI elements like google Streetview
-
Disable scrolling in and out
-
Disable dragging the map
-
Set Zoom to value 3 (lower number = far / higher number = near)
-
Create map with map options and display it on the "map_canvas" element
When you start the app local or push it to Bluemix you will now see, a map displayed on your screen. In the next step we want to search a City therefore we need a Searchfield.

######Searchfield For the Searchfield we need a Textfield element. When we type Text inside the Textfield it should give as suggestions, with valid places. To allow that we need the Google Places API. When we confirm a city it should give us the coordinates of this place, which we send to our server, and the map should show the place within a 25km radius.
Open your index.ejs again
1 <!DOCTYPE html>
2 <html>
3 <head>
4 <title> MoodLocator </title>
5 <!-- Use Stylesheet --> <link rel='stylesheet' href='/stylesheets/style.css'>
6 <!-- Use GoogleMapsAPI --> <script
7 type="text/javascript"
8 src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?sensor=false">
9 </script>
10 <!-- Use GooglePlaces --> <script
11 type="text/javascript"
12 src="http://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?libraries=places&sensor=false">
13 </script>
14 </head>
15
16 <body onload="initialize()">
17 <input id="pac-input" class="controls" type="text" placeholder="Enter City here">
18 <div id="map_canvas"></div>
19 <!-- Use MyScript --> <script
20 type="text/javascript"
21 src='/scripts/script.js'>
22 </script>
23 </body>
24 </html>-
Insert the Google Places API
-
Create a text input element
Open your script.js again Write the following Code inside the initialize() function Write the following Code beneath the Map function
1 //INPUT ELEMENT
2 var cityCounter = 1;
3
4
5 //Link input variable with the text input from UI TextElement
6 var input = (document.getElementById('pac-input'));
7 map.controls[google.maps.ControlPosition.TOP_LEFT].push(input);
8 var searchBox = new google.maps.places.SearchBox((input));
9
10
11 //Create Event Listener for Selected Place
12 google.maps.event.addListener(searchBox, 'places_changed', function() {
13 var places = searchBox.getPlaces();
14
15 if (places.length == 0) {
16 return;
17 }
18 var searchPlace;
19
20
21 //Get Coordinates for each Place
22 for (var i = 0, place; place = places[i]; i++) {
23 if(cityCounter === 1){
24 document.getElementById('firstCityName').innerHTML = place.name;
25
26
27 //Sent Place and Id to Server
28 var coordinateObj = {
29 coordinates: place.geometry.location,
30 id: cityCounter
31 }
32 socket.emit('chat message', coordinateObj );
33
34
35 //Make Circle to Zoom
36 searchPlace = new google.maps.Circle({
37 center: place.geometry.location,
38 radius:25000,
39 strokeOpacity:0,
40 fillOpacity:0
41 });
42 searchPlace.setMap(map);
43
44
45
46 } else if(cityCounter === 2){
47 document.getElementById('secondCityName').innerHTML = place.name;
48
49 //Sent Place and Id to Server
50 var coordinateObj = {
51 coordinates: place.geometry.location,
52 id: cityCounter
53 }
54 socket.emit('chat message', coordinateObj );
55
56
57 //Make Circle to Zoom
58 searchPlace = new google.maps.Circle({
59 center: place.geometry.location,
60 radius:25000,
61 strokeOpacity:0,
62 fillOpacity:0
63 });
64 searchPlace.setMap(map);
65
66
67 } else {
68 alert('Reload Page to set more Locations');
69 }
70 }
71 cityCounter++;
72 map.fitBounds(searchPlace.getBounds());
73 });-
Create a variable called input wich will get the value from textfield
-
Set textfield element to the top left.
-
Create a searchbox with the value from input this will make suggestions when you search for places
-
When a User confirmed a place this function will fire
-
Create places from confirmded place, Google will provide an object for that place
-
Check if places is in Google Places Libaries or not
-
If it is not return from function
-
Get coordinates for each place, Google found in its libaries for the place the User chose
With Moodlocator you can compare you can compare max. 2 Cities, we have to check if one cities has been chosen
-
Check if it is the first or the second city
-
Set first city name for the text element in progressbar (Which we will create later)
-
Create an coordinate object for the choosen city
-
Set coordinates equal to the coordinates from the choosen place
-
Set id to the value of the first city
In the next step we will send the coordinates to the server, because the Twitter API is only running on server side. I use the socket technology for a quick and easy connection to the server, but we haven't installed it yet. For clarity I will finish the Searchfield and install it afterwards.
