This (Python-based) GUI allows for interactive exploration of the skylight information provided by the different models. The GUI is based on the one implemented by Vévoda et al. (2022) for their Prague Sky Model (original C++ code here). There are three available datasets that work with this model, which can be downloaded form here:
- Google Drive with the near-infrared (SWIR) dataset (omits data in different altitudes)
- Google Drive with the full model (omits near infrared data)
- Google Drive with the hemispherical model (omits polarisation data and different altitudes)
You can easily install the package by using pip as:
pip install git+https://github.com/evgkanias/sky-gui.git
Alternatively you need to clone the GitHub repository, navigate to the main directory of the project, install the dependencies and finally the package itself. Here is an example code that installs the package:
pip install skylight
- Clone this repo.
mkdir ~/src
cd ~/src
git clone https://github.com/evgkanias/sky-gui.git
cd sky-gui
- Install the required libraries.
-
using pip :
pip install -r requirements.txt -
using conda :
conda env create -f environment.yml
-
- Install the package.
- using pip :
pip install . - using conda :
conda install .
- using pip :
Note that the pip project might be needed for the above installation.
To run the GUI, open a Python terminal and run the below.
from skylight_gui import SkyModelGUI
gui = SkyModelGUI()
gui()Alternatively, go to the examples directory and run the script that opens the graphical environment.
cd examples
python run_gui.pyw
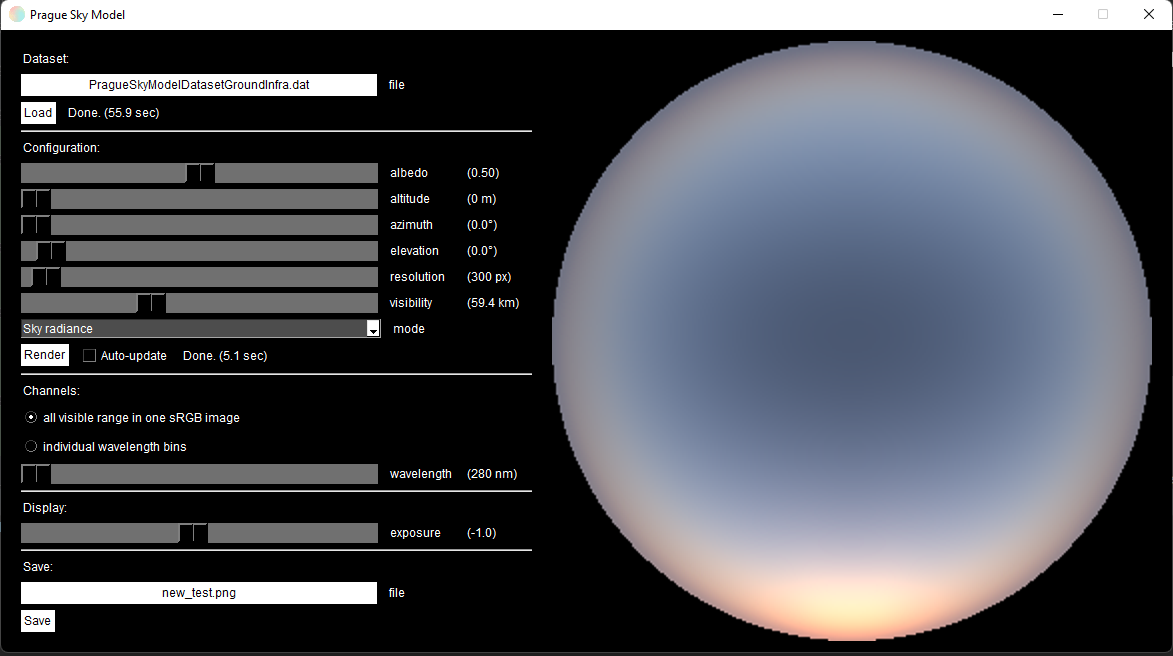
This will open the GUI which should look like this:
By clicking the file-name filed, you can choose the dataset file, which will load automatically. Once loaded, you can click "Render" (or choose the auto-update option) and this will print an image of the sky radiance, sun radiance, degree of polarisation, transmittance, or angle of polarisation (depending on the rendering mode), as shown below:
By clicking the saving file-name, you can define the file-name and type of data you want to save. Theses are:
- Image file (PNG or JPEG)
- Raw data (CSV or EXCEL)
The raw data option will save the data of the chosen mode but for all the available wavelengths and the extracted visible light (RGB).
If you have any issues installing or using the package, you can report it here.
The code is written by Evripidis Gkanias.
The original (C++) code for this model was written by Petr Vévoda et al. from Alexander Wilkie's group in Charles University, which was part of their wide spectral range sky radiance model.
Copyright © 2022, Evripidis Gkanias; Institute of Perception, Action and Behaviour; School of Informatics; the University of Edinburgh.