In this article am creating a LAMBDA function stop a development instance. Generally the devlepers after their work, they will set the development server as ON, which needs to be minimised, so am writing this article to stop an development servers using LAMBDA function with help of python after working hours.
We will be using 1 main EC2 instance for working our codes and there will be extra 3 servers (1 for Production and other 2 for development). Here am using jupyter workspace for my code check and we will be needing of 2 modules:
- import boto3 - for running our codes
- import pprint - for printing and fetch instance details
We need to create 1 IAM user with EC2 full access privilege with programmatic access or you can create IAM role with same privilege but use case EC2, we also need to create 1 IAM role with same privilege but with use case of LAMBDA
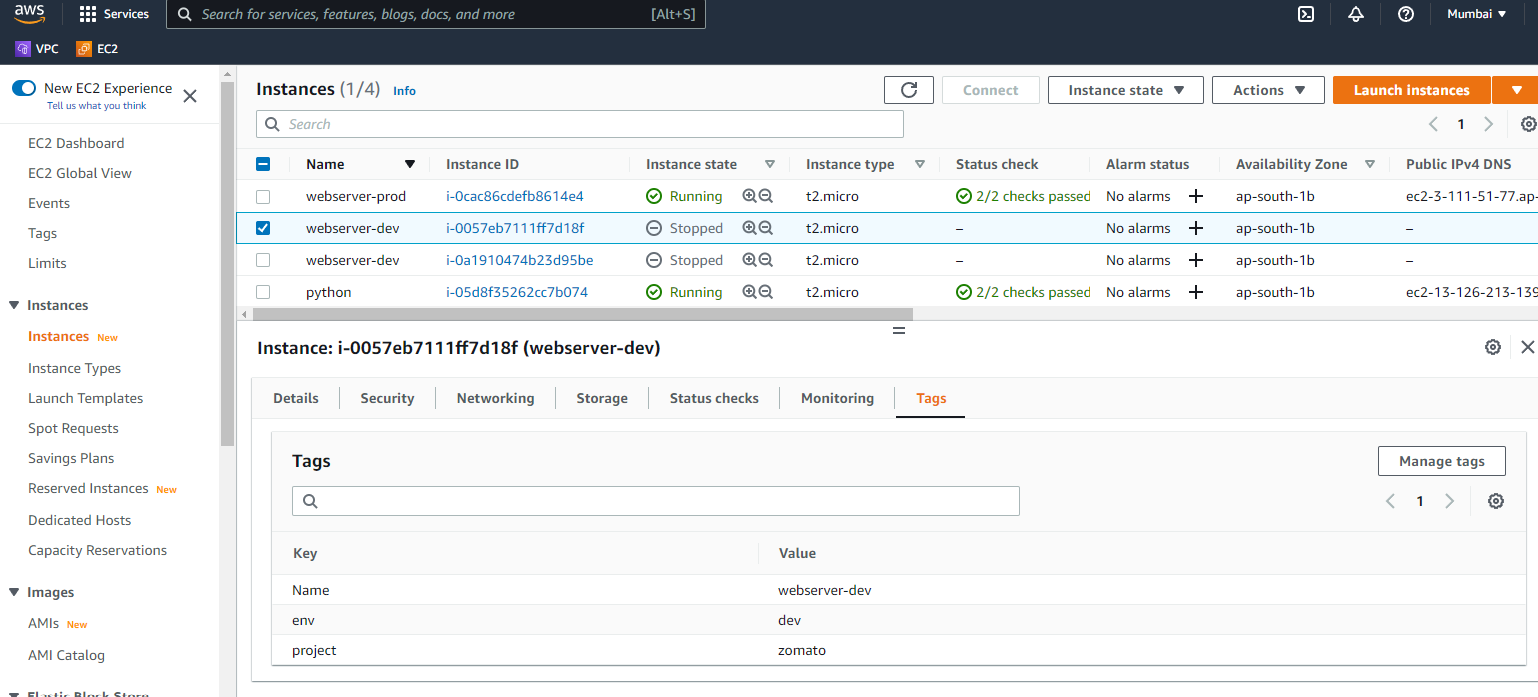
Create production (1) and development (2) servers for our project. Add tags for development servers as:
- Name: webserver-dev
- env: dev
- project: anyname (I used Zomato)
Once those are created and added, we need to get those 2 development servs ID and public IP using python code:
import boto3
import pprint
ACCESS_KEY = "your access key"
SECRET_KEY = "your secret key"
REGION = "ap-south-1"
ec2 = boto3.client("ec2",
aws_access_key_id=ACCESS_KEY,
aws_secret_access_key=SECRET_KEY,
region_name=REGION)
instances = ec2.describe_instances(Filters=[ {'Name':'tag:project', 'Values':["zomato"]},
{'Name':'tag:env', 'Values':["dev"]},
{'Name':'instance-state-name', 'Values':['running']}
])
for item in instances['Reservations']:
print(item['Instances'][0]['InstanceId'] ,item['Instances'][0]['PublicIpAddress'] )
print()We need to write a code for stopping the developer instance:
import boto3
ACCESS_KEY = "your access key"
SECRET_KEY = "your secret key"
REGION = "ap-south-1"
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2',
aws_access_key_id=ACCESS_KEY,
aws_secret_access_key=SECRET_KEY,
region_name=REGION)
instances = ec2.describe_instances(Filters=[ {'Name':'tag:project', 'Values':["zomato"]},
{'Name':'tag:env', 'Values':["dev"]},
{'Name':'instance-state-name', 'Values':['running']}
])
for instance in instances['Reservations']:
instance_id = instance['Instances'][0]['InstanceId']
print("Stopping Instance : {}".format(instance_id))
ec2.stop_instances(InstanceIds=[ instance_id ])We use code and platform(python)for starting and stopping servers, now we need to trigger the code for stoping and starting instances automatically/at a specific time. This coding is called LAMBDA function. To trigger the LAMBDA function we can use cloudwatch service ->-> events section. We can use cron expression for setting time specific time to trigger.
Goto LAMBDA service in AWS >> Create function >> fill the following and create. Now we get a interface where we can add code and deploy.
Code:
import boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context):
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2',region_name="ap-south-1")
instances = ec2.describe_instances(Filters=[
{'Name':'tag:project', 'Values':["zomato"]},
{'Name':'tag:env', 'Values':["dev"]},
{'Name':'instance-state-name', 'Values':['running']}
])
for item in instances['Reservations']:
instance = item['Instances'][0]
instance_id = instance['InstanceId']
print("Stopping Instance : {}".format(instance_id))
ec2.stop_instances(InstanceIds=[ instance_id ])Here there are 2 parameters in lambda_handler fuction: Events and Context:
event is to know what is trigger is running in lambda, like wat event caused the trigger context is to know the memory utilisation of trigger/function
Now we need to set the trigger for our LAMBDA function to work, So we use Cloudwatch for setting trigger.
Goto cloudwatch service in AWS >> events >> rules >> cloudwatch events >> create rule >> schedule >> select cron expression >> add target >> function name >> config details >> add name >> create rule.
You can set any cron as per your need. Once this is added we can see that our development servers has been stopped automatically.
In this article, we created a LAMBDA function for stopping development instances automatically using cloudwatch trigger so that servers will remain OFF once the devlopers job is finished. Please contact me if you have any questions in this section. Thank you!