-C is a Procedure Oriented Programming Language -Java is an Object Oriented Programming Language
- Obejcts mean real world things, real world entities.
-Writing programs to represent real world entities.
-
Eg: C cannot represent real world objects. It only supports to represent behaviours/tasks. (can only write functions)
- Java
- Python
- Kotlin
- C#
- C++
-
once the installation is done, there will be 2 folders inside the Java Folder.
- JDK 🔜 Java Development Kit (contains development and Debugging Tools)
- JRE 🔜 Java Runtime Environment (provides the environment for the application to run. contains Java Virtual Machine, which supports to run the application)
-
Intructions/codes are written on notepad
-
no header files
-
has main function
-
case sensitive
-
platform independent (the .class file can be run on any device)
-
In JAVA, the function(we used in C) is called method.
-
methods are used to execute instructions.
Eg: Access modifier
class Main // public, private, protected are access modifiers.
{
//curly brackets are separators
}public variables are like global variables in C
'.' means = inside
class Main
{ public static void main(String[] args) // NO VALUE INSIDE SQ. BRACKETS MEANS UNLIMITED SIZE**
{
System.out.println("Hello OOP");
}
}.class files contain byte code. the source code is converted into byte code first and then JVM translates it into machine code. Tbh, byte code acts like an intermediary code.
MUST READ BEFORE NEXT DAY - Definitions of - CLASS
- ATTRIBUTES
- METHOD
- PRIVATE LABEL and PUBLIC ACCESSS LABEL
- INSTANCE
- INSTANCE MEMBER and STATIC MEMBER
- CONSTRUCTORS AND INSTRUCTORS*
- Constructors are used to intialize object of the class when the object is created.
- JAVA requires a constructor call for every object that is created.
- a constructor is only used to set values.
class Mask{
private String color;
private String size;
private float price;
public Mask(String color, String size, float price){
this.color= color;
this.size = size;
this.price = price;
/* this means that value of color parameter in "Mask constructor"
is assigned to the color attribute in "class Mask" value. */
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Mask 1 = new Mask("red", "small", 50.00);
}
}- Instances are non static variables which are defined in a class outside any method, constructor or a block. Each instanstiated object of the class has a seperate copy or instance of that variable.
- An instance variable belongs to a class.
class Computer{
private String brand; // this is a instance member. All objects created in this class can have a copy of this instance.
private static String color = "Black"; // this is a static member, which means all the objects created under this class shares this same attribute.
public Computer(String brand){
this.brand = brand;
}
public showDetails(){
System.out.println("color is " + color);
System.out.println("brand is " + brand);
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Computer x = new Computer("HP");
Computer y = new Computer("Dell");
x.showDetails();
y.showDetails();
}
}-
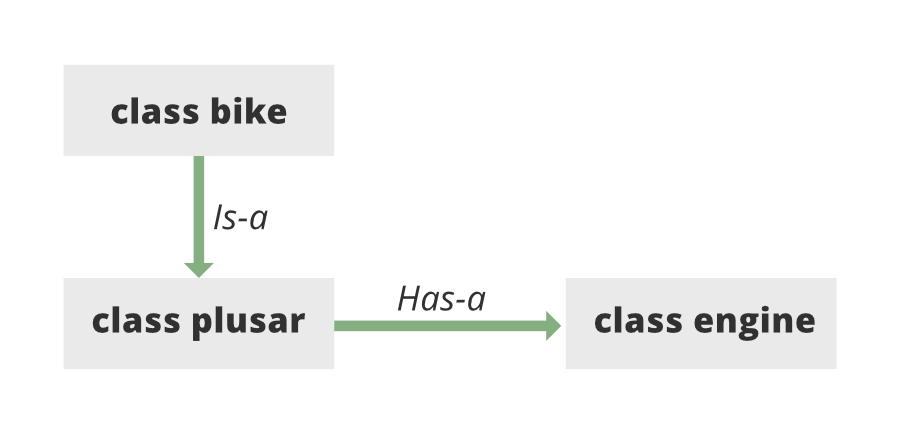
Association in JAVA is a connection or relation between two seperate classes that are set up through their objects. (smh similar to Relationships in DBMS)
-
Composition (HAS-A) simply mean the use of instance variables that are references to other objects. For example Maruti has Engine, or House has Bathroom.
