-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 17
Description
1.2 About the technology
1.2 本书涉及的技术
We’ll use two main technologies in this book: Python and GitHub Copilot.
在这本书中,我们将用到两项主要技术:Python 和 GitHub Copilot。
Python is a programming language. It’s a way to communicate with a computer. People use it to write all kinds of programs that do useful things, like games, interactive websites, visualizations, apps for file organization, automating routine tasks, and so on.
Python 是一门编程语言,是与计算机进行交流的途径。人们使用它编写各种程序来完成有用的事情,比如游戏、交互式网站、数据可视化、文件管理应用以及自动化常规任务等等。
There are other programming languages, like Java, C++, Rust, and many others. Copilot works with those, too, but at the time of this writing, it works really well with Python. Python code is a lot easier to write compared to many other languages (especially assembly code). Even more importantly, Python is easy to read. After all, we’re not going to be the ones writing the Python code. Our AI assistant is!
编程语言还有很多种,包括 Java、C++、Rust 等。Copilot 也支持这些语言,但截至目前,它对 Python 的支持最为出色。相对于其他许多语言来说(尤其是与汇编语言相比),Python 代码写起来要简单得多。更为重要的是,Python 更易于阅读。毕竟,编写 Python 代码的将不是我们,而是我们的 AI 助手!
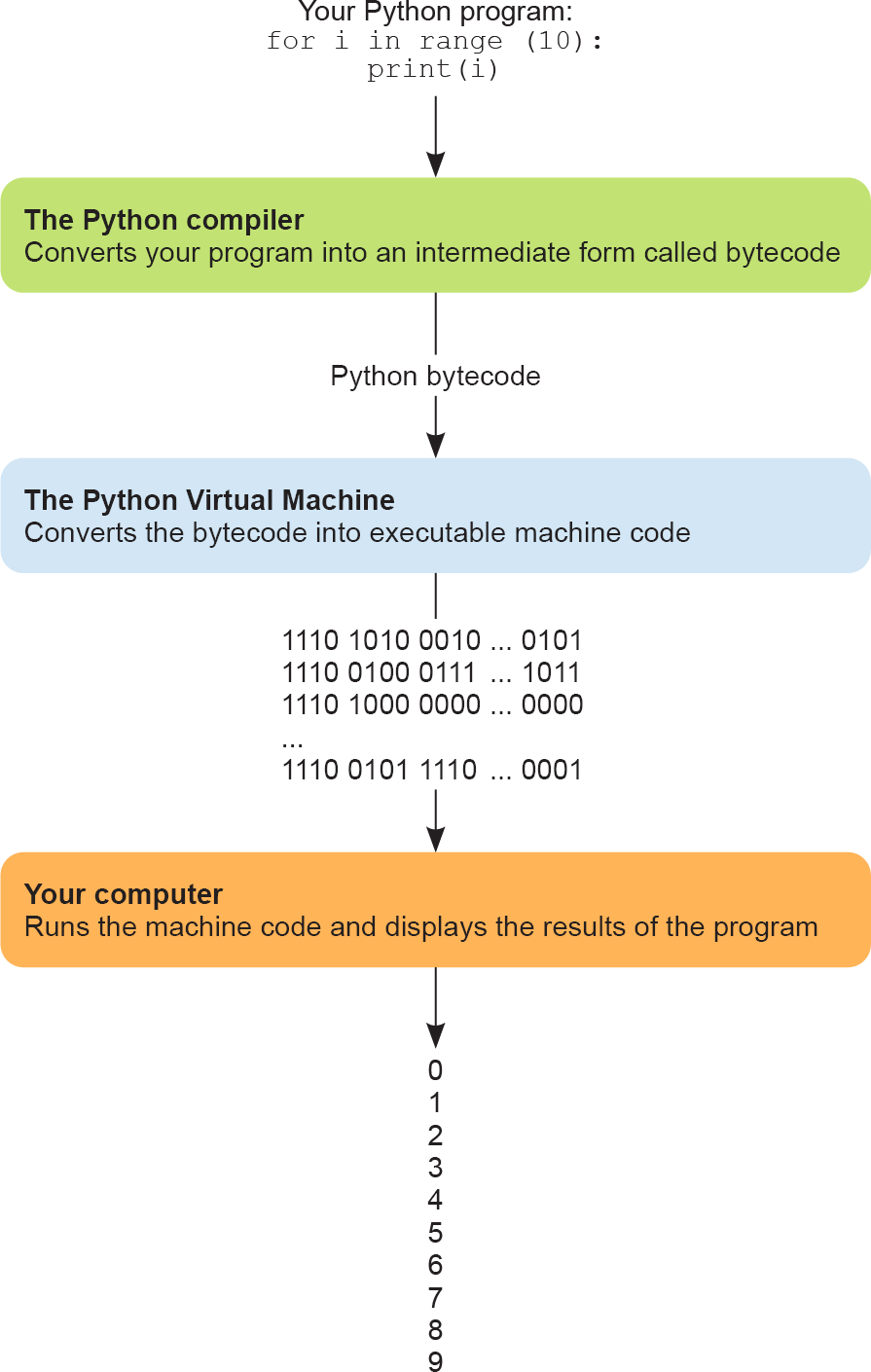
Computers don’t actually know how to read and run Python code. The only thing computers can understand is something called machine code, which looks even more ridiculous than assembly code, because it is the binary representation of the assembly code (yep, just a bunch of 0s and 1s!). Behind the scenes, your computer takes any Python code that you provide and converts it into machine code before it runs, as shown in figure 1.1.
