This document provides a list of the required technologies for anyone who will be going through the Python/Automation program. It details why each technology is required and provides some step-by-step instructions on how to install and configure the technologies. This guide also walks you through any needed environment setup.
NOTE: It is very important that you install these technologies as soon as possible, environment setup will not be covered during the lessons It is also key that you install the correct versions of the tools listed here as not all versions of the technologies we will use are guaranteed to be compatible with each other. If you are unsure about it, check online or with your team. Windows 10 is the assumed default operating system. If you choose to use a different operating system or version of one of the tools listed here, you will be responsible for debugging issues that are specific to your development environment.
The following technologies and/or services are required for this program:
-
Java SE Development Kit 8: We will be utilizing Java 8 as one of our primary languages for the duration of the program. This software development kit will provide the compiler and runtime environment needed to quickly and efficiently develop Java applications.
-
Apache Maven: Maven is a software project management and build automation tool. We will use it to manage our projects' builds as it provides dependency management and streamlines several aspects of the testing life cycle.
-
Git: We'll be using Git as a version control tool during the course of this program. Not only will you use Git to track changes to your projects, but you'll also use it to collaborate with your trainer and with your fellow associates.
-
Git Bash: We will be using git bash as our terminal of choice, while the windows system comes with a built in terminal with CMD or Powershell, most remote servers are built on linux and do not use these terminals. This is where Git Bash comes in, it is a linux-style Command Line Interface for windows and integrates with git cleanly.
-
Amazon Web Services (AWS): Amazon Web Services offers cost-effective, scalable cloud computing solutions. We will be using AWS for its Relational Database Service (RDS). There are no instructions below on how to sign up for an account as the process if straightforward. Simply visit AWS' website and register for an account; make sure that you select a personal account as personal accounts are allotted a year's worth of free tier cloud resources.
-
DBeaver: DBeaver is a free, open source universal database tool that is compatible with several external data sources, PostgreSQL included. We'll use DBeaver in order to modify our databases and persist data using a simple user interface provided to us by the tool. While DBeaver is an IDE for the sql management, I have placed this as required as the alternative will be too much to manage as a new developer.
-
Postman: Postman is used for testing RESTful APIs. We'll use it to set up collections of tests for the RESTful APIs we design throughout the program. It can also be used to quickly test a single endpoint.
-
Python: We will be using Python 3 as one of our primary languages for the duration of the program. Make sure if you do download it to NOT download Python 2 or any versions that begin with Python 2 as we they are not backwards compatible with each other. This Python installation will provide the standard library, preferred installer program, and several other components that make building and running Python applications possible.
-
PostgreSQL ODBC Driver: When building Python applications, we will utilize
pyodbc, a PyPI module that makes accessing ODBC databases easy. As such, you'll need to download and configure a Postgres-specific ODBC driver.
Optional
- PostgreSQL 10: PostgreSQL is an open source relational database. We will leverage this technology in order to persist and organize data. Though you are expected to use AWS' Relational Database Service to host your database for projects in their production environments, you are welcome to download Postgres to your local host while working with your application in a development environment.
Understand that an IDE is not essential to programming, it provides a lot of helpful features like autocorrect and error checking, a handy editor and terminal to make testing and debugging easier, clear file structure, and more. However, the IDE itself is basically a glorified text editor, even notepad.exe is fine to use to make programs so don't confuse the IDE with the program, it is still only a tool used to make the program, not the program itself.
-
Visual Studio Code: This will be the IDE used during training. If you choose to use a different IDE, that is fine too. Visual Studio Code is a text editor that makes viewing and modifying code simple. VS Code provides support for numerous languages and will be the primary IDE of choice during all sessions.
-
Intellij Community Edition (Optional): Intellij community edition is an excellent Java focused IDE. We are not using IntelliJ due to the size of the IDE, while it is a great IDE for programming with Java, it's significant size creates a lot of bloat that is only really viable if you know how to take advantage of it. Make sure to install the community edition instead of the ultimate as that begins with a free trial and then requires a subscription. Intellij also has a plugin market that can further enhance your programming experience.
-
PyCharm (Optional): PyCharm acts as an integrated development environment for Python. Similar to IntelliJ as it is part of the JetBrains family, a powerful IDE but includes a lot of bloat that can significantly reduce your development speed unless your system is able to handle it.
