The follwing files are my first foray into CircuitPython.
Description goes here
Here's how you make code look like code:
import board
import neopixel
dot = neopixel.NeoPixel(board.NEOPIXEL, 1)
dot.brightness = 0.1
print("Make it Cyan!")
while True:
dot.fill((0, 255, 255))Pictures / Gifs of your work should go here
Make an account with your google ID at tinkercad.com, and use "TinkerCad Circuits to make a wiring diagram." It's really easy!
Then post an image here. here's a quick tutorial for all markdown code, like making links
What went wrong / was challenging, how'd you figure it out, and what did you learn from that experience? Your ultimate goal for the reflection is to pass on knowledge that will make this assignment better or easier for the next person.
import time
import board
import pwmio
import servo
# create a PWMOut object on Pin A2.
import time
import board
import pwmio
import servo
import touchio
# create a PWMOut object on Pin A2.
pwm = pwmio.PWMOut(board.A3, duty_cycle=2 ** 15, frequency=50)
# Create a servo object, my_servo.
my_servo = servo.Servo(pwm)
touch_A1 = touchio.TouchIn(board.A1)
touch_A2 = touchio.TouchIn(board.A2)
while True:
if touch_A1.value:
print("Touch A1!")
my_servo.angle = 90
if touch_A2.value:
print("Touched A2!")
my_servo.angle = 0
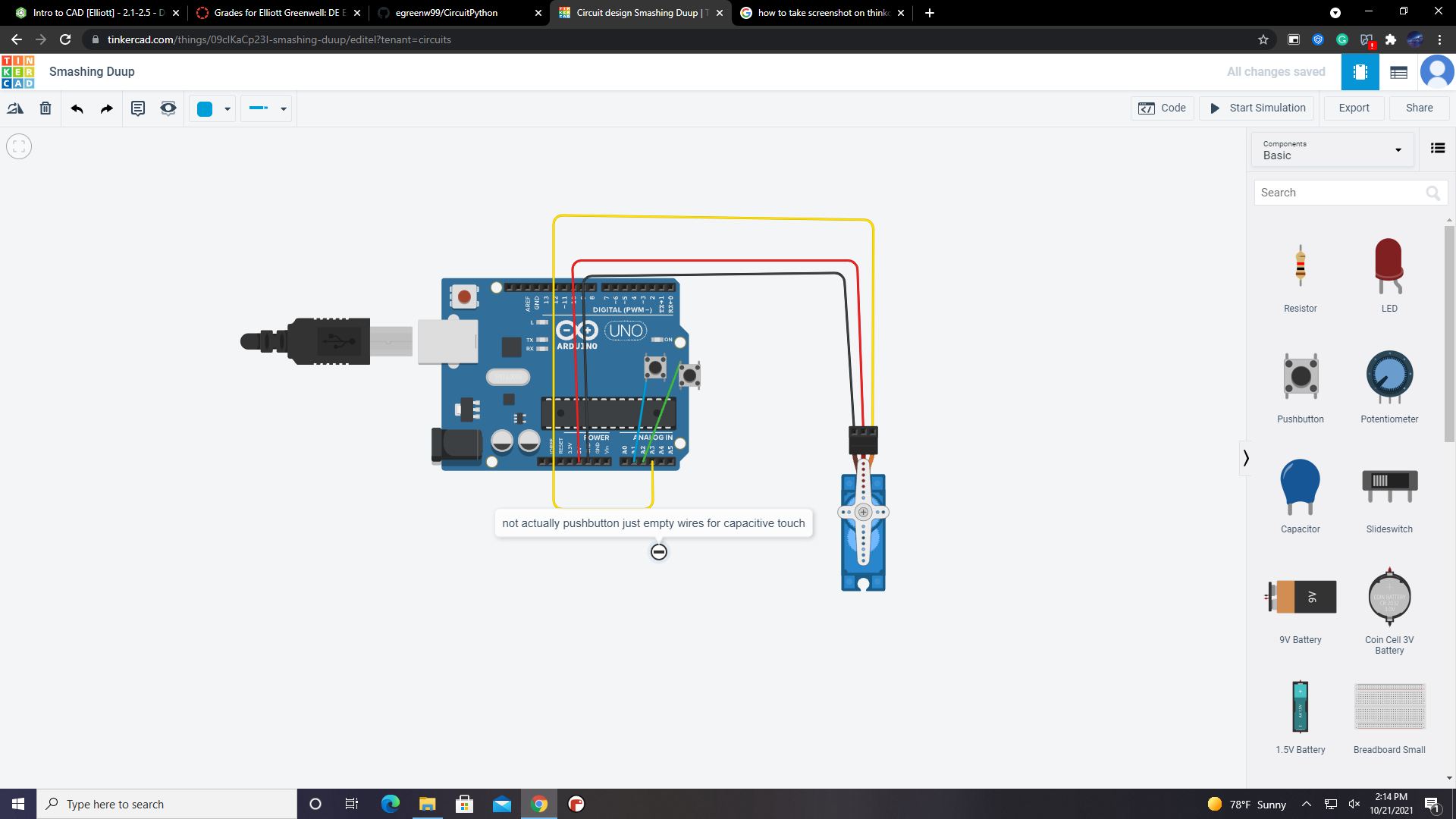
time.sleep(0.05)I was able to get the servo turning with compasitive touch after help from peers. I had some equipment malfunctions and wiring issues so next time I will double check my equipment and learn to code a little bit so im not so reliant on having other poeple code for me