-
Use Socket technology and send the coordinate object to the server
-
Make a circle around the place the User searched
-
Set center of the circle
-
Set radius to 25km
-
Set circle stroke color to none
-
Set circle fill color to none
-
Adress the circle to the map
46 - 70) The same thing for the second City
- Recreate map with a diffrent zoom. Take the zoom form the 25km radius circle
We created a searchfield, attached the Google Places API and wrote a function for what will happen when someone tries to search a place. When a place gets called it will send a coordinate object to the server. To send the object we use socket, which we will build in the next step.

In this section we will cover most of the serversided code. How do we pass data between client and server? What will happen to the coordinates object? How do we do a Twitter request? That are some of the questions we will answere in this section.

As I said, we use socket technology, that means it enables real-time bidirectional event-based communication. In the next steps I will describe how to implement Socket.IO. We have to install Socket.IO on client and server side. First of all we will implement it on clientside.
Open your index.ejs again
1 <!DOCTYPE html>
2 <html>
3 <head>
4 <title> MoodLocator </title>
5 <!-- Use Stylesheet --> <link rel='stylesheet' href='/stylesheets/style.css'>
6 <!-- Use GoogleMapsAPI --> <script
7 type="text/javascript"
8 src="https://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?sensor=false">
9 </script>
10 <!-- Use GooglePlaces --> <script
11 type="text/javascript"
12 src="http://maps.googleapis.com/maps/api/js?libraries=places&sensor=false">
13 </script>
14 <!-- Use Socket.IO --> <script
15 type="text/javascript"
16 src="https://cdn.socket.io/socket.io-1.2.1.js">
17 </script>
14 </head>-
Tell the client to download Socket.IO from the CDN Library
Open your script.js again Write the following line inside the initialize() function Write the following line on top of the Map section
1 var socket = io();
2
3 //MAP
4 var mapOptions = { ... }-
Enable socket as a varible for your javascript code
-
It should just symbolize the map function do not insert this line
Before we will jump to the server sided Code we will install the socket.io module with npm. When you have problem with understanding this part. I recommend a npm modules understanding guide.
Open your Terminal / Console
Change inside your project directory ($cd)
Install socket.io module ($npm install socket.io)
You installed socket.io localy, but we still have to tell our server which version it should use.
Open package.json
1 {
2 "name": "yourApp",
3 "version": "0.0.1",
4 "description": "yourDescription",
5 "dependencies": {
6 "express": "^4.6.1",
7 "socket.io": "*",
8 "ejs": "^1.0.0"
9 },
10 "engines": {
11 "node": "0.10.26"
12 },
13 "repository": {}
14 }- Tell the server it should use the dependencie socket.io with any version
In the last step we have to tell the server he should use socket.io and socket should listen to our server. And add a function to start our socket connection.
Open app.js
1 //Setup Server
2 var host = (process.env.VCAP_APP_HOST || 'localhost');
3 var port = (process.env.VCAP_APP_PORT || 8080);
4
5 //Require Socket.IO, Start The Server
6 var io = require('socket.io').listen(app.listen(port, host));
7 console.log('App started on port ' + port);
8
9 //Start Socket Connection
10 io.on('connection', function(socket){
11 console.log('user connected');
12
13 //On Message from Client
14 socket.on('chat message', function(msg){
15
16 )};
17 )};-
Attach a variable "io" to socket and socket listen to the server
-
Start the socket connection when a user connects
-
When a message with the name "chat message" came call function with value msg of sended data
We installed socket.io on client and server side. As you remember we send our coordinate objecte to the server with the name "chat message". When a user enters a city the coordinates object gets send to the server. And the socket function gets called, the "msg" variable is now our coordinates object.

The coordinates object is now on the server side. It contains the center point in a latitude variable and a longitude variable of the place the user selected. When we make a Twitter Stream request for a certain area, Twitter unfortunately doesn't want a center point and a radius. Twitter needs two points that span a rectangle. In that case we have to edit our coordinates object and make two points, who have the same distance to the center point and lie on the opposite side.