There are two provided methods of attaining and configuring all of the necessary tools listed above:
- Via a package manager or command-line installer
- Manually downloading the necessary software
It is recommended to use a package manager as the manual method is prone to issues. If for some reason the recommended package n
Neither method is more "correct" than the other. You should choose the method of attaining the tools that works best for you. You may even choose to mix both methods, downloading some tools manually and others via a package manager.
Method 1: Installation Guide Using A Package Manager
A *package manager* is a command line tool that allows you to install and manage software. You can use a package manager to install all of the software listed here.
The package manager that we'll be using for this guide is called "Scoop". It's a command-line installer for Windows, which means that you'll have to be running Windows in order to use this tool. You'll also need PowerShell 5 (or a later version) installed.
Note: If you are not running Windows and still want to use a package manager, for MacOS there is HomeBrew. You'll have to, however, know how to use your package manager of choice as there won't be instructions provided here since there are many package managers available. If you do not wish to use a package manager, please skip to method 2.
In order to use Scoop, you'll first have to install it. This installation requires that you have PowerShell 5 or later.
Once you've verified that you have a compatible version of PowerShell, launch PowerShell. You can launch PowerShell by searching for it in the Windows search bar. Then go to Scoop's official website. Once on the homepage, scroll to the bottom of the page until you see the following:
As Scoop's installation instructions indicate, you can run one of the following commands in PowerShell (NOT both):
Option 1:
Invoke-Expression (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://get.scoop.sh')
Option 2:
iwr -useb get.scoop.sh | iex
If you run one of these commands and it fails, you'll need to first run the following command:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -scope CurrentUser
After you've run this command, you should then attempt to run one of the first two commands again.
When installed, Scoop comes with a default bucket titled "main". Since some of the programs we'll install using Scoop aren't contained in this bucket, we'll add some additional buckets before we begin installing our programs.
Open a new terminal and run the following commands (one by one):
scoop bucket add extras
scoop bucket add java
scoop bucket add versions
Note: If you receive a warning that says that the bucket you're attempting to add already exists, you don't have to worry as this means that you already have that bucket.
Now that you've installed Scoop and added some additional buckets for downloading software, open a new terminal and run the following command in order to install Git:
scoop install git
After the installation is complete, verify that you have installed Git properly by typing the following in your terminal:
git --version
In order to install Java, run the following command in your terminal:
scoop install ojdkbuild8-full
Now verify that you have installed Java properly by typing this command:
java -version
In order to install Maven, run the following command in your terminal:
scoop install maven
Verify that your Maven installation was successful by typing the following:
mvn -version
In order to install DBeaver, run the following command in your terminal:
scoop install dbeaver
You can verify that you have installed DBeaver properly by searching for "DBeaver" in your Windows search bar.
In order to install Postman, run the following command in your terminal:
scoop install postman
Verify that the program was installed properly by searching for "Postman" in your windows search bar.
In order to install Python, run the following command in your terminal:
scoop install python39
Verify that your Python installation was successful by typing the following in your terminal:
python --version
Scoop does not support the installation of the PostgreSQL ODBC Driver. As such, please skip to the manual installation subsection which details how to install the driver.
To install Visual Studio code we can use
scoop install vscode
You can check to see if Visual Studio Code by searching for it in the start menu. You can also open it up using the terminal with the command "code".
In order to install PyCharm, run the following command in your terminal:
scoop install pycharm
If your installation was successful, you should now be able to search for "PyCharm" in your Windows search bar.
In order to install PostgreSQL, we will NOT be using Scoop as we require PostgreSQL 10, a version that is not currently supported by Scoop. That said, we will manually download the PostgreSQL installer visiting the official website.
Once you've navigated to the website, you should see the following:
Please look at the row for version 10.13 as we will downloading this version. Select the download link which corresponds with your system and click it.
You'll then be prompted to save the file. Click "Save File".
The file should now be located in your "Downloads" folder.
Double click the file, which should launch the installer. You might be asked if you want the application to make changes to your device. Say "yes".
You'll be presented with several menus in the Setup Wizard.
Hit "Next" until you get to the "Select Components" menu. Here, you'll want to select and/or deselect the following and then click "Next":
Continue to hit "Next" until you reach the "Password" menu. Here you will be tasked with providing a password for the default Postgres user (which is "postgres"). The password is completely up to you. That said, DO NOT forget your password as you won't be able to login to your database as the superuser. If you have to, write your password down somewhere or use a password manager.
