-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code, or VS Code, as it is often called, is a relatively new lightweight editor that provides tooling support for HTML, CSS, Javascript, TypeScript, Python, and many more programming languages. Some of these languages are supported by default, and others, via plugin (or extension) installation.
VS Code can be installed easily on any platform--Windows, Mac OS X, or LINUX by downloading the appropriate binaries from the VS Code download page.
After downloading the binaries, follow the Setting up Visual Studio Code instructions for your platform posted on the VS Code website.
As part of the setup instructions, it is important that you configure your installation to allow you to run the command code . in a terminal or at the command prompt. This will add code to your PATH environment variable list. Instructions for doing so are also available as part of the Setting up Visual Studio Code instructions. Here's a quick overview of those instructions:
-
Launch VS Code.
-
Open the VS Code Command Palette by typing the fallowing key combinations from your keyboard.
a. Command + Shift + P (if you are using a Mac) b. Control + Shift + P (on Windows or LINUX) -
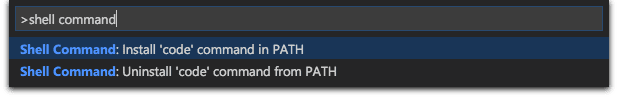
Type
shell commandin the Command Palette to find the Shell Command: Install 'code' command in PATH command. You should see something that looks like this. -
Execute that command, then open a terminal or command prompt so that the new
PATHvariable can take effect. -
From the terminal or command prompt, navigate to a folder of your choice and enter the command
code ., then press ENTER to fire-up VS Code from that folder and begin editing files in that location.
Be sure you have Python 3.4 installed on your machine. If not, download and install it on your machine, using the default options. You can verify that Python is added to your PATH environment variable by typing py -3.4 (in Windows) OR python3 (on OS X or LINUX) at a terminal or command prompt. That should print some information to the console including the version of Python and a prompt to an interactive shell from which you can enter Python code.
If you do not see this information, you need to add Python to your PATH environment variable.
- This entails determining where Python is installed on your machine. If you do not know to do this, you can run a python script with the code below and it will print the information that you need.
import sys
print(sys.executable)
print(sys.exec_prefix)- In Windows you can follow these instructions to add the Python installation directory to your system
PATH. You can instead opt for usingpy -3.4OR justpyif 3.4 is your only installed version of Python. You should not need to update your path in OS X or LINUX.
VS Code provides some rudimentary support for Python. However, to maximize your Python productivity you should install Don Jayamanne’s Python extension. This will give you access to features like Python-aware Intellisense, auto-completion, hover tooltips to view function and method signatures, linting, code formatting, snippets, and more.
- You install the extension by launching VS Code, opening up the Command Palette (Command + Shift + P OR Control + Shift + P) and entering
ext installin the palette and press ENTER. Typepythonto see a list of Python extensions. Be sure to choose the right one.
- Next, you configure the full path to your Python interpreter. It should be noted that this step is optional. You have the option to do so at the user level or at the workspace level. See Doug's World for more detailed information regarding this. To configure the python path at the user level, open up the Command Palette, and enter User Settings. A user setting file that overwrites the default one will open. enter
{
"python.pythonPath": "/usr/local/bin/python3"
}in that file and save it. Be sure to replace /usr/local/bin/python3 with the actual path to your Python executable. You now have access to all the Intellisense, auto-completion, and other features noted above.
You can configure a build task to run the currently opened Python program in your local workspace (local copy of the code that you will be developing and running) when you press Control + Shift + B OR Command + Shift + B in VS Code.
To configure a task in VS Code, press Control + Shift + P OR Command + Shift + P to get to the Command Palette, then type configure task, and press ENTER. This will open a tasks.json file in the .vscode subfolder of your local workspace. You replace the contents of tasks.json with this snippet to make Control + Shift + B OR Command + Shift + B run the Python program you’re currently editing.
{
"version": "0.1.0",
"command": "python", // or "python3" if that's the name of your executable
"isShellCommand": true,
"args": ["${file}"],
"showOutput": "always"
}If the above does not work in Windows, use the the following instead.
{
"version": "0.1.0",
"command": "py",
"isShellCommand": true,
"args": ["-3.4", "${file}"],
"showOutput": "always"
}Visual Studio Code is a lightweight, cross-platform editor from Microsoft that is in the same family as Atom, Brackets, Sublime, etc. It provides basic support for Python programming, but it lacks a built-in way to execute a Python program. However, this is easily solved by installing the right extension and creating a custom build task.