1 //Start Socket Connection
2 io.on('connection', function(socket){
3 console.log('user connected');
4
5 //On Message from Client
7 socket.on('chat message', function(msg){
8
9 //Get Coordinate Rectangle For Twitter
11 var lat = msg.coordinates.k;
12 var lon = msg.coordinates.D;
13 var x = lat;
14 var y = lon;
15 var distance = 0;
16
17 function getDistanceFromLatLonInKm(lat1,lon1,lat2,lon2) {
18 var R = 6371;
19 var dLat = (lat2-lat1)* (Math.PI/180);
20 var dLon = (lon2-lon1)* (Math.PI/180);
21 var a =
22 Math.sin(dLat/2) * Math.sin(dLat/2) +
23 Math.cos((lat1)* (Math.PI/180)) * Math.cos((lat2)* (Math.PI/180)) * Math.sin(dLon/2) * Math.sin(dLon/2)
24 ;
25 var c = 2 * Math.atan2(Math.sqrt(a), Math.sqrt(1-a));
26 var d = R * c;
27
28 distance = d;
29 x += 0.0001;
30 y += 0.0001;
31 }
32
33 do {
34 getDistanceFromLatLonInKm(lat,lon,x, y);
35 if (distance > 25){
36 twitterFeed();
37 }
38 } while (distance < 25);
39 )};
40 )};11 / 13) Create two latitude variable from coordinates object
12 / 14) Create two longitude variable from coordinates object
-
Set distance between the two points we just created to 0
-
Create a function which calculates the distance between two coordinate points
-
Variable for earth radius
19 - 26) Calculate the distance
29 / 30) Increment one points variables
-
Make a do-while loop, wich repeats this function until the distance between both points is 25km
-
When the distance is greater than 25km call function twitterFeed();
We createt one point wich has a 25 km distance from the center in a second step we have find the point from the opposite side.
Before we do that, we have to set up everything for our Twitter request.

We can implement the Twitter Stream API as a module for node. But when we ask for a Twitter Stream API request, Twitter needs an authentication, who is
---> Twitter Key ---> Twitter Module
1 //Call Twitter with Strings
2 function twitterFeed(){
3 var dx = x - lat;
4 var dy = y - lon;
5 var x_ = lat - dx;
6 var y_ = lon - dy;
7 var locationString = x_ + ',' + y_ + ',' + x + ',' + y;
8 var reversedLocationString = '' + y_ + ',' + x_ + ',' + y + ',' + x + '';
9 console.log('Location for: ' + reversedLocationString);
10
11 //Setup Twitter
12 var twit = require('twitter');
13 var twitter = new twit({
14 consumer_key: 'insert_consumer_key',
15 consumer_secret: 'insert_consumer_secret',
16 access_token_key: 'insert_access_token_key',
17 access_token_secret: 'insert_access_token_secret'
18 });
19
20 twitter.stream('filter', {locations: reversedLocationString}, function(stream){
21 stream.on('data', function(data){
22
23 //Send Twitter Data to Client
24 if (data.geo != null){
25 var twitterObj = {
26 text: data.text,
27 name: data.user.name,
28 coordinates: data.coordinates
29 }
30 socket.emit('chat message', twitterObj);
31 }
32 });
33
34 //On Disconnect stop Stream
35 socket.on('disconnect', function () {
36 stream. destroy();
37 console.log('user disconnected');
39 });
40 });
41 }#Presentation
Welcome to the presentation view of my Bluemix demo application.
Here you will find everything you'll need to run and present my code.
This section will be split in two parts. One part is for the preparation to set up everything to run the application and the other part is to run the application to present it.
###Preparation This preparation documentation is made, so that you can jump over sections which you’ve completed already. But take a quick look into each section and be sure you didn’t miss a step.
####Overview
- Get your Accounts
- Twitter Developer Account
- Bluemix Account
- Create Bluemix Application
- Install the Software
- cf Command Line Tool
- Other recommended Tools
- Change Settings in your Application
- mainfest.yml
- app.js
- Add Watson Service
- How to upload MoodLocator
- Further reading
#####1. Get your Accounts You need to get Tweets. So we have to create a Twitter Developer Account and we need a Bluemix Account where we can upload our application and add the services.
######Twitter Let’s get started with the Twitter Developer Account. Open your browser and go to the Twitter homepage. If you don’t already have a Twitter account register for it and create one. If you do have a Twitter account be sure to log off and reload the Twitter homepage again. On the bottom of the page you will see a blue line with several options.
