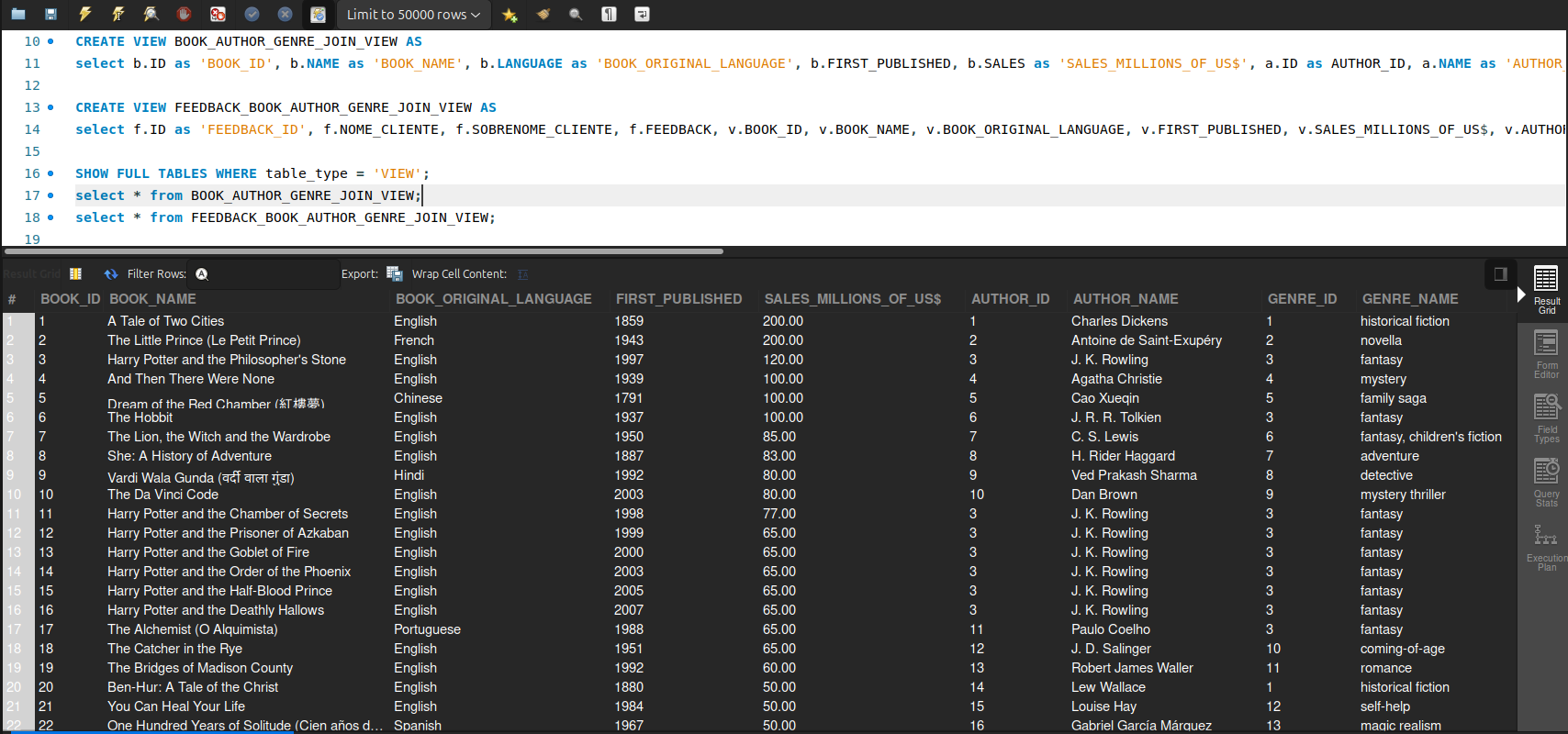
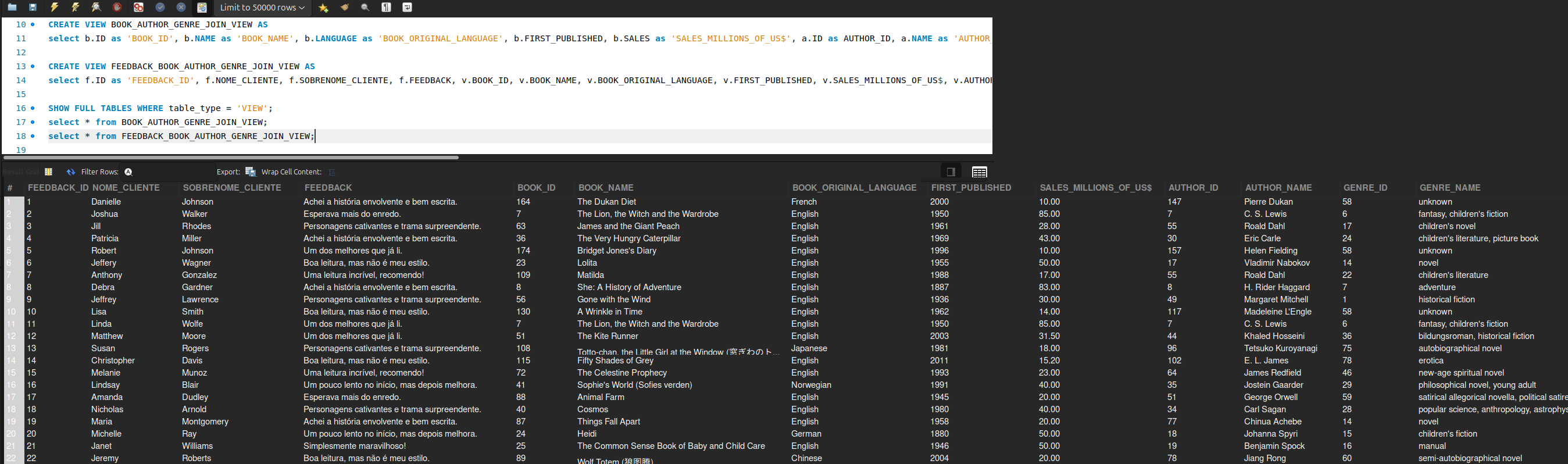
This is a sample app that exemplifies how to access a MySQL DB data set and manipulate its data by using Python and Pandas along with Anaconda managed environments.
