Code that implements the proximal asynchronous SAGA (ProxASAGA) method described in the paper "Breaking the Nonsmooth Barrier: A Scalable Parallel Method for Composite Optimization", F. Pedregosa, R. Leblond and S. Lacoste-Julien, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS) 2017
The code depends on the following tools and libraries:
- gcc (clang will probably work too but you'll need to edit the Makefile accordingly).
- The following python libraries: CFFI, NumPy and SciPy.
The code has been tested on OSX and Linux.
The algorithmic parts are implemented in C++. To use the code, first type make from the command line. That should compile the code and generate a binary file called libasaga.so. Once this is done you can launch the example in prox_asaga:
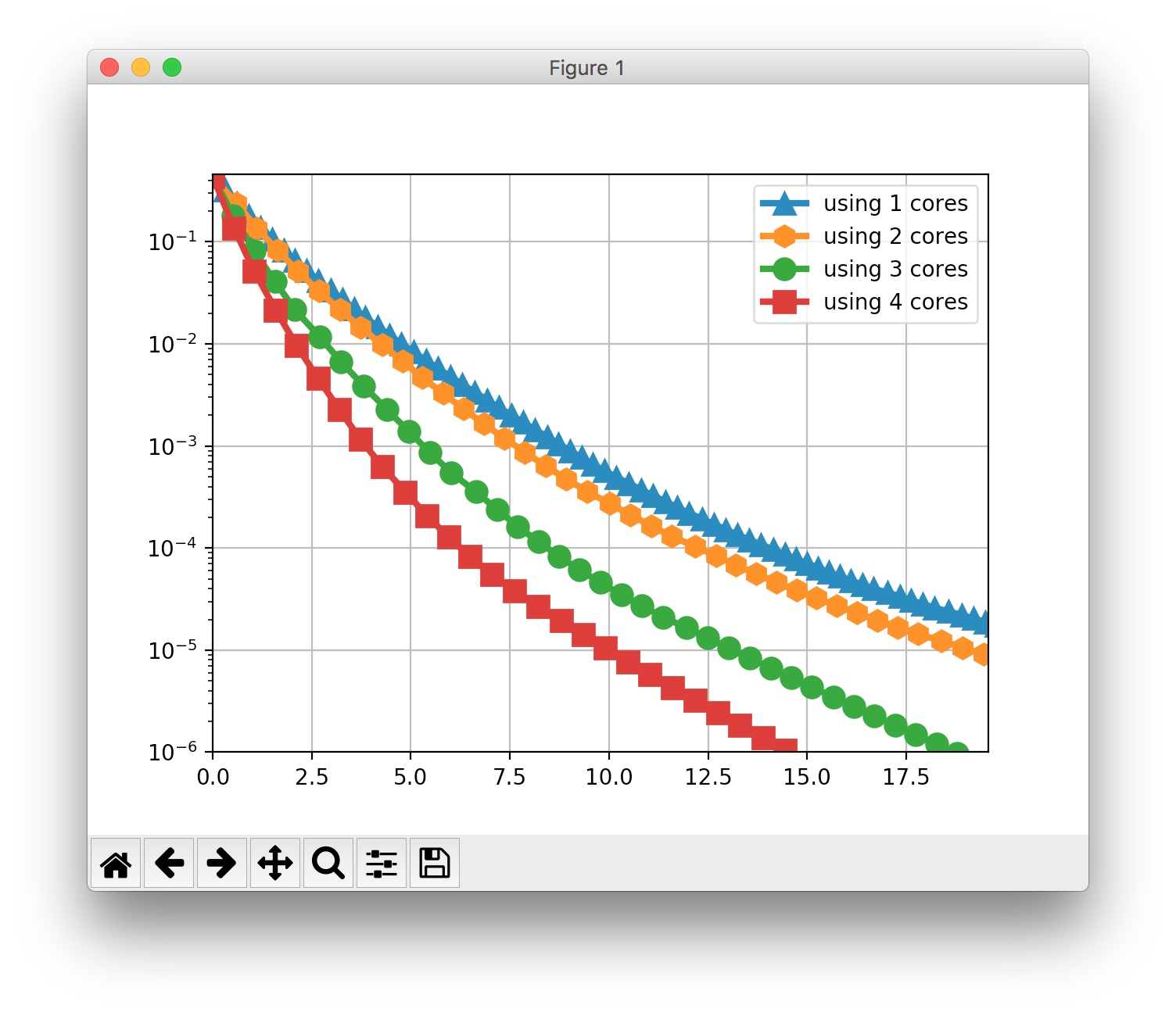
$ python prox_asaga.pyThis script trains a logistic regression model using ProxASAGA on 1, 2, 3 and 4 processors respectively. If everything worked fine, after ~10 minutes you should see a matplotlib plot like this:
The C-OPT library contains a pure Python implementation (using Numba) of the sequential algorithm. Note that because Numba lacks atomic types, a pure Python implementation of the parallel algorithm is not straightforward.