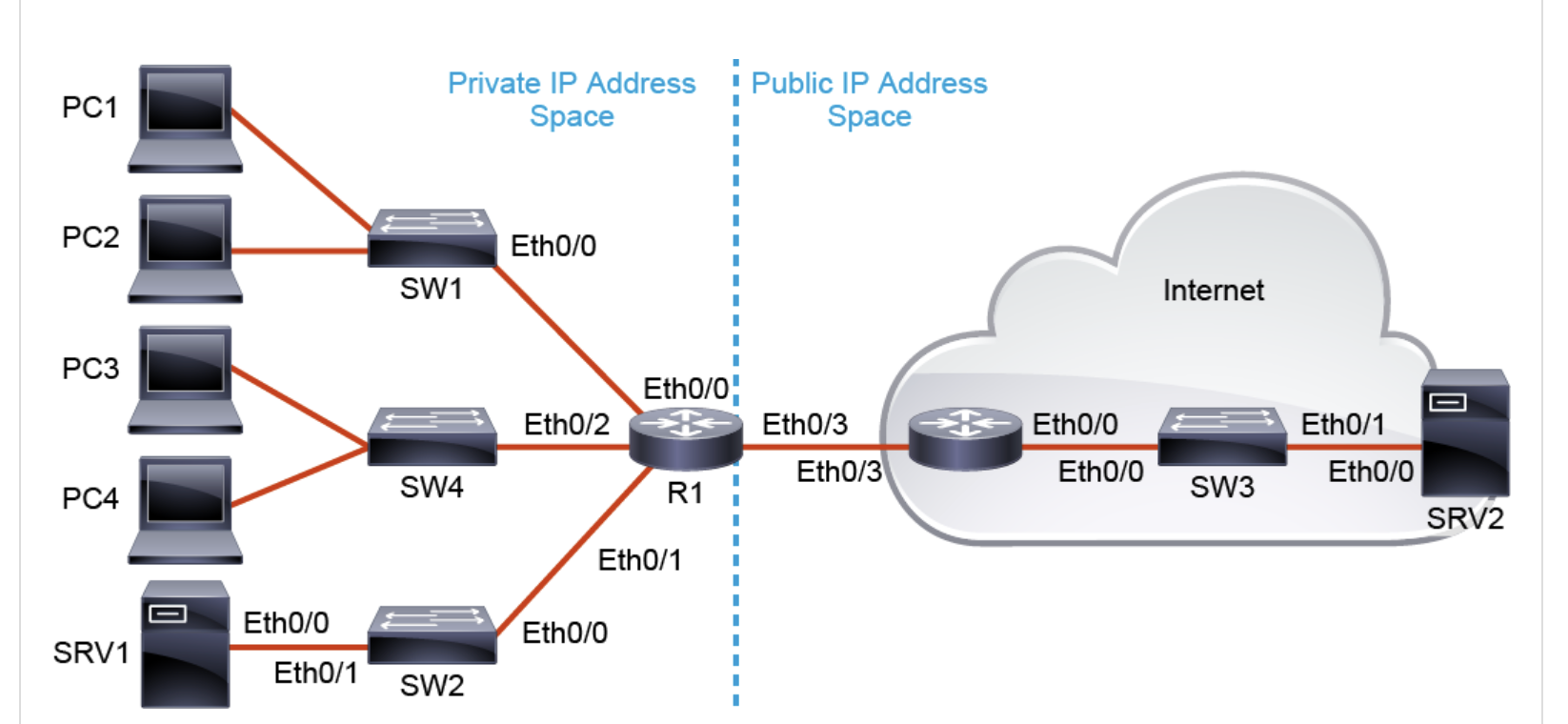
Configuring static NAT is a simple process. You have to define inside and outside interfaces using ip nat inside and ip nat outside interface configuration commands and specify which inside address should be translated to which outside address using the ip nat inside source static inside_address outside_address global configuration command.
Configure R1 interfaces for static NAT. Ethernet0/1 is on the inside, and Ethernet0/3 is on the outside.
R1(config)#int e0/1
R1(config-if)#ip nat inside
R1(config-if)#exit
R1(config)#int e0/3
R1(config-if)#ip nat outside
R1(config-if)#exit
Add a static NAT configuration entry that translates the SRV1 IP address private ip (10.10.2.20) to public ip 198.51.100.20, then leave configuration mode.
R1(config)#ip nat inside source static 10.10.2.20 198.51.100.20
verify configuratiion
R1#show ip nat translations
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
--- 198.51.100.20 10.10.2.20 --- ---
Dynamic NAT configuration differs from static NAT, but it also has some similarities. Like static NAT, it requires the configuration to identify each interface as an inside or outside interface. However, rather than creating a static map to a single IP address, a pool of inside global addresses is used, and an ACL that identifies which inside local addresses are to be translated. The ACL-to-NAT pool mapping is defined by the ip nat inside source list acl pool pool_name global configuration command.
On R1, define a pool of inside global addresses(public ip) named "NatPool" by specifying the address range from 198.51.100.100 to 198.51.100.149.
R1(config)#ip nat pool NatPool 198.51.100.100 198.51.100.149 netmask 255.255.255.0
Configure access list number 10 to identify addresses within the 10.10.1.0/24 subnet as addresses eligible to be translated.
R1(config)#access-list 10 permit 10.10.1.0 0.0.0.255
Define a dynamic translation rule that specifies access list 10 as the source and that uses addresses from the pool NatPool.
R1(config)#ip nat inside source list 10 pool NatPool
Configure the R1 Ethernet0/0 interface as a NAT inside interface.
R1(config)#interface ethernet 0/0
R1(config-if)#ip nat inside
Configure the interface as the outside NAT interface.
R1(config-if)# ip nat outside
verify the configuration
do show ip nat statistics
To configure PAT, identify the inside and outside interfaces by using the ip nat inside and ip nat outside interface configuration commands, respectively. An ACL must be configured that will match all inside local addresses that need to be translated, and NAT will need to be configured so that all inside local addresses are translated to the address of the outside interface. This solution is achieved by using the ip nat inside source list acl interface interface overload global configuration command.
Configure the access-list number 20 to identify addresses within the 10.10.3.0/24 subnet as addresses eligible to be translated.
R1(config)#access-list 20 permit 10.10.3.0 0.0.0.255
Add a NAT statement that enables PAT by translating the addresses that are permitted by access list 20 into the IP address that is assigned to the interface Ethernet0/3.
R1(config)#ip nat inside source list 20 interface e0/3 overload
Configure the R1 Ethernet0/2 interface as a NAT inside interface.
R1(config)#int e0/2
R1(config-if)#ip nat inside
Configure the interface as the outside NAT interface.
R1(config-if)# ip nat outside
verify the configuration
R1# show ip nat translation