Matrix createMat(int _rows, int _cols);
- parameter
- int rows : rows of Matrix
- int cols : rows of Matrix
Example code
Matrix A = createMat(2, 3);
Matrix A = createMat(5, 5);void printMat(Matrix _A, const char* _name)
- parameter
- _A : printed Matrix
- _name : title
Example code
printMat(matA, "matA");
printMat(matB, "matB");Matrix mulScalar(Matrix _A, double B)
- parameter
- _A : subject Matrix A
- _B : scalar number
Example code
Matrix X = mulScalar(matA, 2);
Matrix X = mulScalar(matB, 5);Matrix mulMat(Matrix _A, Matrix _B);
- parameter
- A : first Matrix
- B : second Matrix
Example code
mulMat(matA, matB);void initMat(Matrix _A, double _val);
- parameter
- A : subject Matrix
- B : initial value
Example code
initMat(matA, 1);Matrix zeros(int _rows, int _cols);
- parameter
- _rows : rows of Matrix
- _cols : columns of Matrix
Example code
Matrix X = zeros(3, 4);create Matrix of all zeros
Matrix ones(int _rows, int _cols);
- parameter
- _rows : rows of Matrix
- _cols : columns of Matrix
Example code
Matrix X = ones(3, 3);Matrix transpose(Matrix _A);
- parameter
- A : subject Matrix
Example code
transpose(matA);Matrix copyMat(Matrix _A);
- parameter
- A : subject Matrix
Example code
matB = copyMat(matA);void copyVal(Matrix _A, Matrix _B);
- parameter
- _A : subject Matrix
- _B : replicated Matrix
Example code
copyVal(matA, matB);These functions are useful tools for making any function in Numerical Programming Class
#include "myNP.h"- select a, b
- if f(a)*f(b) appear negative sign, there is a value
- it selects (a+b)/2, a | if f((a+b)/2)*f(a)< 0 : b =x;
double bisection(double fn(double _x), double _a, double _b, double _tau)- fn : function
- a : initial value 1
- b : initial value 2
- tau : error value
double init_1 = -3;
double init_2 = 5;
double tau = 0.00001;
BS_result = bisection(function, init_1, init_2, tau);- select a
- it finds roots as x-intercept of the straight line tangent to the curve at a
double newtonRaphson(double fn(double x), double dfn(double x), double _x0, double _tol)- fn : function
- dfn : differential function
- x0 : initial value
- tol : tolerance error
float tol = 0.00001;
double NR_result;
double x0 = 1;
NR_result = newtonRaphson(fn, dfn, x0, tol);double secant(double function(double _x), double _x0, double _x1, double _tau)- function : function
- x0 : initial value 1
- x1 : initial value 2
- tau : error value
float tau = 0.00001;
double SC_result;
double x0 = 1;
double x1 = 3;
SC_result = secant(fn, x0, x1, tau);Matrix newtonRoots(Matrix X0, Matrix myJacob(Matrix X), Matrix myFunc(Matrix X), float tol)- X0 : initial value Matrix
- myJacob : Jacobian Matrix
- myFunc : Function Matrix
- tol : tolerance error
Matrix X= zeros(2, 1);
X.at[0][0] = 2.5;
X.at[1][0] = 2;
float tol = 1e-9;
newtonRoots(X, myJacob, myFunc, tol);Differential operation based on data array
void gradient1D(double x[], double y[], double dydx[], int m) - x[] : x data
- y[] : y data
- dydx[] : differential coefficient array to return
- m : array
int m = 21;
double t[21] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) t[i] = 0.2 * i;
double x[] = { -5.87, -4.23, -2.55, -0.89, 0.67, 2.09, 3.31, 4.31, 5.06, 5.55, 5.78, 5.77, 5.52, 5.08, 4.46, 3.72, 2.88, 2.00, 1.10, 0.23, -0.59 };
double dxdt[21] = { 0 };
gradient1D(t, x, dxdt, m); //m : 데이터 갯수 dxdt : 업데이트할 변수
printVec(dxdt, m);Differential operation based on function
void gradientFunc(double func(const double x), double x[], double dydx[], int m)- func : function
- x[] : x data
- dydx[] : differential coefficient array to return