实际上,计算机并不能直接读取或执行 Python 代码。它们唯一能够理解的是所谓的 “机器码”,这种代码比汇编语言还要难以理解,因为它是汇编语言的二进制形式——没错,就是一连串的 0 和 1!在幕后,你的计算机将接收你所提供的任何 Python 代码,并在执行之前把它转换成机器码,正如图 1.1 所展示的那样。
Figure 1.1 Your Python program goes through several steps before you see the output on your screen.
图 1.1 在屏幕上看到输出之前,Python 程序需要经历的几个步骤
1.2.1 Copilot, your AI Assistant
1.2.1 Copilot,你的 AI 助手
What is an AI assistant? An AI assistant is an artificial intelligence (AI) agent that helps you get work done. Maybe you have an Amazon Alexa device at home, or an iPhone with Siri—these are AI assistants. They help you order groceries, learn the weather, or determine that, yes, the woman who played Bellatrix in the Harry Potter movies really was in Fight Club. An AI assistant is just a computer program that responds to normal human inputs like speech and text with human-like answers.
什么是 AI 助手?AI 助手是一种人工智能代理(AI agent),它帮助你完成任务。你可能在家里使用亚马逊的 Alexa 设备,或拥有一部集成了 Siri 的 iPhone——这些都属于 AI 助手。这类助手能帮你订购生鲜、查询天气,或是确认那位在《哈利·波特》电影中饰演贝拉特里克斯的女演员是否也参演了《搏击俱乐部》。AI 助手只不过是一个响应人类语音和文本输入的计算机程序,并以类人的方式给出答案。
Copilot is an AI assistant with a specific job: it converts English into computer programs. (It can also do a whole lot more, as we will soon see.) There are other AI assistants like Copilot, including CodeWhisperer, Tabnine, and Ghostwriter. We chose Copilot for this book by a combination of the quality of code that we have been able to produce, stability (it has never crashed for us!), and our own personal preferences. We encourage you to also check out other tools when you feel comfortable doing so.
Copilot 是一款能执行特定任务的 AI 助手:它能将英语转换成程序代码(我们很快就会看到,它还能做更多的事情)。与 Copilot 功能类似的 AI 助手还有不少,比如 CodeWhisperer、Tabnine 和 Ghostwriter 等。我们选择 Copilot 作为本书的主角,是基于它生成代码的质量、稳定性(它从未发生过崩溃!)以及我们个人的偏好。我们也鼓励你在合适的时候探索其他工具。
1.2.2 How Copilot works behind the scenes—in 30 seconds
1.2.2 一分钟搞懂 Copilot 的幕后原理
You can think of Copilot as a layer between you and the computer program you’re writing. Instead of writing the Python directly, you simply describe the program you want in words—this is called a prompt—and Copilot generates the program for you.
你可以把 Copilot 想象成你和你正在编写的程序之间的一个中介层。你不必直接编写 Python 代码,只需用文字描述你想要的程序功能(这些文字称作 “提示词”),Copilot 便能生成相应的程序代码。
The brains behind Copilot is a fancy computer program called a large language model, or LLM. An LLM stores information about relationships between words, including which words make sense in certain contexts, and uses this to predict the best sequence of words to respond to a prompt.