Click on "developer"
The Twitter developer will open. It should look like that:
Go to the bottom of the page and search for the menu point "Tools“.
Click on "Manage Your Apps“
Sign in with your Twitter account.
You will see a button in the middle of the page which says "Create New App“
Click on "Create New App“
You now will create your own Twitter application
Name your new app
Describe your new app
Add a placeholder homepage to your app „http://yourappname.com“
Confirm the developer agreement
Click on „Create your Twitter Application“.
You have created your own Twitter app, now let's create the keys you need for your application.
Select "Keys and Access Tokens“
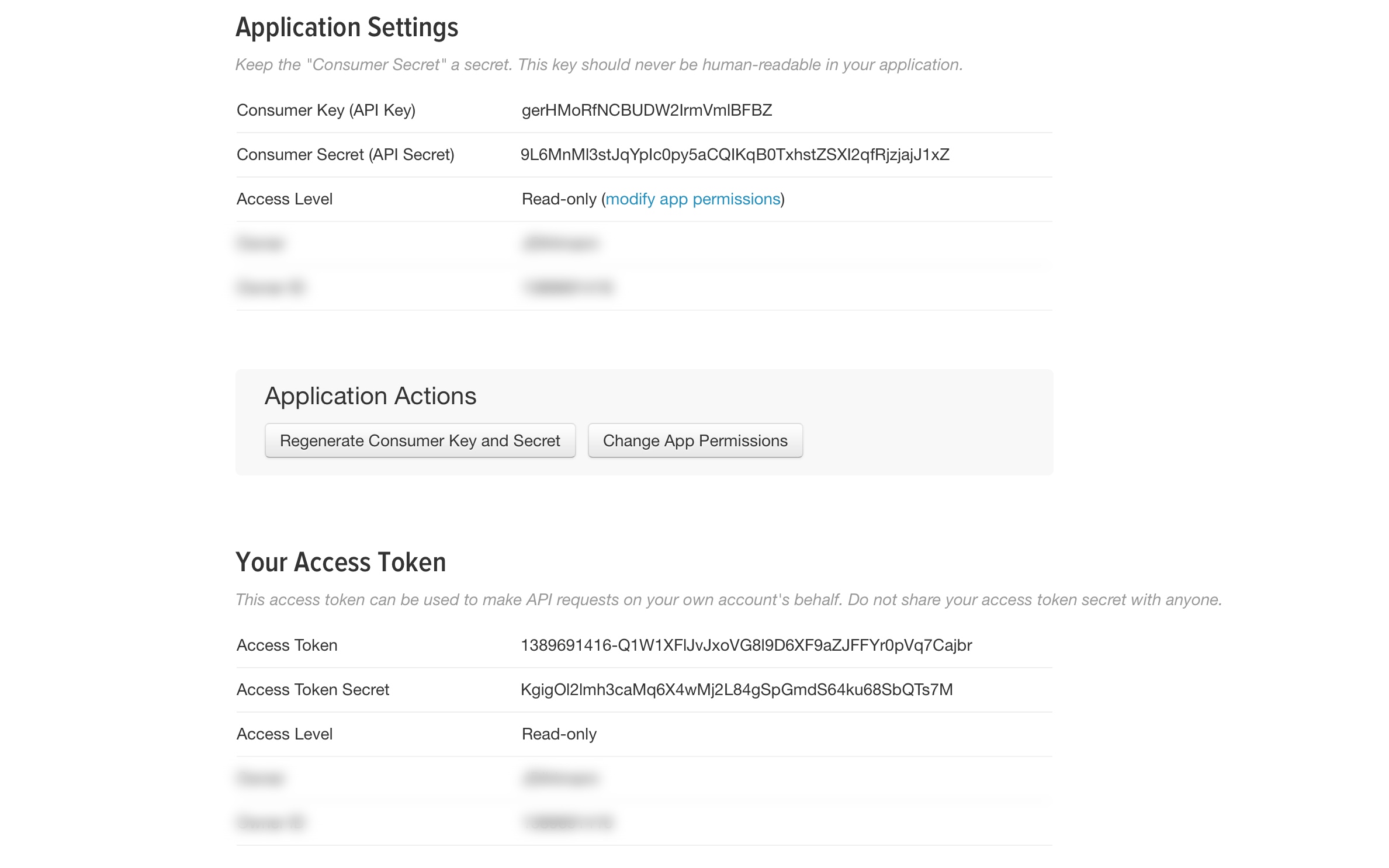
You will see your Application Settings
You already have a Consumer Key and a Consumer Secret but you also need an Access Token. Scroll to the bottom of the page until you see the button "Create my access token“.
Click on "Create my access token“
This step may take 1 minute. Your Access Token have been created.
It should look like that:
Copy these four Keys (Consumer Key, Consumer Secret, Access Token, Access Token Secret) and save them, do not give them to anybody. You need these keys, to connect to Twitter and authorize that it is your application which is connecting to Twitter. You will paste them later inside your application.
######Bluemix Let’s go further on and look at our Bluemix account we open our browser, if nor already opened, and go to the Bluemix website.
You have to create a Bluemix account.
Click on “Sing Up“, if you don’t have a Bluemix account
Follow the steps and log in afterwards.
Click on “Log In“, if you already have a Bluemix Account
You will land on your Bluemix Dashboard, where you can see, which application you have and which do run and which don’t. Also you can create new application and services.
#####2. Create Bluemix Application Now you have to create an application on Bluemix, where we can upload our MoodLocator.
Click on “Create new App“
You are now in the catalog section where you can select your starter kits or a plain Runtime / programming language. MoodLocator is written in plain Node.js, so take a look in runtimes and select Node.js
Click one “Node.js“
Now you will see the application information window, where you can name your application.
Choose a unique name like "YourNameMoodLocator"
Click on "Create"
When the application is created, you will see to a new window.
Right now a demo application is running, you can find it, by clicking the URL beneath your application name or pasting your ApplicationName.mybluemix.net inside your browser bar.
#####3. Install the Software You have to install some Software to be able to upload an application to Bluemix. There is an easy tutorial provided by Bluemix to help you install the cf Command Line Tool.
######cf Command Line Tool Go inside your application you just created and take a look at "View Quick Start". In case you logged out or won’t find it, here is the way to it.
Log in to your Bluemix account
Go to "Dashboard"
Click on your application
Click in the left corner beneath your application name on "View Quick Start"
A window will open, which describes you in small steps how to upload an application to Bluemix. Because we haven't got any application yet, we just focus on the first step.
Click on "Install the cf command-line tool"
Follow the steps, download and install the tool for your device
Your just installed the cf command-line tool, you could upload an application right now, but first we have to make some changes.
######Other recommended Tools In order to make changes, you need a tool to open my application. I recommend Sublime or Notepad++ they are free, easy to use and there are a lot of tutorials, how to use them.
#####4. Change Settings in your Application We have to make two small changes to our application, but first we have to download the application form GitHub. I'm expecting you are reading this documentation on GitHub, scroll to the top of the site, you will see a button with a cloud on the right site of the page.
Click on "Download ZIP"
A zip file of my application will be downloaded.
Unpack the zip file and move it to a place where it is easy to access.
In the next step we move the folder node outside of current folder
Open the folder you just unpacked
Take the folder "node" and move it outside of the current folder onto your Desktop.
We just need the folder "node" you can delete the other folder where you just moved node out.
You unpack the folder and moved it to a position where it is easy to access it. Now we have to make two changes, first we have to set the name you gave to your Bluemix application equal to application name you just downloaded. Second we have to paste our Twitter credentials to our application. Go inside the folder node and search for "manifest.yml".
Open "manifest.yml" with a text editor (Sublime, Notepad++)
######manifest.yml For example I named my application "JanMoodLocator".
It should look like that
Enter in Line 3 "host:" "YourApplicationName" (without quotation marks)
Enter in Line 3 "host:" "YourApplicationName" (without quotation marks)
Save your changes
Great when you upload your application Bluemix will now know that it is the application you just created on Bluemix
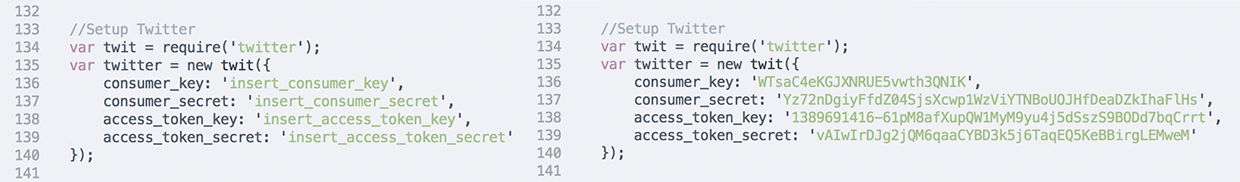
######app.js I hope you saved your Twitter credentials, we will now put them inside the code.
