Extracting data from multiple source files in diffrent format. datasource.zip contain .CSV, .JSON, and .XML files for used cars data which contain features named:
| car_model | year_of_manufacture | price | fuel |
|---|
So we are going to extract and transform raw data, then load into a target tables in the database.
- Python (Pandas)
- SQL (SQL Server 2019)
After analyzing source data, implementation of this project is divided into two steps. first is to implement target tables in the database depending on the following Entity-Relationship Diagram (ERD):
Create Table FuelType(
id tinyint primary key,
fuel_type nvarchar(10)
)create Table UsedCars(
car_model nvarchar(20),
year_of_manufacture smallint,
price float,
fuel_id tinyint references FuelType(id)
)Second is to implement python ETL process:
Import used libraries
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
import datetime
import pyodbc Extract functions that will extract data from multiple sources in diffrent formats (CSV, JSON, XML) using pandas dataframe
def extract_CSV(path_to_csv):
df = pd.read_csv(path_to_csv)
return dfdef extract_JSON(path_to_json):
df = pd.read_json(path_to_json, lines= True)
return dfdef extract_XML(path_to_xml):
df = pd.read_xml(path_to_xml,'/root/row')
return dfdef extract(path_to_src_data):
df = pd.DataFrame(columns=['car_model','year_of_manufacture','price','fuel'])
for f in os.listdir(path_to_src_data):
fpath = os.path.join(path_to_src_data,f)
if f.endswith('csv'):
df = df.append(extract_CSV(fpath))
elif f.endswith('json'):
df = df.append(extract_JSON(fpath))
elif f.endswith('xml'):
df = df.append(extract_XML(fpath))
return dfThis function will convert the column price to 2 decimal places and replace column fuel to the corresponding index using enumerate(). Then return transformed data and dict of unique columns replaced with its index, in our project fuel column only is transformed and returned as dict {fuel_type as a key : its index as a value }.
def transform(data):
#round price to 2 decimal places
data['price'] = round(data['price'],2)
#get unique values from fuel column
uniqueFuel = data['fuel'].unique().tolist()
#create dict of {oldValue : newValue} to replace fuelType with its corresponding index
uniqueFuel = dict((value,index+1) for index, value in enumerate(uniqueFuel))
data['fuel'] = data['fuel'].map(uniqueFuel)
return data, {'uniqueFuel' : uniqueFuel}It’s time to load the data into the target tables created in our database.
def load(data, uniqueDict, server, database, username, password):
conn = pyodbc.connect('DRIVER={SQL Server};SERVER='+server+';DATABASE='+database+';UID='+username+';PWD='+ password)
cursor = conn.cursor()
#inserting into FuelType target table
for key in uniqueDict['uniqueFuel']:
fuel_type = key #{fuel_type as a key : its index as a value }
index = uniqueDict['uniqueFuel'][key]
cursor.execute("Insert into Demo.dbo.FuelType(id,fuel_type) values(?,?)",index ,fuel_type)
#inserting into UsedCars target table
for index,row in data.iterrows():
cursor.execute("Insert into Demo.dbo.UsedCars(car_model,year_of_manufacture,price,fuel_id) values(?,?,?,?)",
row.car_model, row.year_of_manufacture, row.price, row.fuel)
conn.commit()
cursor.close()This function is to monitor and keep track of ETL process and write down its details into a .txt file
def log_message(message, log_file_path):
timestamp_format = '%d-%h-%Y %H:%M:%S:%f' #Day-Month-Year Hour:Minute:Second:MSecond
now = datetime.datetime.now() # get current timestamp
timestamp = now.strftime(timestamp_format)
with open(log_file_path,"a") as f:
f.write(f'{message}\t{timestamp}\n')
f.close()Finally
def ETL(src_path, log_path, server, database, username, password):
try:
log_message('ETL Process Started',log_path)
log_message('Extract Phase Started',log_path)
EData = extract(src_path)
log_message('Extract Phase Ended',log_path)
log_message('Transform Phase Started',log_path)
TData, uniqueDict = transform(EData)
log_message('Transform Phase Ended',log_path)
log_message('Load Phase Started',log_path)
load(TData, uniqueDict, server, database, username, password)
log_message('Load Phase Ended',log_path)
log_message('ETL Process Ended',log_path)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
else:
print('ETL Done Successfully')Calling ETL(src_path, log_path, server, database, username, password)
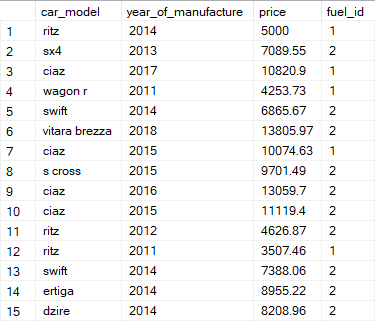
Query UsedCars Table:
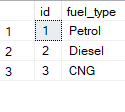
select * from UsedCarsQuery FuelType Table:
select * from FuelTypeJoining two tables:
select c.car_model, c.year_of_manufacture, c.price, f.fuel_type
from UsedCars c
join FuelType f
on c.fuel_id = f.idLog file: