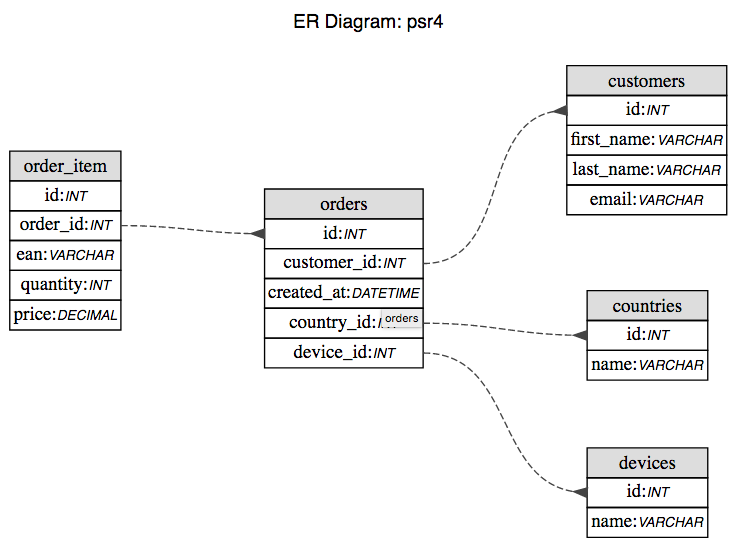
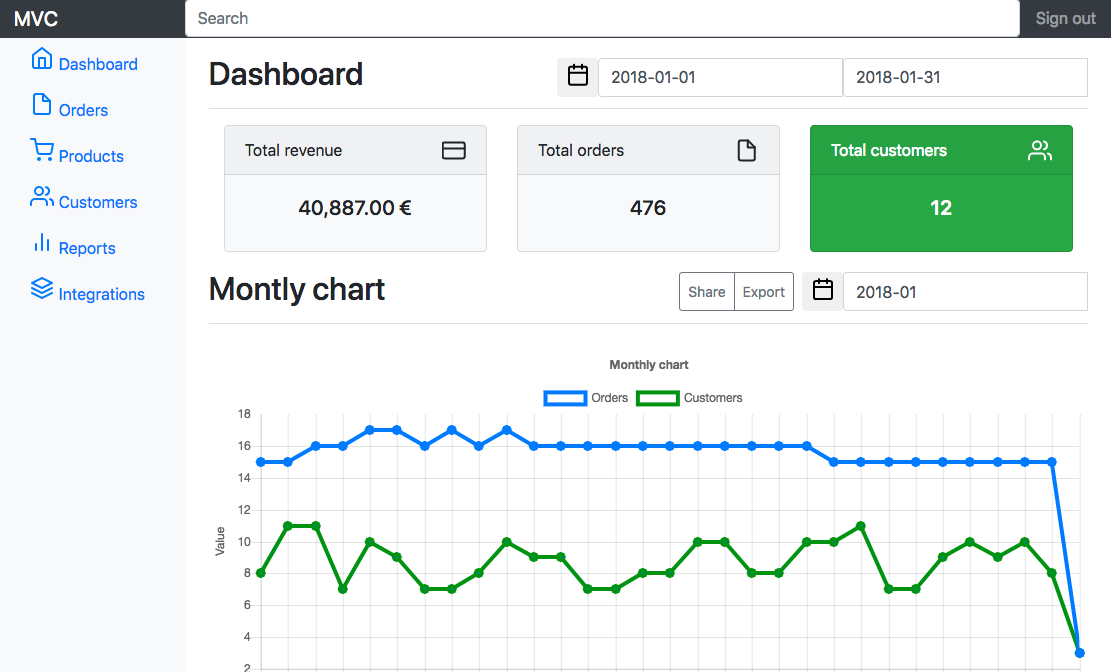
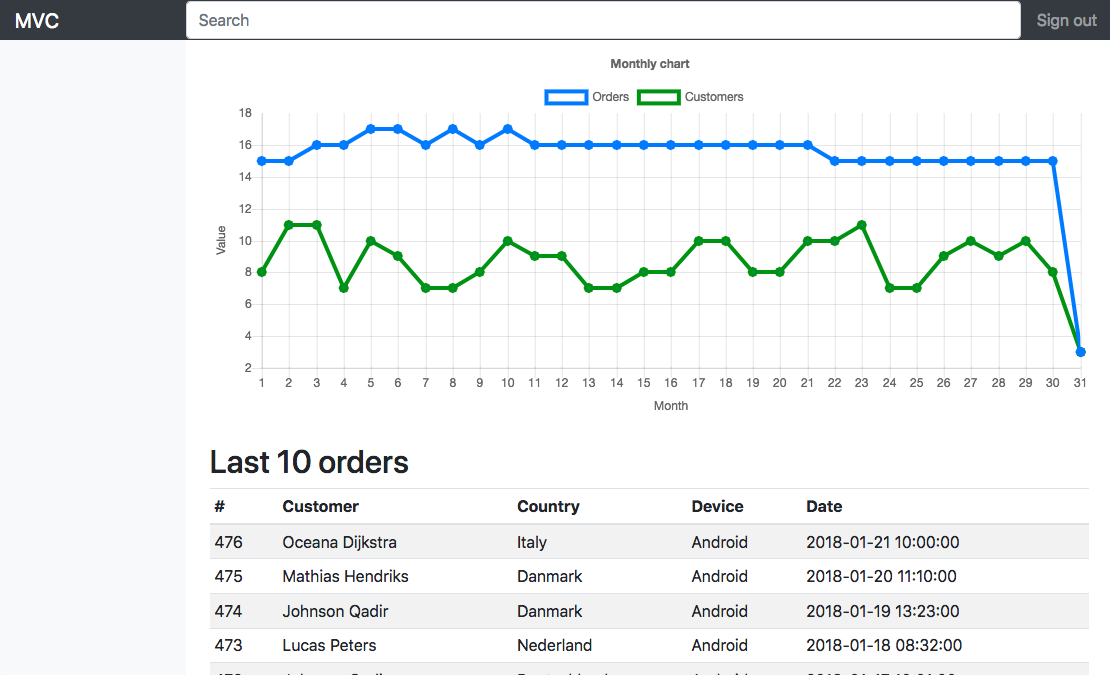
This is simple example of creating MVC framework with php.
- App (All classes related to the application)
- Controllers
- Models
- Views
- Page
- Config (Contains all of application's configuration files)
- database (Contains database dumps and seeds)
- logs (Contains application logs if the display of the error on the screen is turned off)
- public (Contains the front controller and assets (images, JavaScript, CSS, etc)
- src (All core classes)
The following packages were used:
- jQuery - JavaScript Library.
- Bootstrap - The most popular HTML, CSS, and JS library in the world.
- Feather - Simply beautiful open source icons.
- bootstrap-datepicker - A datepicker for Bootstrap.
- Chart.js - Simple, clean and engaging HTML5 based JavaScript charts.
In order to run the application, it is necessary to create a virtual host and setup database.
Application tested on:
- PHP 7.1.14
- Nginx 1.13.8
To start this project, you need to have the following components installed:
- PHP - PHP is a widely-used open source general-purpose scripting language that is especially suited for web development and can be embedded into HTML.
- MySQL - MySQL is an open source relational database management system (RDBMS) based on Structured Query Language (SQL).
- Apache or Nginx - An HTTP server.
Transfer files to the folder that watches the web server and import database. The configuration parameters for the database are in /Config/Database.php.
This example includes a simple method of seeding database with test data using seed classes.
Seeders can be defined in a /database directory. Seeder needs to implement the core seeder interface.
You can run the seeder by calling the php seeder command with name of the seeder class as first parameter.
