Disclaimer:
The base URL used in the tests for the Urban Grocers API is private and temporary. It is accessible only to those enrolled in the TripleTen Sprint 4 QA Engineer course. The base URL may change or be regenerated periodically, making it inaccessible to others. The purpose of this repository is to provide an overview of the work and experience with Postman. Due to the private nature of the base URL, the tests cannot be recreated outside of the specified course environment.
The node-tests directory includes scripts written in JavaScript using Node.js to test the Urban Grocers API.
get.kits.list.js: Retrieves kits and filters those with fewer than 30 items.exceeding30items.js: Tests adding multiple quantities of the same product to a kit, checking if the 30-item limit is enforced.exceeding30items.2.js: Tests adding multiple different products, each with a quantity of 1, to a kit, checking if the 30-item limit is enforced.package.json: Contains metadata about the project and its dependencies.package-lock.json: Locks the versions of dependencies to ensure consistent installations.
This summary outlines the testing of the Urban Grocers API, focusing on:
- Adding products to a kit.
- Calculations for fast delivery.
A total of 57 tests were conducted: 28 for the first requirement and 29 for the second.
(👇 Full test case data sheet available 👇)
- Total Tests: 28
- Parameters: Tested scenarios around the 30-item limit, invalid product IDs, and kit IDs.
-
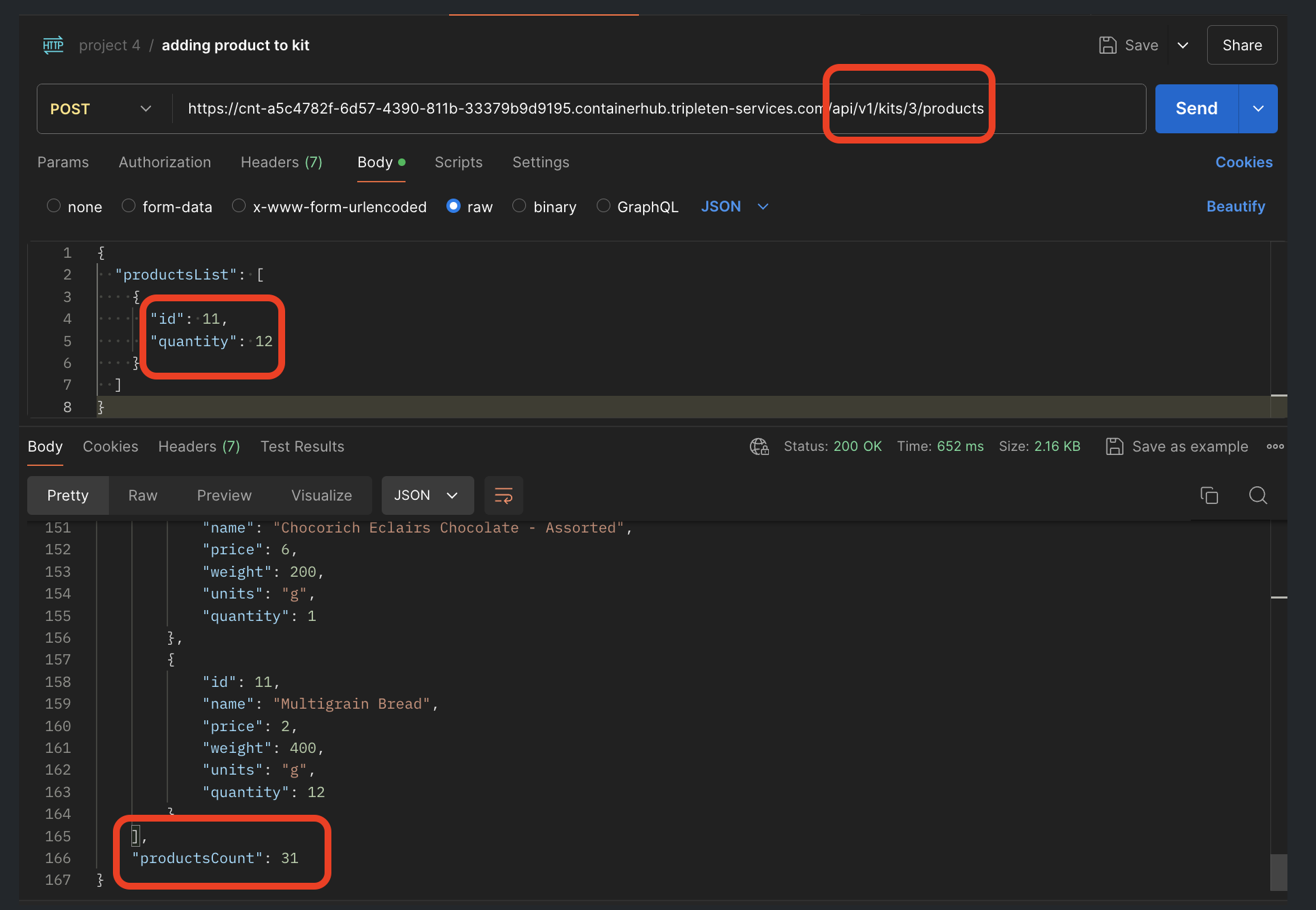
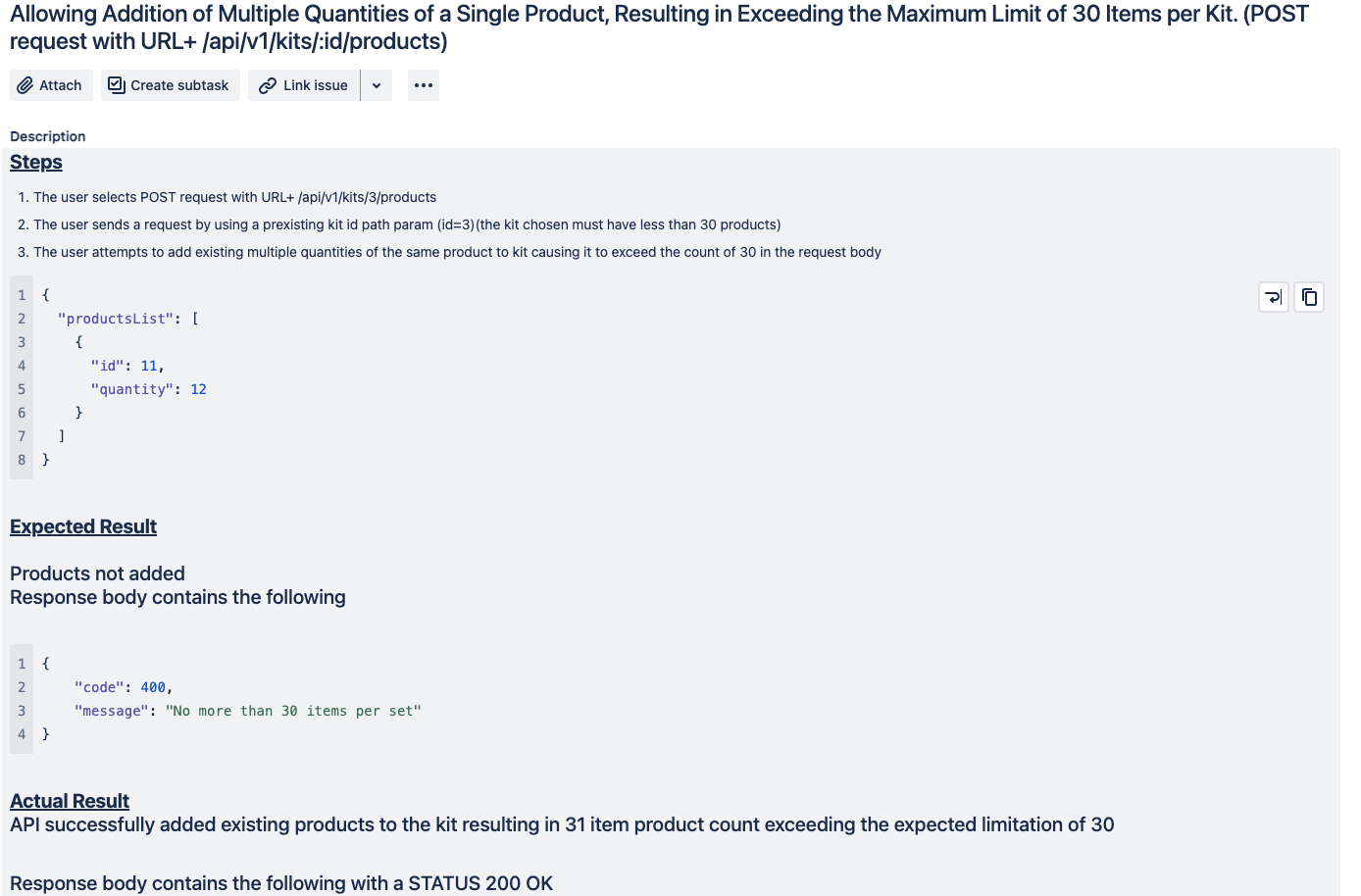
The API incorrectly allowed multiple quantities of the same product to be added to a kit, causing it to exceed the 30-item limit (expected HTTP 400, received HTTP 200).
