-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
IncrementalModel_step7
This step illustrates how to use differential equations.
We are interested in the spreading of the disease inside the buildings. In order to model it, we will use differential equations. So, we will need to:
- Add two global variables to define the building epidemic properties (
beta) and numerical integration parameter (h). - Add new variables for the buildings (
I,S,T,t,I_to1) to manage epidemic; - Define differential equations for disease spreading inside buildings.
- Add one behavior for buildings for the spreading of the disease.
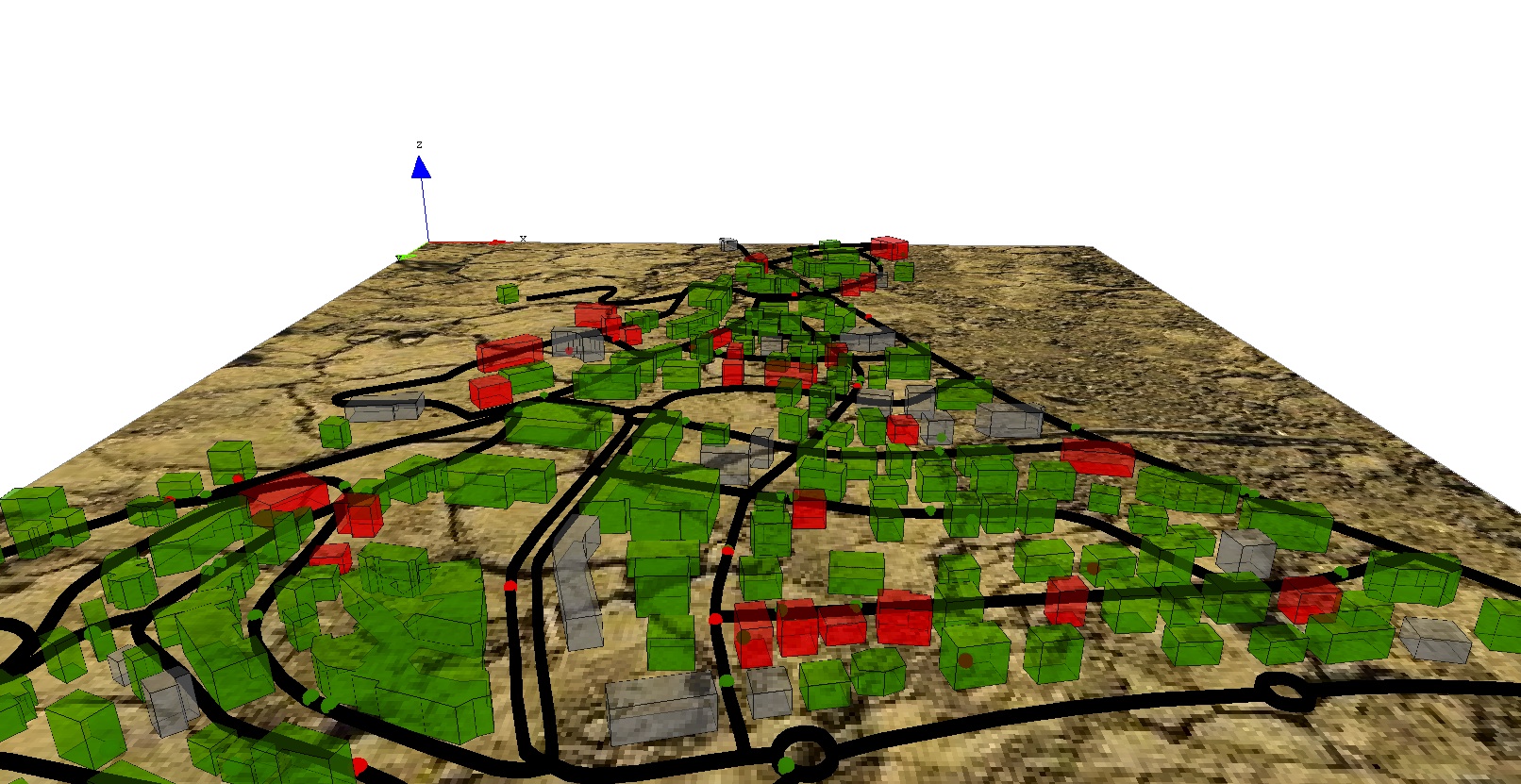
We define two new global variables used in the disease spreading dynamic inside the buildings: (i) beta is the contamination rate, and h is the integration step (used in the solve statement).
global {
...
float beta <- 0.01;
float h <- 0.1;
...
}
In order to define the disease spread dynamics, we define several variables that will be used by the differential equations:
-
I: float, number of people infected in the building. -
S: float, number of people not infected in the building. -
T: float, the total number of people in the building. -
t: float, the current time of the equation system integration. -
I_to1: float, the remaining number of people infected (float number lower between 0 and 1 according to the differential equations).
species building {
...
float I;
float S;
float T;
float t;
float I_to1;
...
}
Then, we define the differential equations system that will be used for the disease spreading dynamic. Note that to define a differential equation system we use the block equation + name. These equations are the classic ones used by SI mathematical models.
species building {
....
equation SI{
diff(S,t) = (- beta * S * I / T) ;
diff(I,t) = ( beta * S * I / T) ;
}
...
}
At last, we define a new reflex for the building called epidemic that will be activated only when there is someone inside the building. This reflex first computes the number of people inside the building (T), then the number of not infected people (S) and finally the number of infected ones (I).
If there is at least one people infected and one people not infected, the differential equations is integrated (according to the integration step value h) with the method Runge-Kutta 4 to compute the new value of infected people. We then sum the old value of I_to1 with the number of people newly infected (this value is a float and not an integer). Finally, we cast this value as an integer, ask the corresponding number of not infected people to become infected, and decrement this integer value to I\_to1.
species building {
...
reflex epidemic when: nb_total > 0 {
T <- float(nb_total);
S <- float(nb_total - nb_infected);
I <- T - S;
float I0 <- I;
if (I > 0 and S > 0) {
solve SI method: #rk4 step_size: h;
I_to1 <- I_to1 + (I - I0);
int I_int <- min([int(S), int(I_to1)]);
I_to1 <- I_to1 - I_int;
ask (I_int among (people_in_building where (!each.is_infected))) {
is_infected <- true;
}
}
}
...
}
https://github.com/gama-platform/gama.old/blob/GAMA_1.9.2/msi.gama.models/models/Tutorials/Incremental%20Model/models/Incremental%20Model%207.gaml
- Installation and Launching
- Workspace, Projects and Models
- Editing Models
- Running Experiments
- Running Headless
- Preferences
- Troubleshooting
- Introduction
- Manipulate basic Species
- Global Species
- Defining Advanced Species
- Defining GUI Experiment
- Exploring Models
- Optimizing Model Section
- Multi-Paradigm Modeling
- Manipulate OSM Data
- Diffusion
- Using Database
- Using FIPA ACL
- Using BDI with BEN
- Using Driving Skill
- Manipulate dates
- Manipulate lights
- Using comodel
- Save and restore Simulations
- Using network
- Headless mode
- Using Headless
- Writing Unit Tests
- Ensure model's reproducibility
- Going further with extensions
- Built-in Species
- Built-in Skills
- Built-in Architecture
- Statements
- Data Type
- File Type
- Expressions
- Exhaustive list of GAMA Keywords
- Installing the GIT version
- Developing Extensions
- Introduction to GAMA Java API
- Using GAMA flags
- Creating a release of GAMA
- Documentation generation