- m : array size
double xin = -5.87;
double y = myFunc(xin);
double dydx[21];
gradientFunc(myFunc, t, dydx, m);
printVec(dydx, m);double Derivative operation based on function
void acceleration(double x[], double y[], double d2ydx2[], int m)- x[] : x data
- y[] : y data
- dy2dx2[] : double derivative coefficient array to return
- m : array size
int m = 21;
double t[21] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) t[i] = 0.2 * i;
double x[] = { -5.87, -4.23, -2.55, -0.89, 0.67, 2.09, 3.31, 4.31, 5.06, 5.55, 5.78, 5.77, 5.52, 5.08, 4.46, 3.72, 2.88, 2.00, 1.10, 0.23, -0.59 };
double dx2dt2[21] = { 0 };
acceleration(t, x, dx2dt2, m);
printVec(dx2dt2, m);Integration using Rectangular method for discrete data inputs
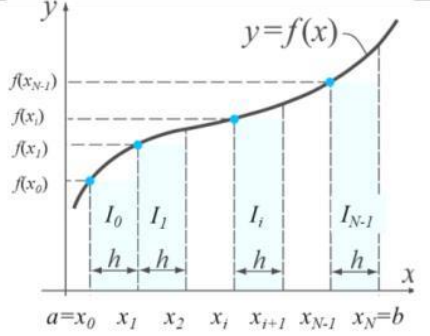
double IntegrateRect(double x[], double y[], int m)- x[] : x data
- y[] : y data
- m : array size
double x[] = { 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60 };
double y[] = { 0, 3, 8, 20, 33, 42, 40, 48, 60, 12, 8, 4, 3 };
int M = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]);
double I_rect = IntegrateRect(x, y, M);
printf("I_rect = %f\n\n", I_rect);Integration using Trapezoidal method for discrete data inputs
double trapz(double x[], double y[], int m)- x[] : x data
- y[] : y data
- m : array size
double x[] = { 0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60 };
double y[] = { 0, 3, 8, 20, 33, 42, 40, 48, 60, 12, 8, 4, 3 };
int M = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]);
double I_trapz = trapz(x, y, M);
printf("I_trapz = %f\n\n", I_trapz);Integration using Simpson 1/3 method for discrete data inputs
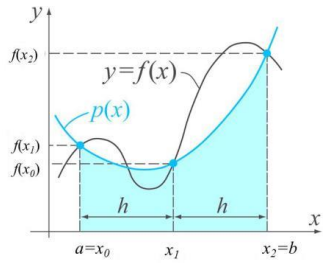
double simpson13(double x[], double y[], int m) {- x[] : x data
- y[] : y data
- m : array size
double x[] = { -3, -2.25, -1.5, -0.75, 0, 0.75, 1.5, 2.25, 3 };
double y[] = { 0, 2.1875, 3.75, 4.6875, 5, 4.6875, 3.75, 2.1875, 0 };
int M = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]);
double I_simpson = simpson13(x, y, M);
printf("I_simpson13 = %f\n\n", I_simpson);Integration using Simpson 3/8 method for discrete data inputs
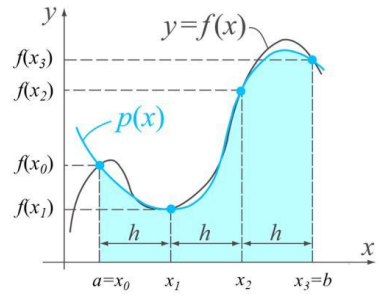
double simpson38(double x[], double y[], int m) {- x[] : x data
- y[] : y data
- m : array size
double x[] = { -3, -2.25, -1.5, -0.75, 0, 0.75, 1.5, 2.25, 3 };
double y[] = { 0, 2.1875, 3.75, 4.6875, 5, 4.6875, 3.75, 2.1875, 0 };
int M = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]);
double I_simpson = simpson38(x, y, M);
printf("I_simpson38 = %f\n\n", I_simpson);Integration using Simpson 1/3 method for function inputs
double integral(double func(const double _x), double a, double b, int n)- func : function
- a : initial value 1
- b : initial value 2
- n : array size
int a = -1;
int b = 1;
int n = 12;
double Integrals = integral(myFunc, a, b, n);
printf("func_simpson13 = %f\n\n", Integrals);solves for vector x from Ax=b, a linear system problem Using Gauss Elimination
gaussElim(Matrix A, Matrix vecb, Matrix U, Matrix d, Matrix P)- A : Matrix A in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
- vecb : vector vecb in structure Matrix form. Should be (nx1)
- U : Matrix U in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
- d : vector d in structure Matrix form. Should be (nx1)
- P : Partial Pivoting P in structrue Matrix form. Should be (nxn)
Matirx A and vecb data is already filled in notepad
Matrix matA = txt2Mat(path, "prob1_matA");
Matrix vecb = txt2Mat(path, "prob1_vecb");
Matrix matU = copyMat(Q1_matA);
Matrix d = zeros(vecb.rows, 1);