© 2025 Daniel Pinheiro Maia All Rights Reserved
(see Copyright© License at the end of this text).
[Description of this repository]
This is a sample app that exemplifies how to access a MySQL DB data set and manipulate its data by using Python and Pandas along with Anaconda managed environments. At this project, different data sources (local .csv and remote .json) are integrated to generate .sql files and then these scripts are executed at MySQL Workbench to populate a pre-created DB schema compatible with that data. Later on, it is shown how to use Connector/Python driver from inside the .ipynb file to access and manipulate the DB directly (without using MySQL Workbench for that). Jupyter Lab as MySQL Workbench work here as clients to the DBMS running at a Docker container, being their scripts the python code itself (inside the .ipynb) and the .sql file, respectively.
[Content and Run]
Source code available at github.com, through the following link:
https://github.com/danielpm1982/sample-mysql-python-pandas-data-engineering
The source code includes the Jupyter Notebook .ipynb file itself, as well as the environment.yml file, which can be used to generate an Anaconda environment for running this project locally (don't forget to customize the env paths to your own filesystem and OS when creating the environment).
You can also run this Jupiter Notebook project remotely at https://colab.research.google.com/notebook, importing the content directly from this github repository to your Colab account, without having to create any Anaconda environment locally.
Regarding the database, in order that Python can manipulate it, you should have a MySQL server instance running (either at your host OS or at a Docker container), with an active connection available. You may also use MySQL Workbench as a test suite client to the MySQL DBMS server, in case you wanna access the DBMS server from it, in addition to accessing the same DBMS server from Python scripts themselves (.ipynb files). You can either create the DB schema for this project from the scratch, by executing the schema.sql DDL script (from MySQL Workbench, for instance), and later populating it with the population .sql files generated from the python scripts (.ipynb), or you can copy this project's DB data folder (with the DB schema already created and populated), to the specific MySQL storage folder at your host file system, where MySQL DB data is stored. The default path for this MySQL data storage folder depends on the host OS type. On Linux, it is /var/lib/mysql/ ; on MacOS, it is /usr/local/mysql/data/ ; and on Windows, it is C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server{version}\Data. These default data storage directories can be customized at the MySQL configuration file - my.cnf or my.ini - if this config file is optionally created at one of the following default paths: /etc/my.cnf or /etc/mysql/my.cnf or ~/.my.cnf (on Linux). You can read more about it at MySQL documentation. Otherwise, in case you're running MySQL from inside a Docker container - as I always do, instead of from your host OS, you can simply map this projects' DB data folder - mysql (host side) - to the default DB data storage folder path inside the MySQL container - /var/lib/mysql (container side). This way, any existing DB data will be synchronized between these two DB Data folders, and the data will be turned available to the running MySQL services inside the container. If you ever need to change the mysql DB data ownership or access permissions to your own OS user and/or group, because of eventual access issues to this DB data folder - mysql (host side), you can do that by applying chown and chmod commands (on Linux) iteratively (-R) to the root path of this project. More on that at my detailed tutorial: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1KMBPmXU5vI_1uWlxQ3wHjqniV6He7OhV .
[Printscreen samples]
[Support]
If you have any suggestion or correction about the content of this repository, please, feel free to open an issue at the project issues' section:
https://github.com/danielpm1982/sample-mysql-python-pandas-data-engineering/issues
[Copyright© License]
© 2025 Daniel Pinheiro Maia All Rights Reserved
This GitHub repository - and all code (software) available inside - is exclusively for academic and individual learning purposes, and is NOT AVAILABLE FOR COMMERCIAL USE, nor has warranty of any type. You're authorized to fork, clone, run, test, modify, branch and merge it, at your own risk and using your own GitHub account, for individual learning purposes only, but you're NOT ALLOWED to distribute, sublicense and/or sell copies of the whole or of parts of it without explicit and written consent from its owner / author. You can fork this repository to your individual account at GitHub, clone it to your personal notebook or PC, analyse, run and test its code, modify and extend it locally or remotely (exclusively at your own GitHub account and as a forked repository), as well as send issues or pull-requests to this parent (original) repository for eventual approval. GitHub is in charge of explicitly showing whom this respository has been forked from. If you wish to use any of this repository content in any way other than what is expressed above, or publish it anyway or anywhere other than as a forked repository at your own GitHub account, please contact this repository owner / author using GitHub or the contact info below. For the meaning of the technical terms used at this license, please refer to GitHub documentation, at https://help.github.com/en/github .
[Owner and Author of this GitHub Repository]
Daniel Pinheiro Maia
danielpm1982.com
danielpm1982@gmail.com
linkedin.com/in/danielpm1982
Brazil
.