vgrep is a pager for grep, git-grep, ripgrep and similar grep implementations, and allows for opening the indexed file locations in a user-specified editor such as vim or emacs. vgrep is inspired by the ancient cgvg scripts but extended to perform further operations such as listing statistics of files and directory trees or showing the context lines before and after the matches. vgrep runs on Linux, Windows and Mac OS.
Please, feel free to copy, improve, distribute and share. Feedback and patches are always welcome!
- You can install
vgrepon Fedora, openSUSE, archlinux, Gentoo, and on Mac OS via MacPorts and Homebrew. - On other systems, you can build and install
vgrepmanually viamake buildandmake install.
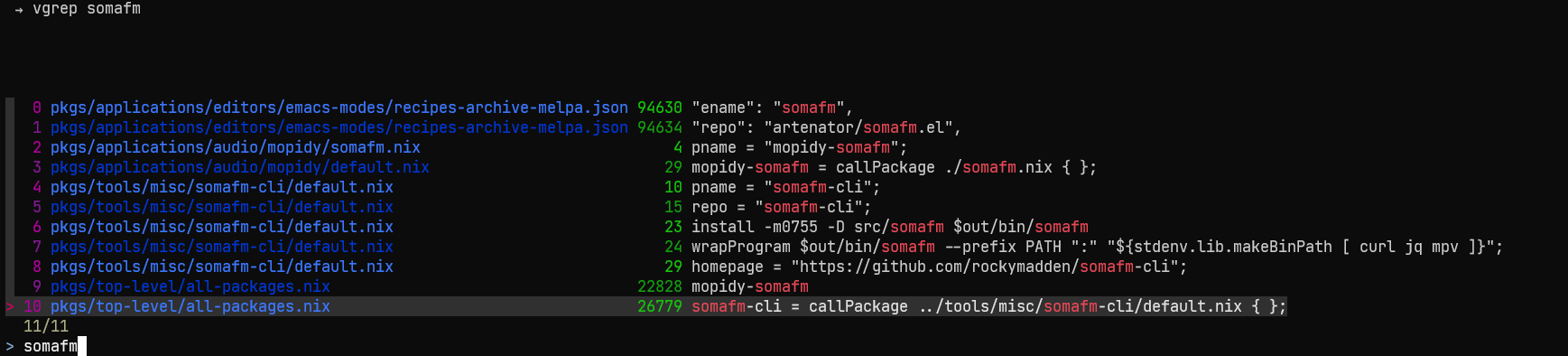
The basic functionality of vgrep is to perform textual searches. On a technical level, vgrep serves as a front-end to grep or git-grep when invoking vgrep inside a git tree and uses less for displaying the results. All non-vgrep flags and arguments will be passed down to grep. Results of the last search are cached, so running vgrep without a new query will load previous results and operate on them.
An example call may look as follows:
By default, the output will be written to less to make browsing large amounts of data more comfortable. vgrep --no-less will write to stdout.
vgrep can open the indexed file locations in an editor specified by the EDITOR environment variable. Opening one of the file locations from the previous example may look as follows:
# export EDITOR=gedit
# vgrep --show 4
The default editor of vgrep is vim with the default flag to open a file at a specific line being + followed by the line number. If your editor of choice hits the rare case of a different syntax, use the EDITORLINEFLAG environment variable to adjust. For example, a kate user may set the environment to EDITOR="kate" and EDITORLINEFLAG="-l".
Note that vgrep does not allow for searching and opening files at the same time. For instance, vgrep --show=files text should be split in two commands: vgrep text and vgrep --show=files.
Note that if you run vgrep inside a terminal of VSCode or Goland, the format of listed files changes to "$PATH:$LINE" to allow for opening the matches in the editor via a simple mouse click.
Once vgreped, you can perform certain operations on the results such as limiting the range of indexed matches, listing matching files and directories and more.
Enter a vgrep command: ?
vgrep command help: command[context lines] [selectors]
selectors: '3' (single), '1,2,6' (multi), '1-8' (range), 'all'
commands: print, show, context, tree, delete, keep, refine, files, grep, quit, ?
vgrep commands can be passed directly to the --show/-s flag, for instance as --show c5 1-10 to show the five context lines of the first ten matched lines. Furthermore, the commands can be executed in an interactive shell via the --interactive/-i flag. Running vgrep --interactive will enter the shell directly, vgrep --show 1 --interactive will first open the first matched line in the editor and enter the interactive shell after.
vgrep supports the following commands:
printto limit the range of matched lines to be printed.p 1-12,20prints the first 12 lines and the 20th line.showto open the selectors in an user-specified editor (requires selectors).contextto print the context lines before and after the matched lines.c10 3-9prints 10 context lines of the matching lines 3 to 9. Unless specified, vgrep will print 5 context lines.treeto print the number of matches for each directory in the tree.deleteto remove lines at selected indices from the results, for the duration of the interactive shell (requires selectors).keepto keep only lines at selected indices from the results, for the duration of the interactive shell (requires selectors).refineto keep only lines matching the provided regexp pattern from the results, for the duration of the interactive shell (requires a regexp string).fileswill print the number of matches for each file in the tree.grepstart a new search without leaving the interactive shell (requires arguments for avgrepsearch). For example,g -i "foo bar" dir/will trigger a case-insensitive search forfoo barin the files underdir. The cache will be updated with the results from the new search.quitto exit the interactive shell.?to show the help for vgrep commands.
If you desire a more interactive experience than running vgrep twice to first search and then to open an editor, you may have a look at fzf. The below function uses fzf to interactively search with vgrep and open your editor with one enter at the correct line.
To use it add the following function to your .bashrc and install fzf alongside vgrep and ripgrep.
vgrep() {
INITIAL_QUERY="$1"
VGREP_PREFIX="vgrep --no-header "
FZF_DEFAULT_COMMAND="$VGREP_PREFIX '$INITIAL_QUERY'" \
| fzf --bind "change:reload:$VGREP_PREFIX {q} || true" --phony --tac --query "$INITIAL_QUERY" |
| awk '{print $1}' | xargs -I{} -o vgrep --show {}
}