Ex: - A student has a module - A driver has a vehicle - seller sells products
class Student {
private String name;
Module m1; // module class object created inside student class.
public Student(String name){
this.name = name;
m1 = new Module(30); // Association
}
public void showDetails(){
System.out.println("Name is " + name);
// System.out.println("Module duration =" + duration);
// (this line won't work as duration is a private attribute in another class)
System.out.println("Module duration is " + m1.getDuration() );
}
}
class Module{
private int duration;
public Module(int duration){
this.duration = duration; // Association
}
public int getDuration(){
return duration;
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("Pasindu");
s1.showDetails();
}
}MUST READ BEFORE NEXT DAY - Definitions of
- < INHERITANCE
- < BENEFITS OF INHERITANCE
- < DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INHERITANCE AND ASSOCIATION
- < MODELS OF INHERITANCE
- Inheritance in Java is the method to create a hierarchy between classes by inheriting from other classes.
class Furniture{
public void display(){
System.out.println("It is a furniture");
}
public void test(){
System.out.println("It is testing");
}
}
class Chair extends Furniture{
//keyword "extends" is used to indicate that a class is inherited from another class.
//TO BE NOTED: private attributes doesn't get inherited as it is defined under private label and only belongs to the specific class.
{
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
// now you can call methods in Furniture class to the objects of Chair class.
Chair c = new Chair();
c.display();
c.test();
}
}TIP : The protected keyword in Java refers to one of its access modifiers. The methods or data members declared as protected can be accessed from
- Within the same class.
- Subclasses of the same packages.
- Different classes of the same packages.
- Subclasses of different packages.
class Product{
protected float unit_price;
public void setPrice(float unit_price){
this.unit_price = unit_price;
}
}
class LocalProdcut extends Product{
private float discount_amt;
public void setDiscount(float disc_amt);{
this.discount_amt = disc_amt;
}
public void getLastPrice(){
System.out.println("Last Price: " + (unit_price - disc_amt));
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String [] args){
LocalProduct lp = new LocalProduct();
lp.setPrice(500.0f);
lp.setDiscount(100.0f);
lp.getLastPrice();
}
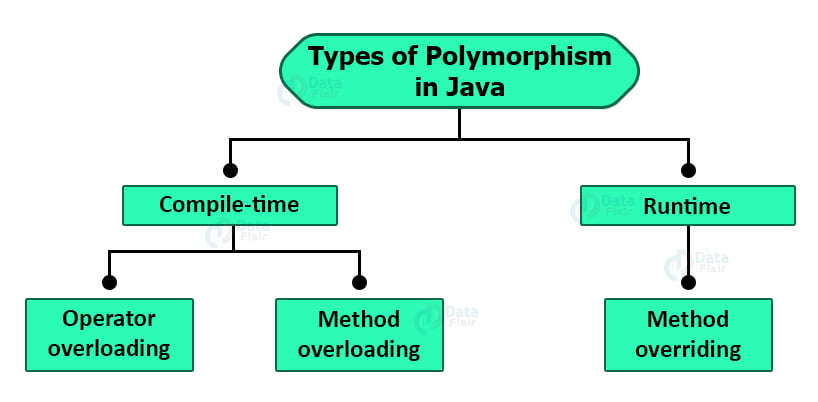
}- Using one name and doing several tasks ( one name + Many tasks)
- There are two types of polymorphism in JAVA.
1. Runtime Polymorphism (Overriding)
2. Compile-Time Polymorphism (Overloading)
-
As the name signifies, method overriding is the process of overriding or redefining a method that was already defined in the parent class.
-
This is efficient and useful in many cases because a lot of the time, there is a need for redefining the function based on the class it is in.
-
For example, a Mercedes car, which is a subclass of the car class will have a different function named engine in comparison to the BMW car’s engine.
class Item{
public void show() // method
{
System.out.println("This is an item");
}
}
class Computer extends Item{
public void show() // method overrriding
{
System.out.println("This is a computer");
}
}
class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Computer c1 = new Computer();
c1.show();
}
}-
Method overloading is the process of having the same function name with different arguments. The compiler decides which function to call while compiling the program.
-
All of the functions have the same method name but they have different arguments which makes them unique.
-
For example, two functions namely area has the same name but one returns the area of a square and the other one returns the area of a rectangle.
class Student{
public void show(){
System.out.println("I am a Student");
}
public void show(int age){
System.out.println("My age is " + age);
}
public void show(int age, double weight){
System.out.println("My age is " + age + "My weight is " + weight);
}
}
class Main{
public staic void main(String[] args){
Student Nimal = new Student();
Nimal.show();
Nimal.show(12);
Nimal.show(12, 50.2);
}
}