After you've decided on a password, hit "Next" on the remaining menus and allow time for Postgres to be installed. Once the installation is complete, you might be asked if you want to launch Stack Builder. You can say "no".
PostgreSQL should now be successfully installed on your computer.
Method 2: Manual Installation
This method is compatible with all environments as it does not require any platform-specific package managers. You need only visit the official websites for each of the technologies listed and download the version of the tool that is compatible with your system.
Do note, however, that setting system environment variables differs from machine to machine. This guide shows how to set environment variables on a Windows machine.
The first thing you'll want to do is open your web browser of choice. This guide will use Chrome.
Note: Many of the tools that you will install have different system installers that are platform dependent. It is very important that you download the correct installer. The following list details how you should choose the installer for a program:
- If you have a 32-bit version of Windows, use the installer that is marked as the 32-bit version.
- If you have a 64-bit version of Windows, use the installer that is marked as the 64-bit version.
- If you have a Linux distribution (e.g. Debian, Ubuntu, Red Hat, Fedora), you should choose the installer that matches your distribution.
- If you have a Mac, you should choose the installer that is marked as the Mac installer.
These options will be clearly labeled on the websites you visit to download the technologies. If you're not sure how to figure out what version of the Windows operating system you're running, do the following:
- Type "Control Panel" into the Windows search bar and click on the "Control Panel" app.
- Select "System and Security".
- Select "System".
You should now see the following screen:
You should see your operating system listed ("Windows 10" in the above example) and the system type listed under the "System" tab (a 64-bit operating system in the above example).
- Navigate in your browser to Git's Website and click the latest download for Windows. (For those using a different OS click the appropriate OS and look for the most recent stable release.)
-
Click yes to any security/firewall popup asking if you are sure you want to download the file.
-
The install file will begin downloading; most browsers will show the file that has just downloaded, click that file when it completes. If you do so skip to step 6. If the download is not apparent on your browser or disappears upon finishing go to step 4.
- If you were not able to click the install exe file you just downloaded in your browser open your file explorer.
- In the window that opens click the "Downloads" folder, use the search bar in the upper right to search "git", and then double click on the Git installer exe file.
-
Click yes to any security pop-ups asking you if you want to allow the installer to make changes to your computer.
-
The install wizard will open to guide you through the process of installing Git. Read the license agreement and click "Next."
- Accept the default installation path by clicking "Next."
- Select your components. It is recommended to add a desktop icon. Leave the other boxes in their default setting. Click "Next."
- Leave the rest of the set up as the default configuration clicking Next until you get to the experimental options (which you should leave unchecked) and then click Install. This will run the actual install process.
- After install you will get a a final window giving you the options to launch Git Bash and view the Readme notes. Select open Git Bash and deselect the view Readme notes. Click "Next."
- When Git Bash opens type "git --version" and hit Enter. If it return the version of Git you installed it correctly.
-
Navigate in your web browser to Oracle's JDK 8 website. NOTE: If you are experiencing errors when trying to load the webpage try another browser. If you still are having trouble, try again later.
-
In the top right of the website click "View Accounts" and then "Create an Account." (If you already have an Oracle account you can just skip to step 5)
- Fill in the form with your information (you may type "none" for Company Name) and then click the "Create Account" button.
- Check your e-mail account for a new message from Oracle. (This may take a few minutes.) When you receive the e-mail open it and click the "Verify Email Address" button inside. This should direct you to a success screen.
- Return to Oracle's JDK 8 website. Scroll to find the appropriate JDK for your Operating System and Architecture. (Windows 10 will be Windows x64 as shown below) and click to download.
- A popup will ask you to review the license before continuing. Do so and click the check box and then the download button.
- If you are not signed in a pop will appear asking you to do so. Enter your sign in information (your e-mail is your user name) and submit. The download should then begin.
- Once the download is complete, click the file that downloads in your browser to open it and skip to step 11. If you do not see the file in your browser then proceed to step 9 to find it in your downloads folder.
- If you could not open the JDK installer from your browser open your file explorer.
- In the window that opens click the "Downloads" folder, search (in the top right) for "jdk" and double click the jdk installer.
- The installer will inform you that the license has been updated from previous versions. Review the license if you have not already and click next.
- The installer will continue and you should just accept the default setup. IMPORTANT: Make note of the file path for the installation directory! You WILL need this later. Click "Next."
- The install will begin extracting files and will ask to confirm the installation directory of the JRE. Confirm the default directory by clicking "Next."
