Table of Contents
- SatRday2017 (Devops and Shiny)
This is a Repository of all the Resources from my talk (Marko Jakovljevic) at the Cape Town SatrDay Conference
Get started with downloading the Slide Deck here - This is what you can use to follow with the documents
TODO
- Add SSL Encryption into the Docker-compose stack for Auth0 + Shiny + Nginx (Letsencrypt)
- Nginx Optimizations
Assumptions
This document assumes that you are familiar with SSH, SSH Keys, Linux Command line and that you have an Ubuntu 16.04 (Xenial) Server running somewhere.
This document also assumes that you know how to use R and Shiny Server. If you need some instructions on this here are some good articles.
General Resources
But first, let's update the package database:
sudo apt-get update
Now let's install Docker. Add the GPG key for the official Docker repository to the system:
Make sure all system packages are up to date, add the Keyserver repo and update and install docker-engine
sudo apt-get upgrade
sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://p80.pool.sks-keyservers.net:80 --recv-keys 58118E89F3A912897C070ADBF76221572C52609D
sudo apt-add-repository 'deb https://apt.dockerproject.org/repo ubuntu-xenial main'
sudo apt-get install -y docker-engine
Ensure to add the relevant users to the Docker group
sudo adduser USER docker and for current user sudo adduser $USER docker
Here are some commands you can use to get started with exploring Docker.
-
docker searchwill help you find what you are looking for in terms of images that are currently open repositories on the Docker hub -
docker pull owner/image:tag -
So let's start by searching for Docker ubuntu
docker search ubuntuand pull the imagedocker pull ubuntu:16.04 -
To run the docker image run
docker -it ubuntu:16.04 bashwhich means you are getting an interactive shell psuedo tty attached to STDIN/ERR/OUT -
To detach from a container without stopping it you can press
Ctrl+P and Ctrl+Qsuccessively orexit -
List all containers -
docker ps -a/ List all imagesdocker images -
Starting and stopping containers:
docker start <containerid>anddocker stop <containerid> -
Remove all containers and stop them at the same time
docker rm -f $(docker ps -a -q)
Private Image repositories
You can setup your own private emails with quay.io or cloud.docker.com among many others.
docker login quay.io or docker login to login to the Docker Cloud Repository
Let's go ahead an pull the Shiny image created by rocker by running docker pull rocker/shiny - this will pull the latest tag of the Rocker/shiny container
This image is built from the Dockerfile and the Entrypoint command which is shiny-server.sh
To run this container on your host you can now run
docker run -d -p 3838:3838 rocker/shiny This command exposes the HOST:CONTAINER ports 3838:3838 respectively and runs the shiny image in the background.
You can now access the container by going to a browser and typing in http://IPADDRESSOFHOST:3838
You should see "Welcome to Shiny Server"
Shiny Apps
In order to share your shiny apps from your host to the container you could also run:
docker run -d -v /path/to/your/shinyapps/:/srv/shiny-server -p 3838:3838 rocker/shiny
Let's start by taking hte Dockerfile and shiny-server.sh from the Repository above. I've created a copy of them in /shiny/Dockerfile and /shiny/shiny-server.sh
comes from r-base:latest which is also $VERSION locked
Let's use the Dockerfile from Rocker to generate our own Shiny Server with our own packages we require. From the Dockerfile:
RUN wget --no-verbose https://s3.amazonaws.com/rstudio-shiny-server-os-build/ubuntu-12.04/x86_64/VERSION -O "version.txt" && \
VERSION=$(cat version.txt) && \
wget --no-verbose "https://s3.amazonaws.com/rstudio-shiny-server-os-build/ubuntu-12.04/x86_64/shiny-server-$VERSION-amd64.deb" -O ss-latest.deb && \
gdebi -n ss-latest.deb && \
rm -f version.txt ss-latest.deb && \
R -e "install.packages(c('shiny', 'rmarkdown'), repos='https://cran.rstudio.com/')" && \
cp -R /usr/local/lib/R/site-library/shiny/examples/* /srv/shiny-server/
We can now add RUN R -e "install.packages(c('ggplot2', 'dplyr'))" to the Dockerfile
Building the image
Now we can build our image by cd to the directory that contains the Dockerfile and shiny-server.sh and running
docker build -t yourimage -f Dockerfile .
You now have your own custom Shiny image. To push this to a repo (after logging in) you can run docker push yourimage
Now we can run it docker run -d -p 3838:3838 -v /home/chiron/shinyapps/:/srv/shiny-server yourimage
OK what have we done: We have built our own shiny server that resides in the cloud We bring this down to any computer anywhere and work on it. Share whatever local folder contains the apps
The nginx image we are using is from Github Nginx
I've created a copy of this Dockerfile in /nginx-shiny/web The changes to this file include:
RUN rm -v /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
# Copy a configuration file from the current directory
ADD nginx.conf /etc/nginx/
COPY .htpasswd /etc/nginx/.htpasswd
What this means is that we are removing the nginx.conf that comes with the default install and adding our own nginx.conf which contains the PROXY_PASS (Reverse Proxy) + Basic Authentication which is adding basic authentication off the .htpasswd file
From the nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
events { worker_connections 1024; }
http {
sendfile on;
server {
listen 80;
location / {
proxy_pass http://shiny:3838/;
proxy_redirect http://shiny:3838/ $scheme://$host/;
auth_basic "Username and Password are required";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.htpasswd;
}
}
}
The important part is near the bottom. Take a look at the last location / block. This block tells Nginx to handle all requests. Inside this block you will find two directives: proxy_pass and proxy_redirect. These directives tell Nginx to proxy requests to the host passed as parameter to them. This is were you should edit the configuration file to point it to your shiny-auth0 authentication server, which we will setup later on in this guide.
On your host sudo apt-get install apache2-utils
Make sure you are sitting in the nginx-shiny directory. You can now run
~/nginx-shiny/web$ htpasswd -c .htpasswd your_user_name
Now build your web image in your /nginx-shiny/web path
docker build -t webimage -f Dockerfile .
Let's now use the principles in PART A To set-up a Shiny + Nginx container stack so that we have basic HTTP authentication on the Shiny Container
We can now put this together
Install Docker-compose
In order to ensure that v2 and v3 of Docker-compose.yml files will work you'll need to install docker compose from Docker and not from the Ubuntu Repo.
-
Make sure to remove your current docker-compose (if it was installed via apt-get)
sudo apt-get remove docker-composesudo apt-get purge docker-compose -
Run
sudo -i -
Grab the binary
curl -L "https://github.com/docker/compose/releases/download/1.11.1/docker-compose-$(uname -s)-$(uname -m)" -o /usr/local/bin/docker-compose -
Apply executable permissions to the binary:
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose -
Logout and login again
-
Check your versions / (Note at writing 20/02/2017)
docker-compose --version should output docker-compose version 1.9.0, build 2585387
docker --version should output Docker version 1.13.1, build 092cba3
Check our the docker-compose.yml to see how this works. Basically we are stacking TWO containers (Shiny from rocker/shiny) and our web container which is built from the /web directory.
From the ~/nginx-shiny directory you can run docker-compose up
You can now access the container by going to a browser and typing in http://IPADDRESSOFHOST
You'll need to login with your_user_name as per the Nginx steps above and should see "Welcome to Shiny Server"
If you want to now run this stack in the background then run docker-compose up -d and to run it while ensuring that you build the Web container each time (otherwise you'll run the built image) docker-compose up -d --build
As per the .yaml file you can see we are using the following images:
rstudio:
image: rocker/hadleyverse
and
shiny:
image: myshiny:v1
You can use the rocker/shiny image if you prefer as it will be pretty much the same except won't have the ggplot and dplyr packages we installed from CRAN
You can now go ~/shiny-rstudio and then check out the docker-compose.yml
To run this stack you can enter the directory and run docker-compose up or docker-compose up -d
There are now other opportunities. If you want to STACK all three containers you can add the WEb container into the stack and then point various ports on the web container to reverse proxy to Rstudio and to shiny.
You'll need to update the nginx.conf file to pass through to shiny:3838 and rstudio:8787 but the options are limitless.
This is a placeholder - Due to popular demand will put a tutorial up here on this
These instructions are from the following Auth0 Article - For now I suggest using this article as I am still putting together the documentation
You can now put the learnings above into a central easy to set-up Shiny Server authentication from Auth0.com We can start with the nginx.conf that we are going to use instead of the previous nginx.conf
Check it out here:
Modified the proxy_pass from localhost:3000 to shiny:3838 as this is the hostname and port as per the docker-compose stack.
Step 3: Setting up and Auth0 Account for shiny-auth0
Since authentication will be handled by Auth0, a free Auth0 account is required to work with shiny-auth0. Don't panic, it's as simple as signing-up and setting a few knobs here and there. Let's take a look.
First, head over to https://auth0.com and signup. Follow the steps to fill in your details. For simple use cases, a free account is more than enough. With a free account you get up to 7000 users. If you need more than that, check our pricing page.
After you have completed the signup process, access the Auth0 Dashboard and create a new client for our shiny-auth0 app. This client will let you setup how your users will log-in through shiny-auth0. You have several options you must consider: will you use a standard username/password database? Or will you allow social logins (through Facebook or Google, for example)? It is up to you to decide what fits best your use case. For simplicity, we will go with a simple social login through Google. We will only allow certain users access to our Shiny Server.
