-
When we build web components, there are 3 fundamental building blocks. (HTML, CSS, Javascript)
-
Web components brings all these 3 technologies together to build truly encapsulated, self-containing components for the web.
-
Some of the popular web components frameworks are:
- Polymer
- SkateJS
- x-tag
-
These components not only built on top of web-components, they also provide additional capabilities. For example, Polymer provides data-binding capabilities.
-
But using 3rd party libraries, we will lose interoperability and portability.
-
Web components does not rely on 3rd party libraries and only relies on Web standards. This means that web components are more portable and reusable.
-
One of the other important features of web-component is the ability to create a Sub DOM tree exclusively for a single web component.
-
This Sub DOM Tree does not inherit styles from other components and the component styling does not leak to the other outside components.
-
Therefore the major advantages of web components are
- Style Encapsulation
- Fewer dependencies and pre-requisites
- Framework / Library Agnostic
- Longer Life components
-
Web Component Specification consist of 4 major areas (Web Standards)
- Custom Elements
- Shadow DOM
- HTML Templates
- HTML Imports
- Web components are just DOM Elements that are created by component author.
- Using Custom Elements Specification it is possible to create our own custom HTML element, define tag and behavior.
- With custom DOM element, we can add Properties, methods and functionality beyond what native DOM elements can provide.
- We can also extend Native DOM elements and custom elements.
- DOM Elements are just JS objects that has prototype JS inheritance.
- If we use console.dir($p) (lets say we have a p tag in HTML), we can see all the properties of
Object
- Look at the example below
- Here we can see all the methods and properties available.
- When we are creating Custom Elements, we define our own interface and its own properties and methods.
-
When creating Web components, we can use ES2015 (or ES6) to define.
-
First, we extend all the HTMLElement interface which will give us all the properties and method a typical DOM element required to have without having to do any work.
-
We will also define constuctor, where we need to always called super() to constuct the parent.
-
Once this is created, we need to tell the browser about it and specify the HTML tag. To do this, we use window.customElements() API. Using the Define method, we can define the tag Name.
-
Then we pass in the element prototype - which is the class we created.
-
Now, the browser will know how to construct the DOM element with the tag name <my-custom-element)
- Apart from this, we have number of lifecycle callback methods when the custom element is created and destroyed in DOM.
- The 3 most used callbacks are
- connectedCallback() -- This is executed when the element is connected to the DOM