- Java will finish installing and you can then click "Close."
- Use your system search tool (next to the windows button) to look for "Edit the system environment variables" in the control panel. Be sure that you open the SYSTEM environment not the ones just for your account.
- Click the "Environment Variables" button in the window that opens.
- Under "System Variables" click the "New" button.
- Name the new variable "JAVA_HOME" and give it the value of the directory where your JDK was installed to. (See Step 12.) If you are unsure of your directory path you can go to C:\Program Files\Java in your file explorer then click on the JDK folder to open it. You can then copy the path from the navigation bar at the top of the file explorer.
- In your system variables then select the "Path" variable and click "Edit."
- Click "New" to create a new line. Add the path to the JDK bin folder in this line, it will be the same as the path in JAVA_HOME with a "\bin" at the end.
- Click "OK" to close the Environment Variables window.
- Open Git Bash, type "java -version" and hit Enter. If the JDK is installed correctly you should see Java with the version number you downloaded.
- Navigate in your web browser to the Maven Download Page and scroll down to the "Files" section. Click the Binary zip archive link to download. Approve any firewall/security popups asking if you are sure you want to download the file.
- The download should appear in your browser. When it completes right-click and click "Show in folder." Skip to step 4. If you were unable to right-click and show in folder proceed to step 3.
- If you could not open the file location from your browser, open your file explorer, click downloads, and search "maven" in the upper right search bar. You should see the file you just downloaded.
- Right click the Maven zip archive you just downloaded and click "Extract All..."
- Your extraction wizard will open. Set the file path to "C:\Maven" and click the box to show extracted files when complete. Then click "Extract."
- Your file will be unzipped and your file explore will open a window to C:\Maven containing the folder with your maven version. Double click to open that folder.
- Now inside the versions specific folder, click the navigation bar and the top and copy the file path. You will need this for your environment variables.
- Use your system search tool (next to the windows button) to look for "Edit the system environment variables" in the control panel. Be sure that you open the SYSTEM environment not the ones just for your account.
- Click the "Environment Variables" button in the window that opens.
- Under "System Variables" click the "New" button.
- Name the new variable "M2_HOME" and give it the value of the file path you copied in step 7. Then click "OK."
- Click the new button again. Give the variable the name "M2" and the file path "%M2_HOME%\bin" then click "OK."
- In your system variables then select the "Path" variable and click "Edit."
- Click new to open a new line and type in "%M2%" then click "OK."
- Click "OK" to close the Environment Variables window.
- Open Git Bash and type "mvn -v" then hit Enter. If that returns the maven version you have it set up correctly.
In order to install PostgreSQL, please visit PostgreSQL's official website.
Once you've navigated to the website, you should see the following:
Please look at the row for version 10.13 as we will downloading this version. Select the download link which corresponds with your system and click it.
You'll then be prompted to save the file. Click "Save File".
The file should now be located in your "Downloads" folder.
Double click the file, which should launch the installer. You might be asked if you want the application to make changes to your device. Say "yes".
You'll be presented with several menus in the Setup Wizard.
Hit "Next" until you get to the "Select Components" menu. Here, you'll want to select and/or deselect the following and then click "Next":
Continue to hit "Next" until you reach the "Password" menu. Here you will be tasked with providing a password for the default Postgres user (which is "postgres"). The password is completely up to you. That said, DO NOT forget your password as you won't be able to login to your database as the superuser. If you have to, write your password down somewhere or use a password manager.
After you've decided on a password, hit "Next" on the remaining menus and allow time for Postgres to be installed. Once the installation is complete, you might be asked if you want to launch Stack Builder. You can say "no".
PostgreSQL should now be successfully installed on your computer.
In order to install DBeaver, please visit DBeaver's official website.
Once you navigate to the website, you should see the following:
You'll notice that there are two options: Community Edition and Enterprise Edition. Please select the Community Edition as it is free. Do NOT select the Enterprise as it is not free.
You will find the installers for the Community Edition if you scroll down the page. They should be located directly beneath the the box which says "Community Edition 7.1.1". As with all other software listed here, please make sure that you choose the correct installer for your system.
Once you've clicked on the installer that is compatible with your system, you'll be prompted to save the file. Save it and note where you've saved it on your machine. These files are usually stored in your computer's "Downloads" folder by default.
Now navigate to the folder where the installer is stored. For this example, we've downloaded the file to the "Downloads" folder.
