This shell script is based on a pair of shell scripts authored by Jeff Severns Guntzel.
Jeff's first script helped data journalists use Christopher Groskopf's 'csvkit' library to audit a csv file without opening it.
Jeff's second script created a backup of a csv file, and then moved the backup and the original to a project directory structure.
-
Install csvkit using the Terminal on Linux or MacOS
easy_install pip pip install csvkit -
Download the csv_audit_and_backup shell script repo to your desktop
-
Unzip the repo and drag the folder to a directory in your home folder. For instance $HOME/Documents. Feel free to rename the folder to something shorter like csv_audit. There is a variable called BASEDIR in the script based on the following file path, so any changes will need to be made there.
-
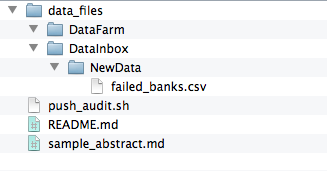
Also, the script is based on Jeff's directory structure, and assumes the same:
data_files /DataInbox /NewData /DataFarm
-
Use your Terminal's Change Directory command to enter into the csv_audit folder.
cd $HOME/Documents/csv_audit/ -
Let's change into the New Data folder and list the files so we can see a sample csv file titled failed_banks.csv. We're going to use this to make sure everything works as expected.
cd data_files/DataInbox/NewData ls -
Let's now tell the script to act on the failed_banks.csv file. We'll run the script using the file name as a parameter
bash $HOME/Documents/csv_audit/push_audit.sh failed_banks.csv -
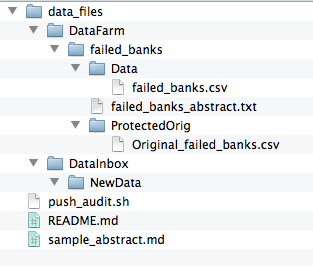
The script will take the csv file, audit it using csvkit, create an audit file, make a copy of the csv and move all three to a new directory in DataFarm based on the name of the csv file.
For this script to work, you must install Christopher Groskopf's csvkit.
Command Line Tutorial, via Jeff's blog