- attributeChangeCallback() -- Subscribes to changes of certain attributes on the element instance. To configure what attributes we need to subscribe to, we need to specify the names of the attributes using static get observedAttributes() by adding array of names.
- disconnectedCallback() -- Executed when the element is removed from the DOM
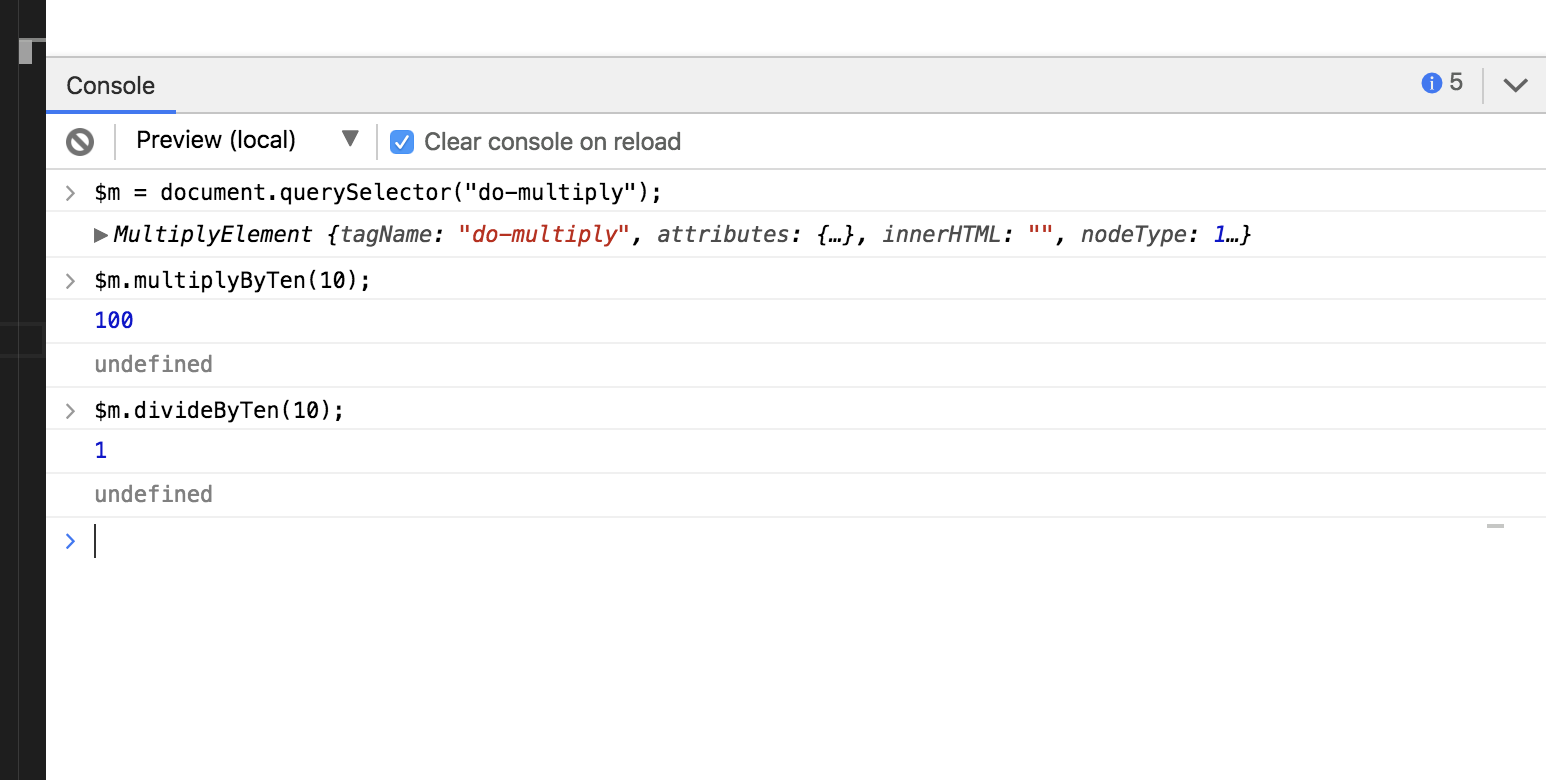
- It is possible to extend custom Elements. For Example:
- Output:
Since this is extended, we have access to both the methods.
-
The main use of extending native element is that we get all the native features of that html attribute we are extending without rebuilding everything from the scratch.
-
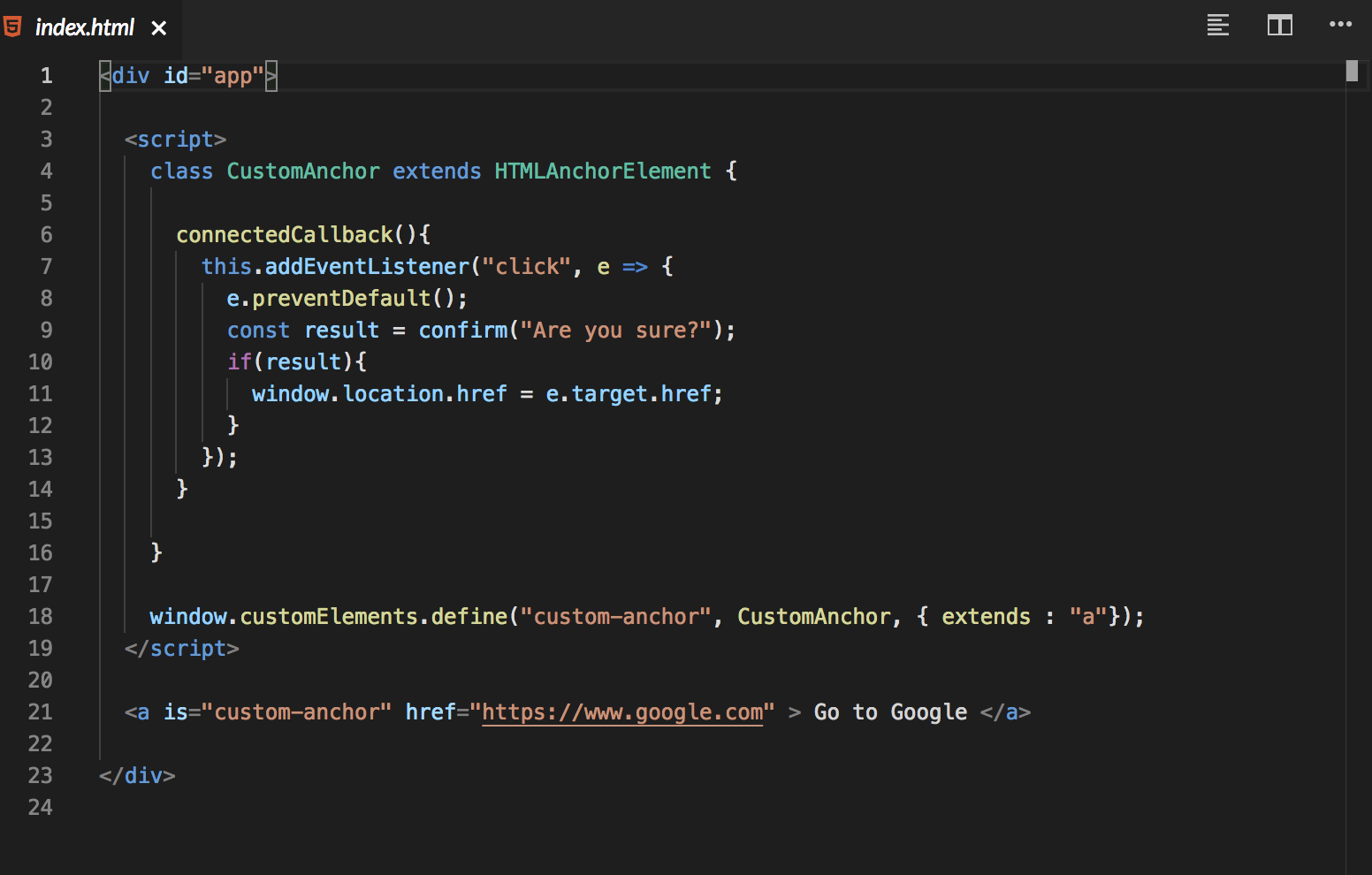
Here in this example, we are extending the Anchor Element HTMLAnchorElement and not the basic HTMLElement
-
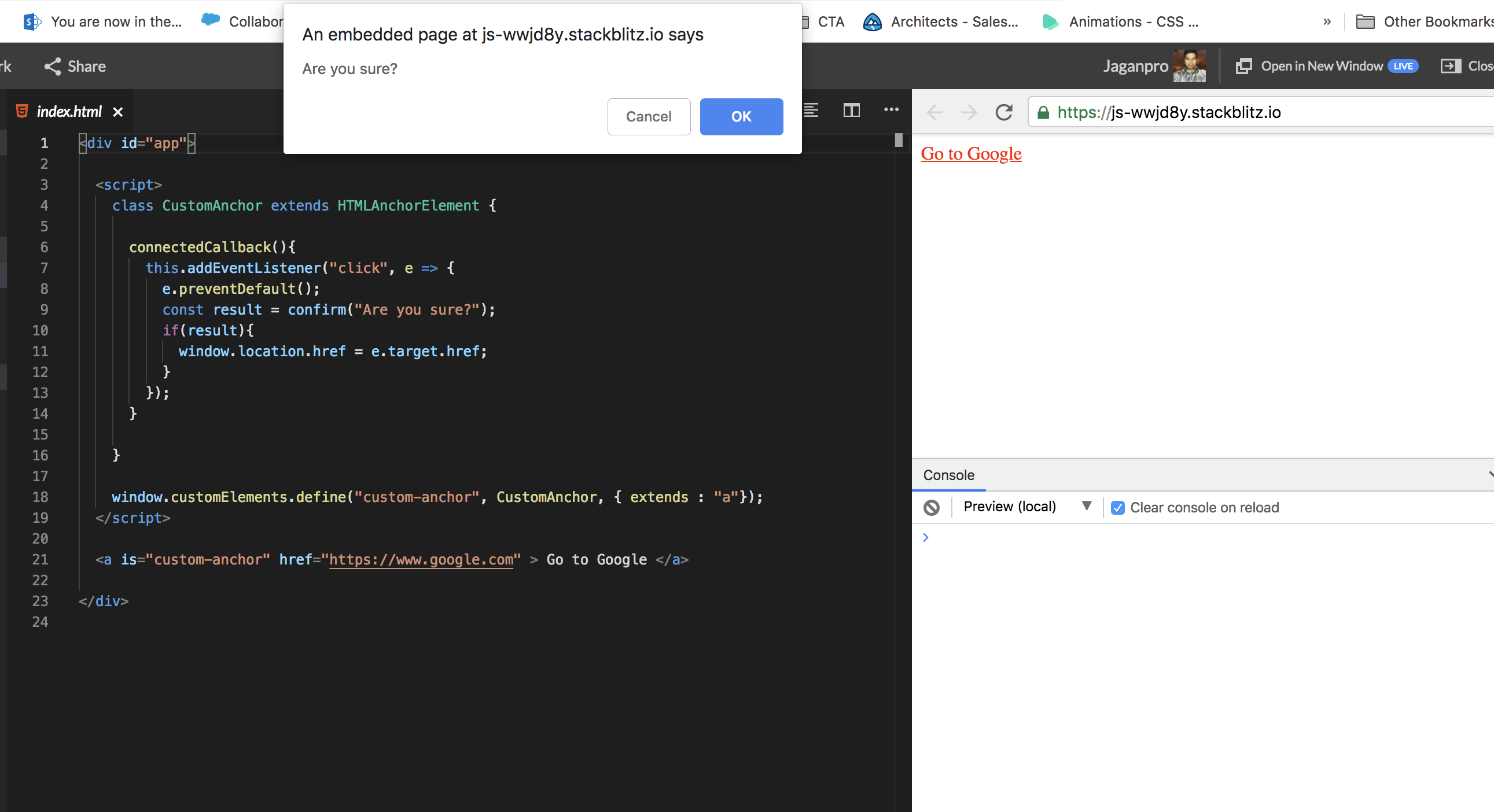
Here we want the user to be prompted an alert message before navigating to the new link. This is the feature we are going to implement in custom Anchor Element.
-
For this we need to add a Custom Event Listener.
-
There are 2 other differences when extending custom element
- We have to use "extends" and specify the standard element we are extending
- In the actual tag, is="custom-anchor" attribute is added.
-
CODE:
- OUTPUT:
Further Reading: https://developers.google.com/web/fundamentals/web-components/customelements
CodeBase for Examples: https://stackblitz.com/edit/js-wwjd8y?file=index.html