Double click the installer. Once you've done so, the installer will be launched. The installer should take you through the process of setting up DBeaver. You'll be asked, for instance, to select a language of choice and review license terms before you install the software.
When you arrive at the portion of the setup which is titled "Choose Components", please select "DBeaver Community" and "Associate .SQL files".
If your installation was successful, you should now be able to search for and find "DBeaver" using your computer's search bar.
In order to download Postman, please visit Postman's official website.
Once you've navigated to the site, you should see the following:
Note that the default download is for Windows. If you wish to download Postman for Mac or Linux, you should click on one of the links highlighted in the small box beneath the version number and "RELEASE NOTES" link. You can see these links at the bottom of the image provided above for reference.
You should now click the "Download" button, at which point you'll be prompted to select either Windows 32-bit or Windows 64-bit (assuming you're downloading Postman for Windows). Choose the option which is compatible with your system. You'll then be prompted to save the file.
Once you've saved the file, open your "Downloads" folder and double click the newly downloaded installer.
Upon double clicking the executable, the installer will be launched and the program will be installed. In order to verify that it has been installed correctly, you can search for "Postman" on your machine by using your search bar.
Note that you'll likely have to sign up for an account to use the application. Please do so as signing up for an account is completely free.
- Navigate in your web browser to the download section of Python's official website. You should see the following:
-
Once there, click the link for your specific operating system.
-
You should now the following screen (or a similar screen depending on which OS you chose in the last step):
Please download the appropriate installer for your machine. Remember which folder you've decided to download the installer to as you'll need to run it in the next step.
- Locate the installer on your machine and run it. Once you've run it, a wizard should pop up. Selection the option for customizing your installation:
Make sure that the following boxes (at a bare minimum) are checked:
- Documentation
- pip
- td/tk and IDLE
- Python test suite
- Hit the "Next" button. You should see the following box:
Make sure the that the following boxes (at a bare minimum) are checked:
- Add Python to environment variables
You also have the option to customize your installation location, though you are not required to do so.
Once you've ensured that all of the necessary boxes are checked, hit the "Install" button.
-
Once your installation is complete, open a new terminal and run the following command:
python --version
If your Python version is displayed, your installation was successful.
Note: If you are not running Windows, this process will look somewhat different for you. You are still responsible for configuring the development environment for your own operating system.
-
Navigate to PostgreSQL's official ODBC download site.