Copilot 的智能引擎是一种精妙的计算机程序,名为 “大型语言模型”(Large Language Model,LLM)。这种模型掌握了单词与单词之间的内在联系,识别特定语境中最合适的词汇搭配,并基于这些信息预测出一段提示词后面最匹配的单词顺序是什么。
Imagine that we asked you what the next word should be in this sentence: “The person opened the ________.” There are many words that you could fill in here, like “door” or “box” or “conversation,” but there are also many words that would not fit here, like “the” or “it” or “open.” An LLM takes into account the current context of words to produce the next word, and it keeps doing this until it has completed the task.
想像一下,我们请你预测这个句子中的下一个单词可能是什么:“The person opened the ________.” 你可以想到很多选择,比如 “door”、“box” 或 “conversation” 等等;但有些单词比如 “the”、“it” 或 “open” 则显然不合适。LLM 会综合考虑当前上下文来生成下一个合适的单词,并且会持续不断地进行这一过程,直至任务完成。
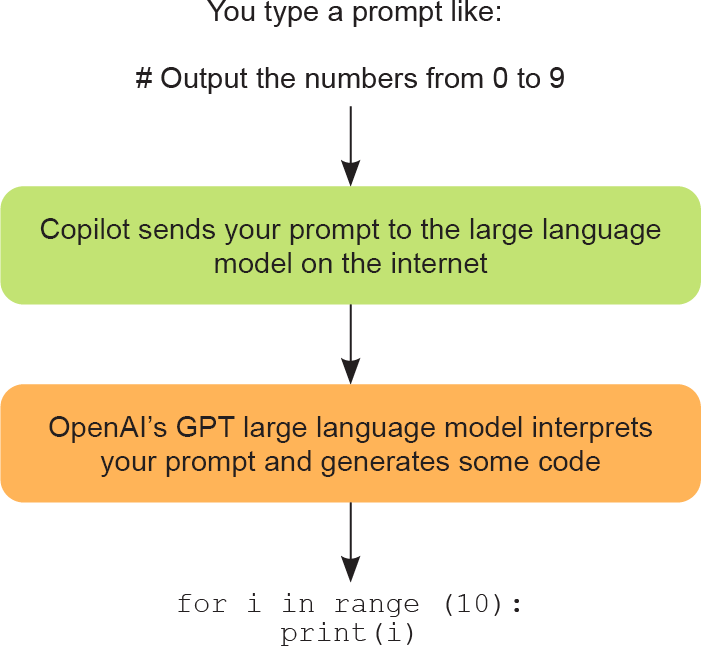
Notice that we didn’t say anything about Copilot having an understanding of what it is doing. It just uses the current context to keep writing code. Keep this in mind throughout your journey: only we know whether the code that’s generated does what we intended it to do. Very often it does, but you should always exercise healthy skepticism regardless. Figure 1.2 gives you an idea of how Copilot goes from prompt to program.
请注意,我们并没有说 Copilot 明白它正在做的事情。它仅仅是依靠当前的上下文来持续生成代码。在你今后的编程之路上,要始终铭记:只有我们能判断生成的代码是否真正实现了我们的意图。虽然大多数情况下它能够做到,但你仍然应该时刻保持适度的怀疑精神。图 1.2 为你描绘了 Copilot 如何根据一段提示词生成一段完整的程序。
Figure 1.2 Going from prompt to program with Copilot
图 1.2 Copilot 由提示词生成程序的过程
You might wonder why Copilot writes Python code for us and not machine code directly. Isn’t Python an expendable intermediate step now? Well, no, and the reason is that Copilot is going to make mistakes. And if it’s going to make mistakes that we need to fix, it’s a lot easier to do that with Python than with machine code.
你或许会好奇,为什么 Copilot 为我们编写的是 Python 代码,而不是直接生成机器码。Python 不就是一个可有可无的中间环节吗?其实不然,我们让 Copilot 编写 Python 代码的原因在于它可能会出错。一旦它出错,我们就需要对这些错误进行修正,那么相比于机器码,处理 Python 代码无疑要简单得多。
In fact, virtually no one checks if the machine code produced from Python is correct. This is partially because of the determinism of the Python language specification. One could imagine a future where Copilot conversations are so accurate that inspecting the Python is unnecessary, but we’re a long way from that.
而另一方面,几乎没有必要检查由 Python 转换而成的机器码是否准确。这在一定程度上归功于 Python 语言规范的确定性。我们可以畅想,或许未来 Copilot 已经精准到无须检查它生成的 Python 代码,但目前我们距离这一目标还有很长的路要走。