php seeder Order
All configuration classes are located in the /Config directory. Currently, there are two configuration classes:
- Configuration parameters for connection to the database.
- Parameters related to the application (SHOW_ERRORS and DEFAULT_ROUTE).
To get the settings in any part of the application:
- use Config\Database; then for example you can get host with Database::DB_HOST.
Namespaces and Routes are located in /App directory. These files return a array of data. These files are automatically loaded by the framework.
One method can have multiple routes. The routes consist of request method and array with URI and controller@action.
return [
"GET" => [
"/home" => "Home@index"
]
];
The model represents an abstract class that contains two attributes:
- private $db; - Represents an instance of a PDO object.
- protected $_table; - The name of the table in database that the model binds.
The _table attribute is very important for the insert() method. Without this information, the insert method will not work.
This method makes it easy to insert data into the database in a quick and easy way. The data set must be associative. Index of array represents the field in the database.
For example: [ "fist_name" => "John" ]
Database:
- E-mail address field changed to 254 characters.
- Added unique index on e-mail address and order_id + ean.
Code:
- Model::$db changed to static. To prevent opening a new database connection for every model.
- Model $_table moved to constructor.
- Using array_keys() and array_values() instead of foreach in Model insert() method.
- Added new Validator class with date validation method.
- Added date validation in Statistic model.
- Added default option in Request::getParam.
- Added type hints.
- Andrej - Initial work - andrejrs