-
You should see several directories:
The directory you click on depends on your operating system. In order to find out which directory to open, take a look at the README file that is listed under the directories on the site. Generally speaking, Windows users will want to use the "msi" directory while *nix users will want to use the "src" directory.
- Once you've clicked the appropriate folder, scroll down to the "psqlodbc_10" files:
Choose any version of 10 which is compatible with your operating system.
- After you've downloaded the file, unzip it. Open the folder to which you extracted the files and run the installer. You should see a setup box:
Move the default options for the driver and hit "Install" once you reach the final screen of the setup box.
This should complete the installation of your ODBC driver.
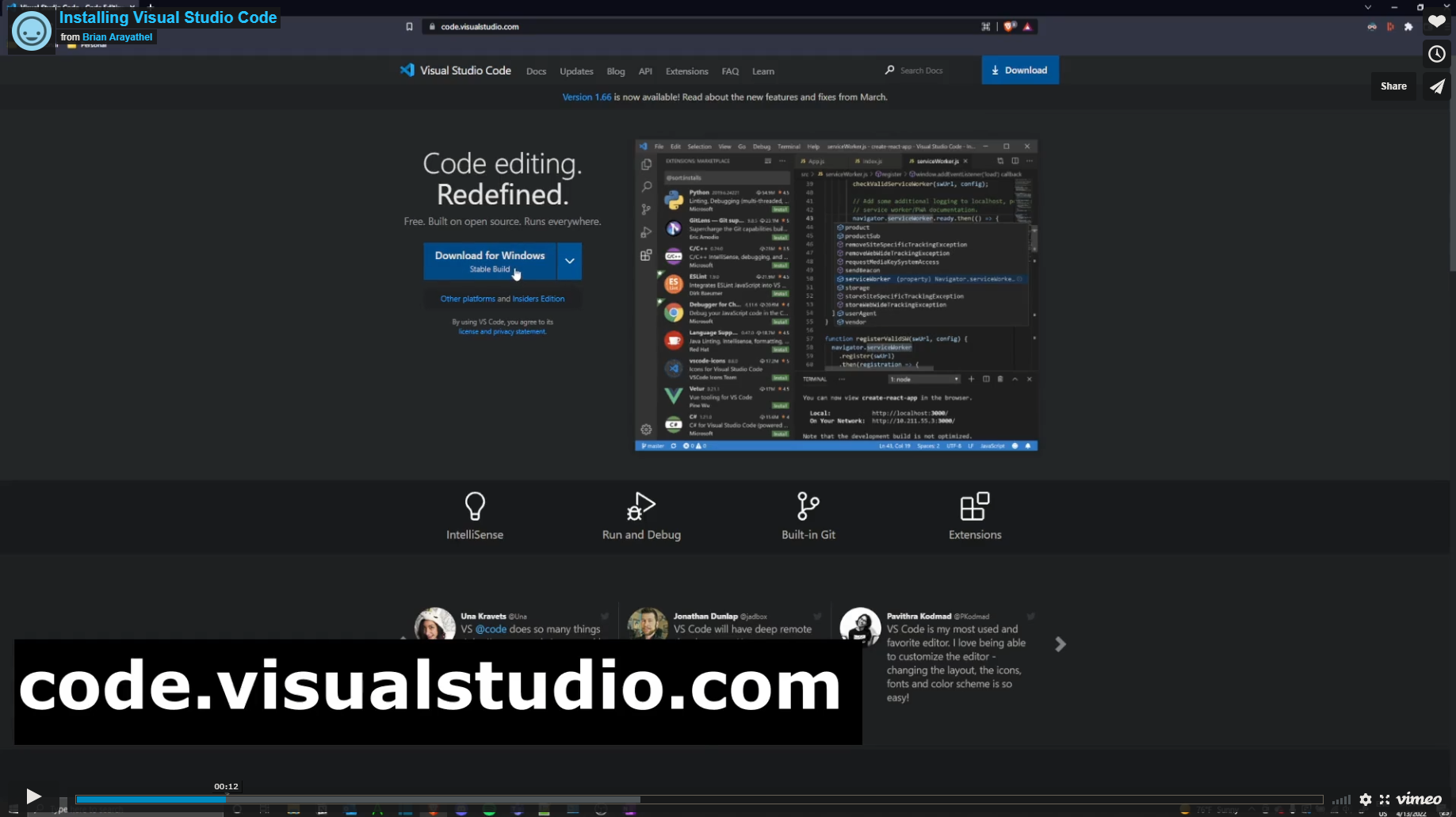
In order to download Visual Studio Code, please visit Visual Studio Code's official website.
Once you've navigated to the website, you should see the following:
Choose the installer that is compatible with your system. Once you've clicked the installer of your choice, you'll be prompted to save the file. Do so.
Once you've saved the installer, it should be located in your "Downloads" folder.
Double click the installer. Once you've done so, the installer should be launched. Accept the license agreement and proceed until you reach a menu titled "Select Additional Tasks". Once you've arrived here, be sure to check all of the boxes that are checked in the image!
After you've done so, hit "Next" and then "Install" on the next menu. If your installation was successful, you should be able to search for "Visual Studio Code" on your machine.
-
Navigate to PyCharm's official website in your web browser.
-
Once there, you should see the following screen:
Select your operating system first. After you've done so, download the Community edition of PyCharm — do NOT download the Professional edition as it is not free.
- Now that you've downloaded the program, run the executable, which should be located in the folder you downloaded the program to. You should see the PyCharm installation box:
-
You will have the option to change the destination folder, though this is optional. If you do not wish to change this folder, then simply hit the "Next" button.
-
On the next screen, make sure the following boxes are checked:
- Hit the "Next" button. On the next screen, hit the "Install" button:
- Once your installation is complete, you should be able to search for "PyCharm" on your machine and launch it.
- Git Cheat Sheet (This is a GitHub-provided cheat sheet for some simple Git commands.): https://github.github.com/training-kit/downloads/github-git-cheat-sheet.pdf
- Java Docs (The official API specification for Java 8): https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/
- Maven Repository (This provides a repository of dependencies which we can add to our Project Object Models.): https://mvnrepository.com/
- Python Package Index (This provides a repository of modules we can add to our Python projects.): https://pypi.org/
- PostgreSQL Docs (This is PostgreSQL's official documentation.): https://www.postgresql.org/docs/