Matrix P = eye(matA.rows, matA.cols);
gaussElim(A, vecb, U, d, P);factors a matrix as the product of a lower triangular matrix and upper triangular matrix
void LUdecomp(Matrix A, Matrix L, Matrix U, Matrix P)- A : Matrix A in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
- L : Matrix U in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
- U : Matrix U in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
- P : Partial Pivoting P in structrue Matrix form. Should be (nxn)
Matirx A and vecb data is already filled in notepad
Matrix matA = txt2Mat(path, "prob1_matA");
Matrix vecb = txt2Mat(path, "prob1_vecb");
Matrix matU = copyMat(Q1_matA);
Matrix matL = createMat(Q1_matA.rows, Q1_matA.cols);
Matrix P = eye(matA.rows, matA.cols);
LUdecomp(matA, matL, matU, P);find y using forward substitution
void fwdsub(Matrix L, Matrix b, Matrix y)- b : vector b in structure Matrix form. Should be (nx1)
- y : vector y in structure Matrix form. Should be (nx1)
- L : Matrix L in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
exsit LUdecomp before
fwdsub(L, vecb, y);find x using back substitution
void backsub(Matrix U, Matrix y, Matrix x)- x : vector x in structure Matrix form. Should be (nx1)
- y : vector y in structure Matrix form. Should be (nx1)
- U : Matrix U in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
exsit LUdecomp before
backsub(matU, y, x);find x forward substitution, backward substitution
void solveLU(Matrix L, Matrix U, Matrix P, Matrix b, Matrix x)- L : Matrix U in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
- U : Matrix U in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
- P : Partial Pivoting P in structrue Matrix form. Should be (nxn)
- b : vector b in structure Matrix form. Should be (nx1)
- x : vector x in structure Matrix form. Should be (nx1)
exsit LUdecomp before
Matrix matL = createMat(matA.rows, matA.cols);
Matrix matU = copyMat(matA);
Matrix P = eye(Q1_matA.rows, Q1_matA.cols);
Matrix vecb = txt2Mat(path, "prob1_vecb");
Matrix x = zeros(vecb.rows, 1);
void solveLU(matL, matU, P, vecb, x);inverse Matrix
double invMat(Matrix A, Matrix Ainv)- A : Matrix A in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
- Ainv : Matrix Ainv in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
invMat using LUdecomp, forward substitution, backward substitution
Matrix matA = txt2Mat(path, "prob1_matA");
Matrix matAinv = copyMat(matA);
invMat(matA, matAinv);QR factorization
void QRHousehold(Matrix A, Matrix Q, Matrix R)- A : Matrix A in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
- Q : Matrix Q in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
- R : Matrix R in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
Matrix matA = txt2Mat(path, "prob_matA");
Matrix matQ = copyMat(matA);
Matrix matR = copyMat(matA);
QRHousehold(matA, matQ, matR);eigenvalue
Matrix eig(Matrix A)- A : Matrix A in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
apply QRHousehold internal
Matrix matA = txt2Mat(path, "prob_matA");
eigenvalue = eig(matA);eigenvector
Matrix eigvec(Matrix A)- A : Matrix A in structure Matrix form. Should be (nxn) square
apply invMat internal
Matrix matA = txt2Mat(path, "prob_matA");
eigenvector = eigvec(matA);solve ordinary differential equation using Euler explicit method ordinary
void odeEU(double myfunc(const double t, const double y), double y[], double t0, double tf, double h, double y0)solve ordinary differential equation using Euler Modified method ordinary