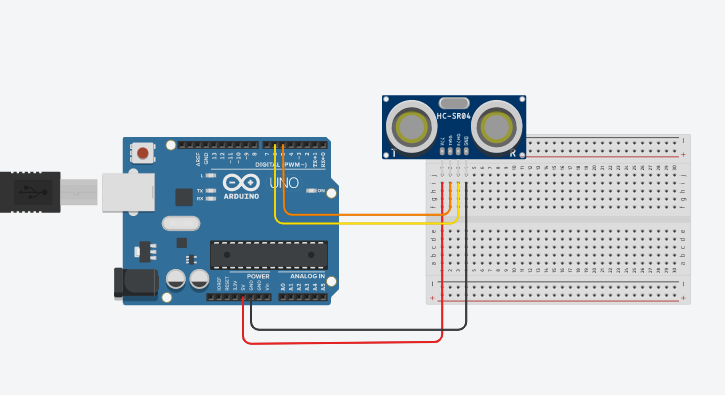
When an object moves away from the ultrasonic sensor the LED on the MetroBoard will change colors
import simpleio
import time
import board
import adafruit_hcsr04
import neopixel
dot = neopixel.NeoPixel(board.NEOPIXEL, 1)
sonar = adafruit_hcsr04.HCSR04(trigger_pin=board.D5, echo_pin=board.D6)
blueValue = 0
redValue = 0
greenValue = 0
while True:
try:
cm = sonar.distance
print((cm,))
if cm < 5:
dot.fill((0, 0, 0))
elif cm < 20:
redValue = simpleio.map_range(cm, 5, 20, 255, 0)
greenValue = 0
blueValue = simpleio.map_range(cm, 5, 20, 0, 255)
print("RGB: (", redValue, ", ", greenValue, ", ", blueValue, ")")
dot.fill((int(redValue), int(greenValue), int(blueValue)))
elif cm < 35:
redValue = 0
greenValue = simpleio.map_range(cm, 20, 35, 0, 255)
blueValue = simpleio.map_range(cm, 20, 35, 255, 0)
print("RGB: (", redValue, ", ", greenValue, ", ", blueValue, ")")
dot.fill((int(redValue), int(greenValue), int(blueValue)))
else:
dot.fill((0, 0, 0))
time.sleep(0.1)
except RuntimeError:
print("Retrying!")This assignment wasn't all that difficult. I've worked with ultrasonic sensors before so this wasn't all that terrible for me
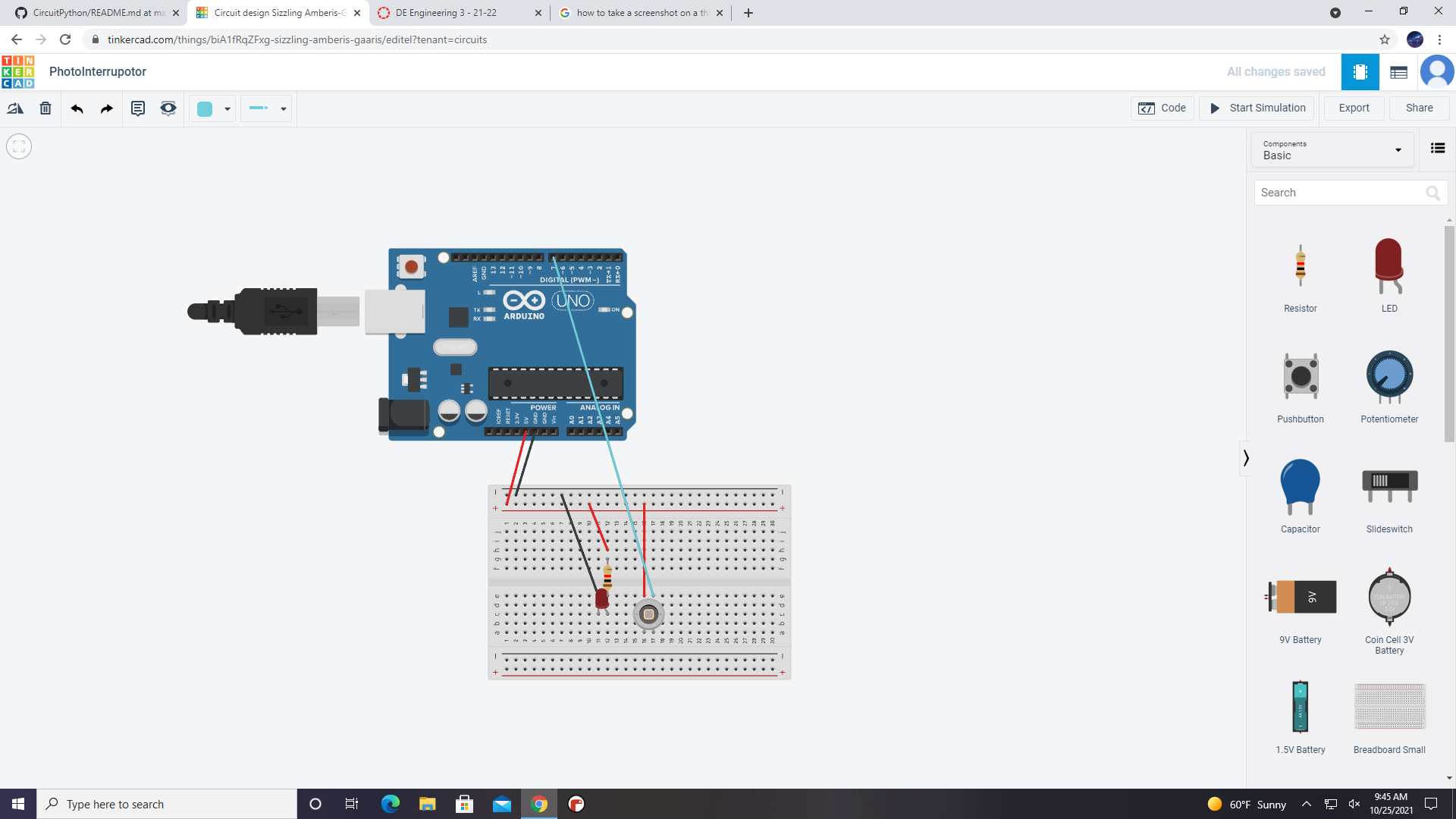
The number of times the photointerrupter is interrupted is recorded on the computer
from digitalio import DigitalInOut, Direction, Pull
import time
import board
interrupter = DigitalInOut(board.D7)
interrupter.direction = Direction.INPUT
interrupter.pull = Pull.UP
counter = 0
counter2 = 0
photo = False
state = False
max = 4
start = time.time()
while True:
photo = interrupter.value
if photo and not state:
counter += 1
counter2 += 1
state = photo
remaining = max - time.time()
if remaining <= 0:
print("Interrupts:", str(counter))
print("I've been interrupted:", str(counter2), "time") # This will inform you on the computer that the total amount of times photo-interrupter was interrupted.
max = time.time() + 4
counter = 0Wiring the interrupter wasn't all that hard but once again the coding part was forign to me so I used someone else's code.
When you touch the wire once on the LCD the number of times you touched it will increase, and when you touch the wire again the number on the LCD will decrease.
import time
import touchio
import board
from lcd.lcd import LCD
from lcd.i2c_pcf8574_interface import I2CPCF8574Interface
# get and i2c object
i2c = board.I2C()
# some LCDs are 0x3f... some are 0x27.
lcd = LCD(I2CPCF8574Interface(i2c, 0x27), num_rows=2, num_cols=16)
# Create a servo object, my_servo
touch_A1 = touchio.TouchIn(board.A1)
touch_A2 = touchio.TouchIn(board.A2)
touchCounter1 = 0
touchCounter2 = 0
variable = 1 # The variabe will allow us to decrease the numbers
while True:
lcd.set_cursor_pos(0, 0)
lcd.print(str(touchCounter1))
lcd.set_cursor_pos(1, 0)
if touch_A1.value:
print("Touch A1!") # When you touch A1 the number desplayed on the LCD will increase
touchCounter1 = touchCounter1 + variable
time.sleep(0.05)
if touch_A2.value:
print("Touch A2") # When you touch A2 the number desplayed on the LCD will decrease
variable = variable * -1This project was a combination of LCD and capacitive touch. the Importaion of the capacitive touch wasn't so bad, but coding required some assistance.