Open "app.js" with a Text Editor you will find it in the folder node.
Scroll down to line 133, where it says "//Setup Twitter"
When you found it, we will put your Twitter credentials inside it.
Paste your Twitter credentials inside the code
Enter in line 136 "insert_consumer_key" (Keep quotation marks)
Enter in line 137 "'nsert_consumer_secret" (Keep quotation marks)
Enter in line 138 "insert_access_token_key" (Keep quotation marks)
Enter in line 139 "insert_access_token_secret" (Keep quotation marks)
Save your changes
Keep in mind to delete your credentials, when you are given your code to anybody else.
We added everything to our code and saved our changes, now we have to add the Watson User Modeling Service and upload our application to Bluemix.
If you want to add the Watson User Modeling Service live. Stop here and open to my Liveslide presentation.
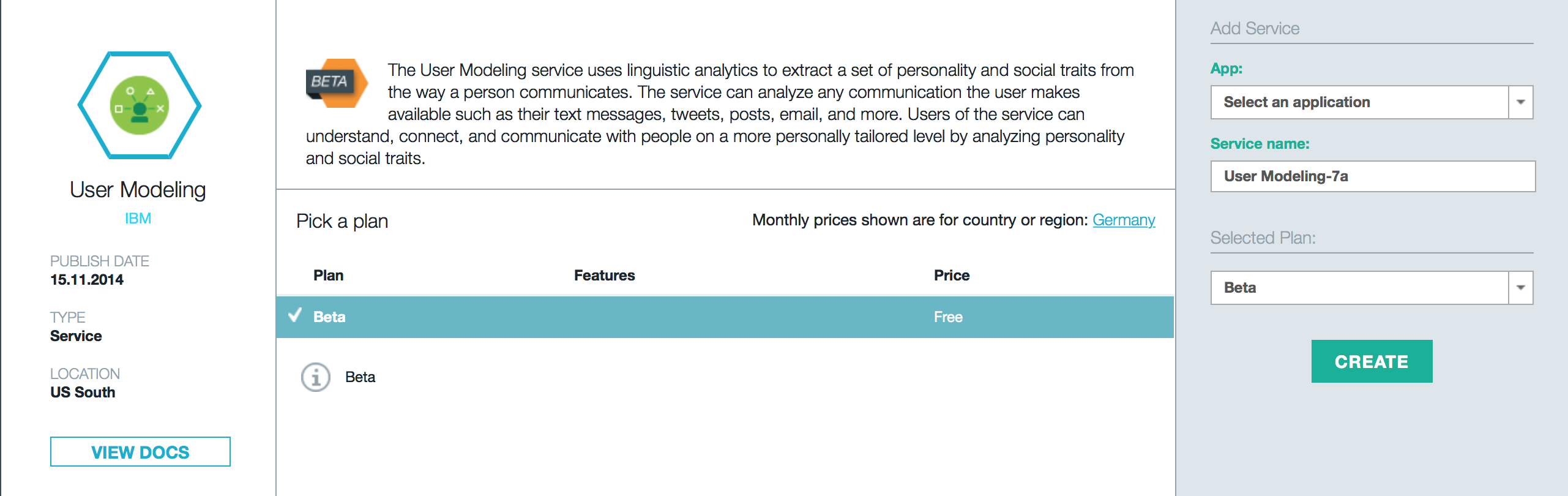
#####5. Add Watson Service In this part, we will add our Watson User Modeling Service to our application. To do that, we have to visit Bluemix Catalog.
Log in to your Bluemix account
Go to "Catalog"
You will see a variety of Bluemix services you can add to your application, but my application is only prepared for Watson User Modeling Service.
Scroll down until you see the section Watson
Click on User Modeling
A window will pop up where you can add the Watson User Modeling Service to our application.
Click on "Select an application"
Search for the name of your application and click on it
Click on "Create"
The service will be prepared and combined to your application. In the last step we have to upload our application to Bluemix
#####6. How to upload MoodLocator We will go back to our application window and look at the other steps of "View Quick Start". "View Quick Start" is the guide to how to upload applications to Bluemix.