void odeEM(double myfunc(const double t, const double y), double y[], double t0, double tf, double h, double y0)solve ordinary differential equation using Runge-Kutta second method ordinary
void odeRK2(double myfunc(const double t, const double y), double y[], double t0, double tf, double h, double y0)solve ordinary differential equation using Runge-Kutta third method ordinary
void odeRK3(double myfunc(const double t, const double y), double y[], double t0, double tf, double h, double y0)- myfunc : function with t, y
- y[] : allocated array y
- t0 : initial time value
- tf : final time value
- h : interval value
- y0 : initial y value
double t0 = 0; double tf = 0.1;
double h = 0.001;
double N = (tf - t0) / h + 1;
double t = 0;
double* y = (double*)malloc(sizeof(double) * N);
double y0 = 0;
/*double myfunc(const double t, const double y)
{
int i = 0;
double tau = 1;
double T = 1 / tau;
double f = 10;
double Vm = 1;
double w = 2 * PI * f * t;
double funcx = -T * y + 1 * Vm * cos(w);
return funcx;
}*/
odeEU(myfunc, y, t0, tf, h, y0);
odeEM(myfunc, y, t0, tf, h, y0);
odeRK2(myfunc, y, t0, tf, h, y0);
odeRK3(myfunc, y, t0, tf, h, y0);solve secondary differential equation using Runge-Kutta second method ordinary
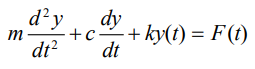
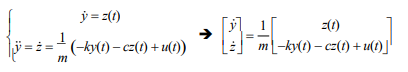
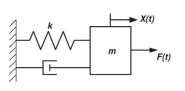
void sys2RK2(void mckfunc(const double t, const double Y[], double dYdt[]), double y1[], double y2[], double t0, double tf, double h, double y1_init, double y2_init)- mckfunc : function with t, y, dydt
- y1[] : y, ex) y[0] = y, y[1] = dy/dt
- y2[] : z, ex) z[0] = dy/dt, z[1] = d2y/dt2
- t0 : initial time value
- tf : final time value
- h : interval value
- y1 : initial y value
- y2 : initial dy/dt value
double t0 = 0; double tf = 1;
double h = 0.01;
double N = (tf - t0) / h + 1;
double t = 0;
double* y1 = (double*)malloc(sizeof(double) * N); //y함수
double* y2 = (double*)malloc(sizeof(double) * N); //z함수
double y1_init = 0;
double y2_init = 0.2;
/*
void mckfunc(const double t, const double Y[], double dYdt[])
{
double m = 1; double c = 7; double k = 6.9; double f = 5;
double Fin = 2 * cos(2 * PI * f * t);
dYdt[0] = Y[1]; //1번째 풀어야 할 미방식
// EXERCISE: MODIFY HERE
dYdt[1] = -Y[1] * c / m - Y[0] * k / m + Fin / m; //z값
}
*/
sys2RK2(mckfunc, y1, y2, t0, tf, h, y1_init, y2_init);straight line that fits the data
Matrix linearRegression(Matrix _x, Matrix _y)- x : x data array Matrix. should be (nx1)
- y : y data array Matrix. should be (nx1)
int M = 6; //number of data
double T_array[] = { 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80 };
double P_array[] = { 1.05, 1.07, 1.09, 1.14, 1.17, 1.21 };
Matrix T = arr2Mat(T_array, M, 1);
Matrix P = arr2Mat(P_array, M, 1);
Matrix z = linearRegression(T, P);
double answer = z.at[0][0] * 100 + z.at[1][0]; //particular y-point at x-point
printMat(T, "T");
printMat(P, "P");
printMat(z, "z");
printf("answer = %lf \n", answer);curve that fits the data
void polyfit(Matrix _x, Matrix _y, Matrix _z, int n)- x : x data array Matrix. should be (nx1)
- y : y data array Matrix. should be (nx1)
- z : coefficient Matrix. should be ((n+1)x1)
- n : curve function order
int n = 4; // curve function order
double strain[] = { 0, 0.4, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, 2.0, 2.4, 2.8, 3.2, 3.6, 4.0, 4.4, 4.8, 5.2, 5.6, 6.0 };
double stress[] = {0, 3, 4.5, 5.8, 5.9, 5.8, 6.2, 7.4, 9.6, 15.6, 20.7, 26.7, 31.1, 35.6, 39.3, 41.5};
Matrix Strain = arr2Mat(strain, N, 1);
Matrix Stress = arr2Mat(stress, N, 1);
Matrix a = zeros(n+1, 1); //function coefficient
polyfit(Strain, Stress, a, n);
printMat(a, "a");