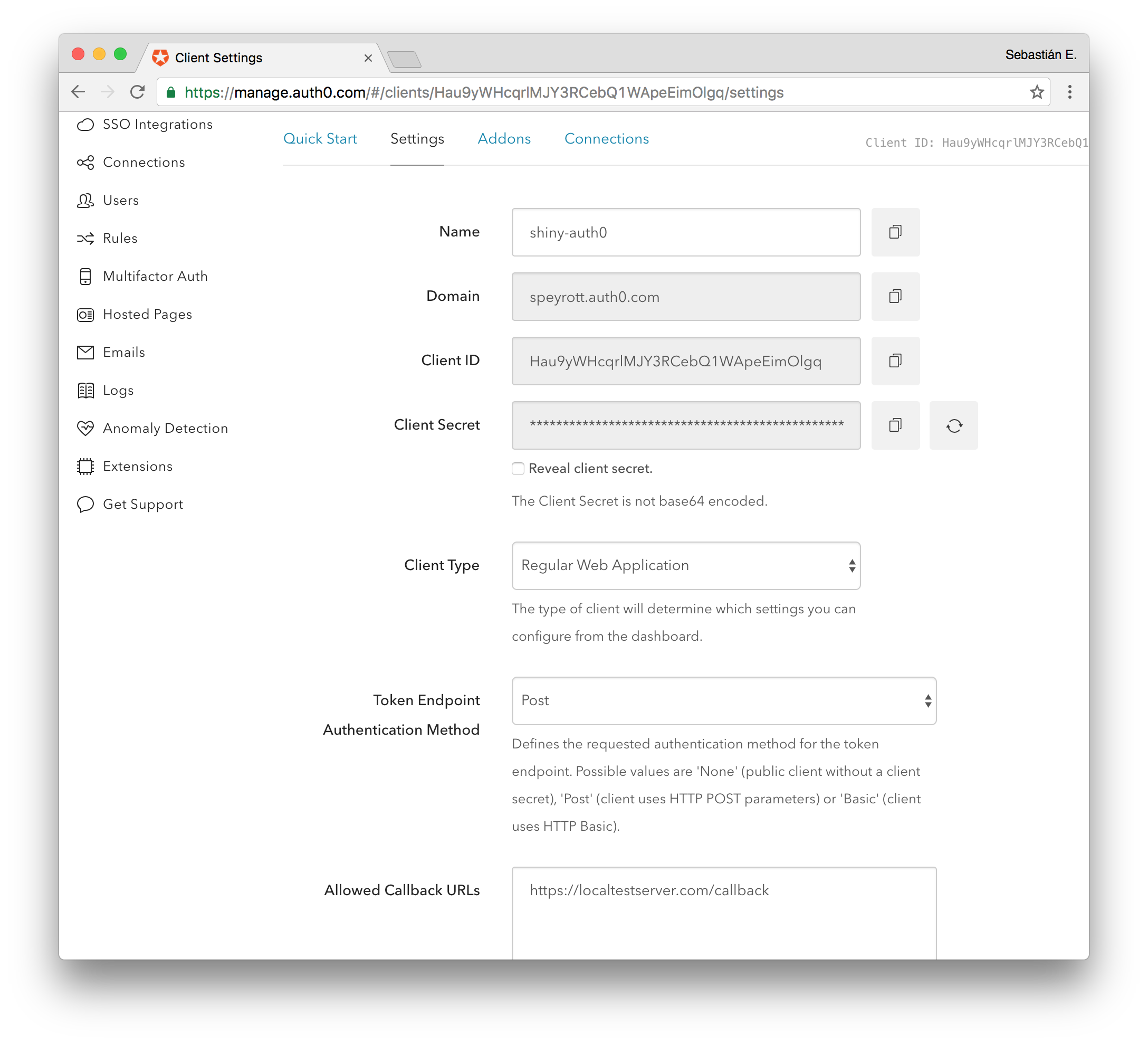
To create a client go to Client on the sidebar and then Create Client on the top right of the screen. Pick a name and then select the type of client. Select Regular Web Applications. Ignore the quickstart that is presented after that and go straight to Settings.
Take note of the Client ID, Domain and the Client Secret.
You will need these later to setup shiny-auth0. Another important setting is the Allowed Callback URLs setting visible below. This is the URL the user will be redirected to after a successful authentication attempt. It is formed by the domain of your public server plus the callback path. For instance: https://shiny.yourhost.com/callback.
- The shiny-auth0-master is a direct download from the Auth0 Shiny Repo
- You'll need to follow the article for the time being
- Make sure to install Node.js and NPm in the SHINY Container (Will update the Dockerfile shortly)