Log in to your Bluemix account
Go to "Dashboard"
Click on your application
Click in the left corner beneath your application name on "View Quick Start"
As you remember we completed the first step and installed the "cf command-line tool" to upload our application we have to complete some other steps. We won’t need the second step, because we already have an application. So go on to the third step.
"(...) and cd to it"
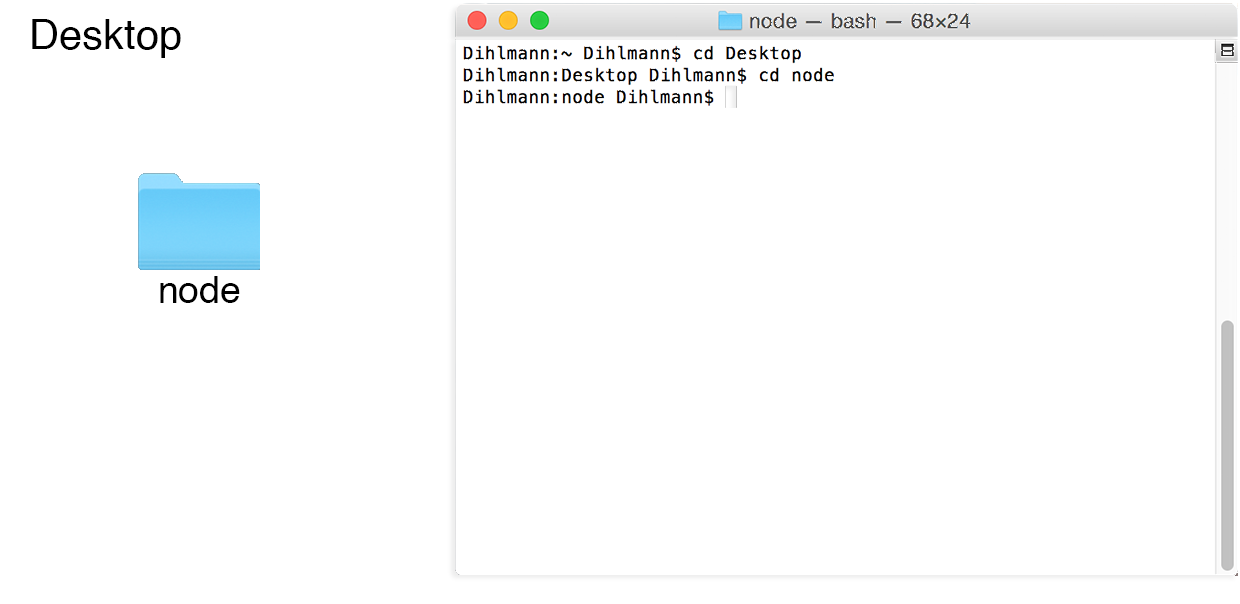
That means we have to open our Terminal (on Linux / Mac) or CMD (on Windows). We now try to find the directory of our application, which is node. I said before, but the directory where it is easy to access and that is necessary now.
Put the node folder on your Desktop
Open Terminal or CMD
Your Terminal or CMD window will open where you can put in commands, like go to this directory.
Type in "$ cd Desktop" (without dollar icon and quotes)
Type in "$ cd node" (without dollar icon and quotes)
We are now inside the node application. Go back to "View Quick Start" and copy paste the next steps into your Terminal or CMD
Type in "$ cf api https://api.ng.bluemix.net" (without dollar icon and quotes)
You are now connected to the Bluemix cloud.
Type in "$ cf login -u jdihlman@de.ibm.com" (without dollar icon and quotes)
Login to your Bluemix account via the console. It will require your password.
Type in your password (you won’t see what your typing)
And last but not least push your application to Bluemix
Type in "cf push YourAppName" (without dollar icon and quotes and add your appname to it)
Your application will now be pushed to Bluemix. This may take 1minute, after it finished click on the link and everything should work fine.
#####7. Further reading
You now can fully use the application on your own Bluemix account. If it doesn't work, do not hesitate to contact me, I will help you.
If you want to add the Watson Service live to your application check out my Liveslide. If you want to use the presentation clean and withoud comments check out my Presentationslide. You will find every presentation file in the presentation folder.