-
Interestingly, when adding multiple different products, each with a single quantity, to a kit that had under 30 items (causing it to exceed 30), the API behaved correctly and returned HTTP 400.
-
Example of the bug in Postman
-
Bug Report in JIRA
-
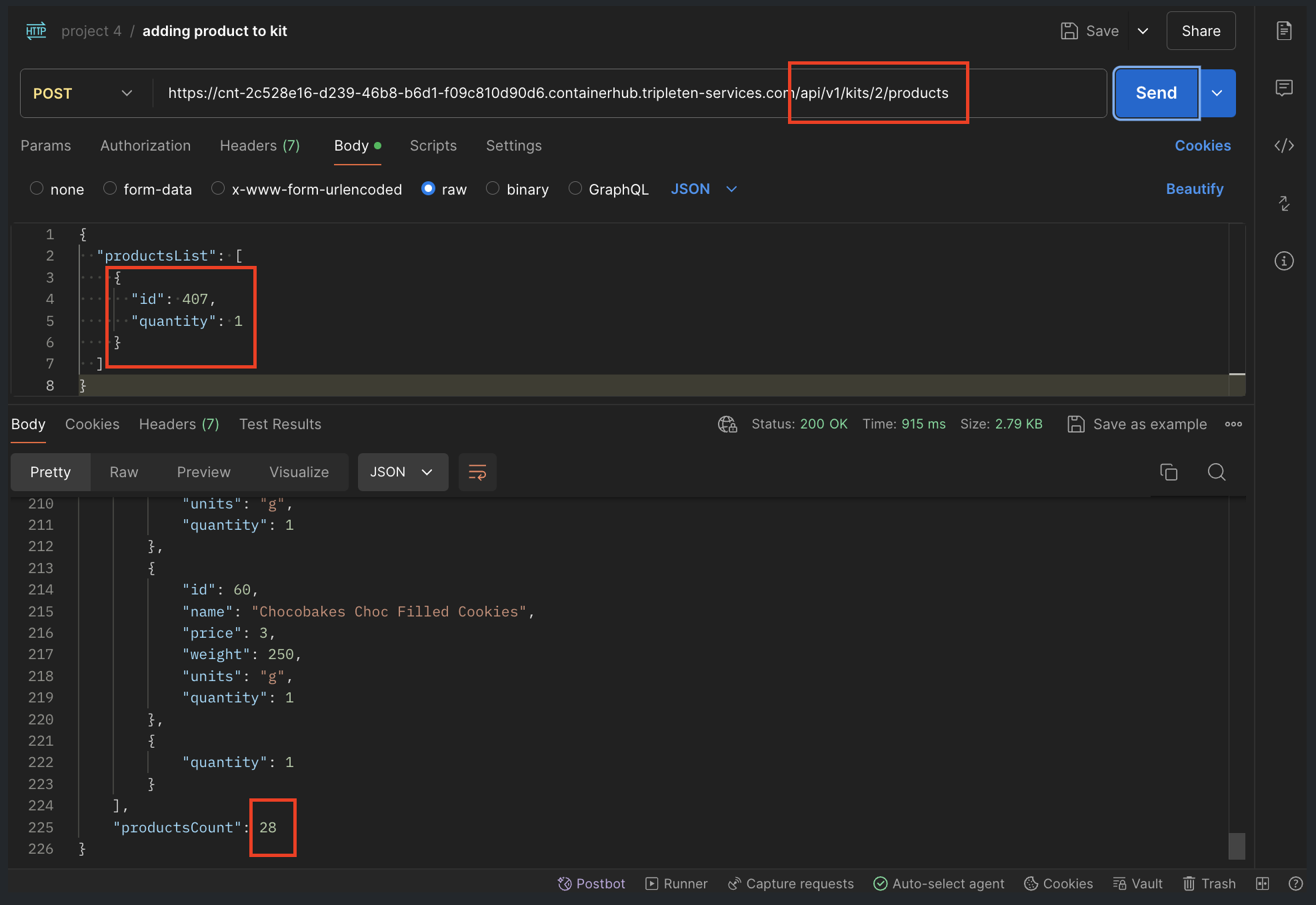
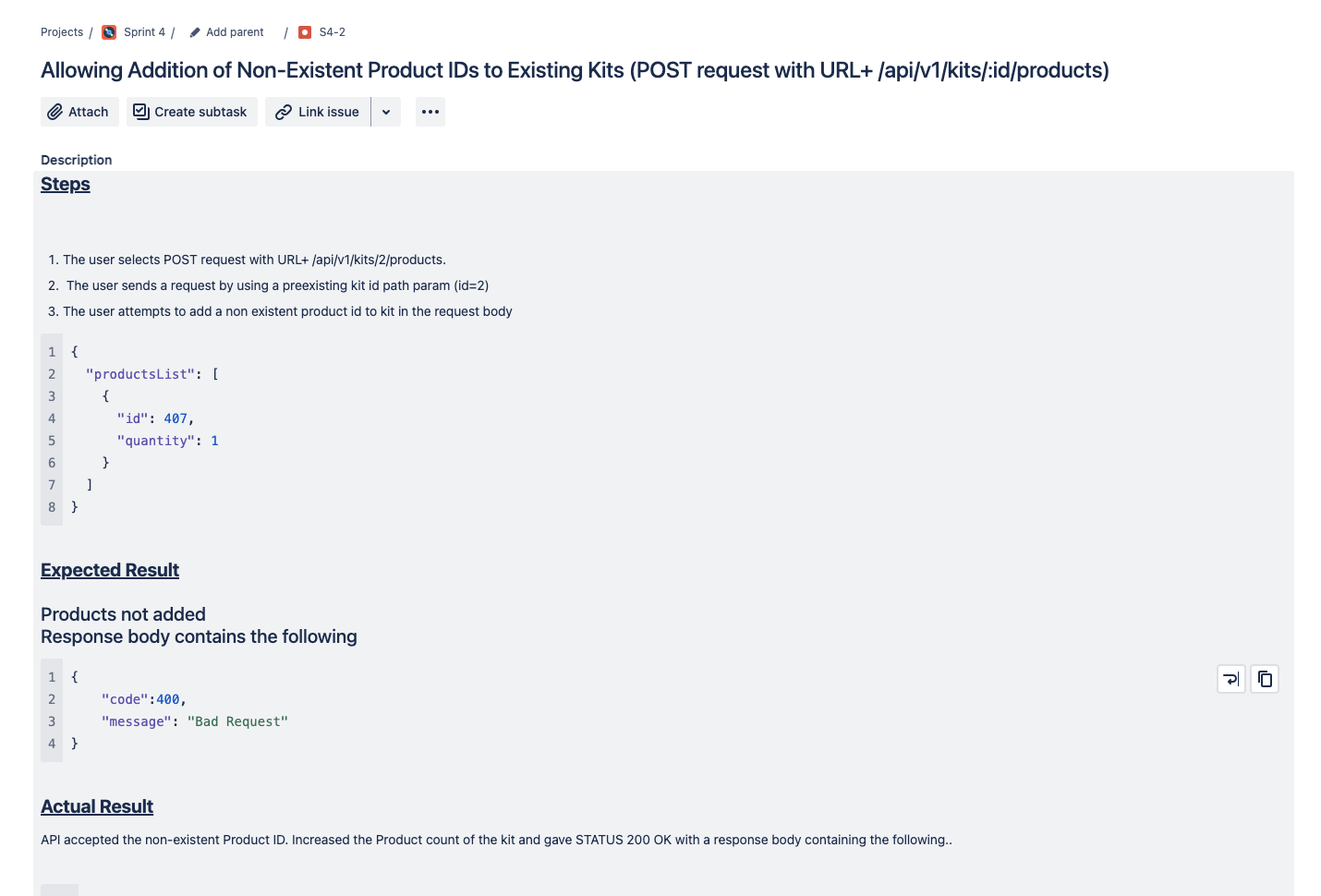
The system accepted non-existent product IDs (e.g., product ID 407 which does not exist) and responded with HTTP 200 OK instead of the expected HTTP 400 Bad Request.
-
This could lead to users believing they have successfully added a valid product to their kit when, in fact, the product does not exist in the system.
-
Example of the bug in Postman
-
Bug Report in JIRA
- The system was tested with various invalid product IDs and kit IDs (e.g., using Latin letters, symbols, decimal points, non-Latin letters).
- All these attempts resulted in HTTP 500 Internal Server Error, which indicates a server-side issue rather than a client error. According to the API documentation, the expected response should have been HTTP 400 Bad Request.
- Total Tests: 29
- Focus: Parameters for the fast delivery method.
Note: While many more test cases could be designed given the different variables and combinations of product count and weight, I optimized by testing edge cases. For full reliability and adherence to the requirement, automation testing is recommended.
- Definition: The price the API charges the internal system for delivery.
- Calculation:
- Based on either the number of products or their total weight, whichever results in the higher cost.
- Examples:
- If
productsCountis 1-7 andproductsWeightis 0-2.5 kg, the host delivery cost is $3. - If
productsCountis 8-14 orproductsWeightis 2.6-6 kg, the host delivery cost is $6.
- If
- Default cost: $7 if conditions do not match specified criteria.
- Definition: The price charged to the customer for delivery.
- Calculation:
- Standard Cost: $0 if the order meets the defined limits for product count and weight.
- Excess Cost: $9 if the order exceeds the maximum limits for product count or weight.
- Examples:
- Within limits (e.g., 1-7 products, 0-2.5 kg): $0
- Exceeding limits (e.g., more than 14 products or more than 6 kg): $9
- Valid Middle-Ground Input:
- Tested the system with valid, middle-range parameters to ensure basic functionality.
- Minimal Product Weight and Middle Values for Other Parameters:
- Ensured the system accepted orders with minimal weight and middle-range product counts and delivery times.
- Minimal Product Weight and Count:
- Verified that the client delivery cost remained $0 for orders with minimal weight and product count within limits.
- Product Weight Exceeding Maximum Limit:
- Scenario: Tested fast delivery with product count within limits but weight slightly over the limit (6.01 kg).
- Expected: Host delivery cost $6, client delivery cost $9.
- Observed: Client delivery cost was incorrectly charged $6 instead of $9.
- Bug: The system failed to apply the excess client delivery cost correctly when the product weight exceeded the maximum limit.
- Product Count Exceeding Maximum Limit:
- Scenario: Tested fast delivery with weight within limits but product count slightly over the limit.
- Expected: Host delivery cost $6, client delivery cost $9.
- Observed: Client delivery cost was incorrectly charged $6 instead of $9.
- Bug: The system failed to apply the excess client delivery cost correctly when the product count exceeded the maximum limit.
- Operating Hours Edge Cases:
- Scenario: Tested ordering one minute before operating hours (06:59).
- Expected:
isItPossibleToDelivershould befalse. - Observed:
isItPossibleToDeliverwastrue. - Bug: The system incorrectly allowed orders one minute before operating hours.
- Expected:
- Scenario: Tested ordering one minute after operating hours (21:01).
- Expected:
isItPossibleToDelivershould befalse. - Observed:
isItPossibleToDeliverwastrue. - Bug: The system incorrectly allowed orders one minute after operating hours.
- Expected:
- Scenario: Tested ordering one minute before operating hours (06:59).
During testing for Requirement Two, two tests were deemed inconclusive, pointing to a significant flaw in the design of the API's cost calculation system. These tests highlighted a gap in the defined ranges for host delivery cost:
-
Ordering Fast Delivery with Product Weight Just Above the Lower Limit (2.51 kg)
- Expected Result: Host delivery cost unknown due to gap in defined ranges.
- Observed Result:
200 OK <response name="Fast Delivery" isItPossibleToDeliver="true" hostDeliveryCost="3" clientDeliveryCost="0"> <toBeDeliveredTime> <min>25</min> <max>30</max> </toBeDeliveredTime> </response>
-
Ordering Fast Delivery with Product Weight Slightly Below the Upper Limit (2.59 kg)
- Expected Result: Host delivery cost unknown due to gap in defined ranges.
- Observed Result:
200 OK <response name="Fast Delivery" isItPossibleToDeliver="true" hostDeliveryCost="3" clientDeliveryCost="0"> <toBeDeliveredTime> <min>25</min> <max>30</max> </toBeDeliveredTime> </response>
Host Delivery Cost Gap: The current requirements have a gap between the $3 price range (0-2.5 kg) and the $6 price range (2.6-6 kg). This ambiguity creates uncertainty in expected outcomes for product weights that fall within this gap (e.g., 2.51 kg and 2.59 kg).