To write a beautiful program, breakdown solution to small pieces. This is called modular programming. Think of lego blocks which allow you to create whatever you imagine by interchanging lego blocks. Same is true with programming. Scratch also allows modular programming using functions.
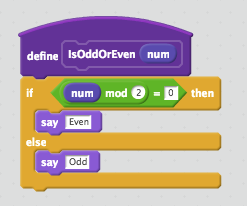
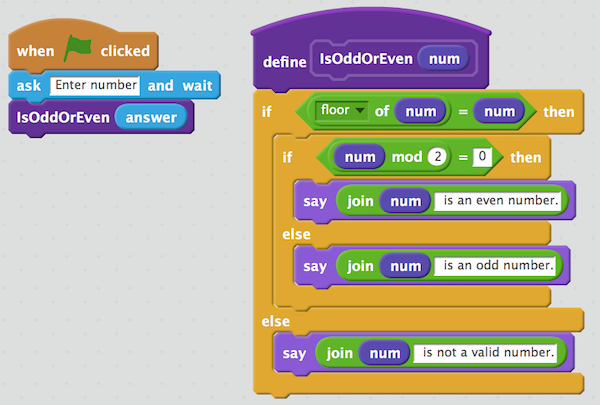
Write a scratch program to accept a number and check if the number is even or odd.
- A number is even if a number is divisible by 2. In other words, a number is a even number if the remainder is zero after the number is divided by 2. Scratch provides "mod" operator for the remainder calculation.
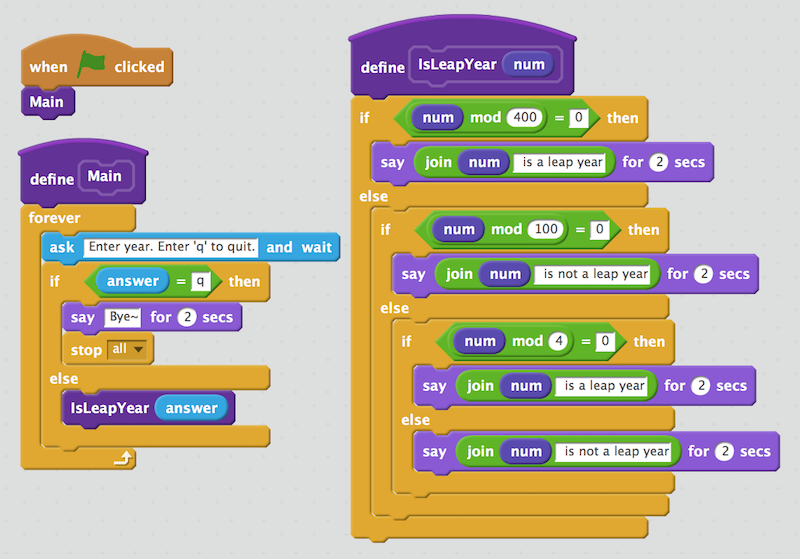
Every year that is exactly divisible by four is a leap year, except for years that are exactly divisible by 100, but these centurial years are leap years if they are exactly divisible by 400. For example, the years 1700, 1800, and 1900 were not leap years, but the years 1600 and 2000 were.
Write a scratch program to check if a given year is a leap year.
- Using a pencil and paper, write down several examples such as 400, 1700, 1800, 1900, 1600, 2000 and 2004.
- Write down the logic with a pencil and paper before starting to write code.
- Test if the logic is correct.
- Once logic is complete, start to write down beautiful code that means code should be modular, simple and optimized.
If num % 400 == 0
Leap
Else If num % 100 == 0
NoLeap
Else If num % 4 == 0
Leap
Else
No Leap
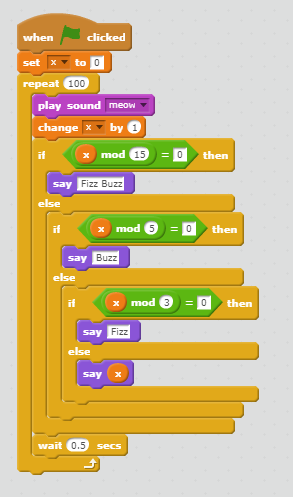
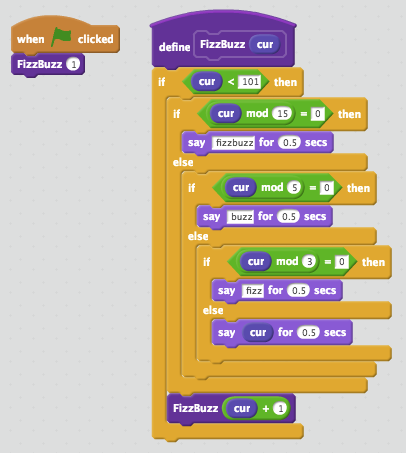
Nice job for solving the homework. There are many different ways to solve this problem. Here are three examples each of which uses different techniques:
This is a pretty general way for solving the fizzbuzz problem.
Instead of handling the case for "15 (3 and 5)", this uses a string to join "fizz" and "buzz" when necessary.
Instead of using loop, this example uses a technique called recursion.
Pseudo means fake. Pseudocode is not a real code, but a human readable description of a computer program. Let's look at real examples:
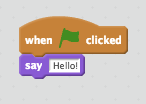
Example 1 - Scratch Programming - Say "Hello"
Say "Hello!"
Example 2 - Scratch Programming - Even or Odd
EvenOrOdd(num)
if num % 2 = 0
Say "Even"
else
Say "Odd"
Isn't it fairly easy to understand? As long as you or your friend understands how to read your pseudocode, your pseudocode is doing its job. There is no standard for pseudocode syntax. Why do you need to know how to write pseudocode?
First of all, pseudocode will help you get warmed up with the upcoming python class and c++ languages. You will later find that python looks surprisingly similar to pseudocode.
Last but not least, it is a good practice to solve a problem with pencil and paper before writing program because writing program is much more time consuming than writing on a paper. By writing pseudocode, you can draw the logic of your program quickly on paper without needing to worry about the details of actual program.
Here are some examples of pseudocode:
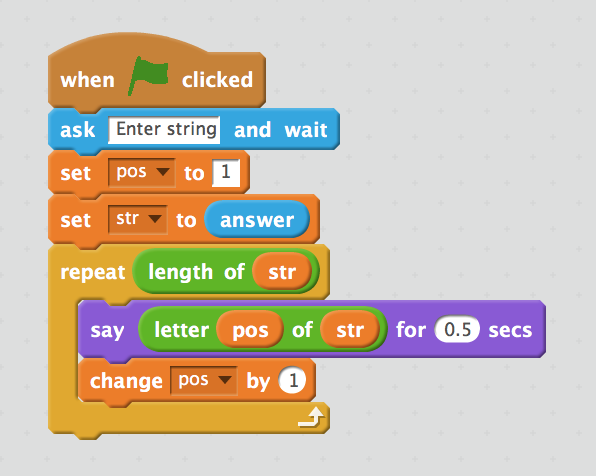
A string is a series of characters that is treated as a single unit.
Pseudocode
for pos = 1 to str.length
Say str[pos]
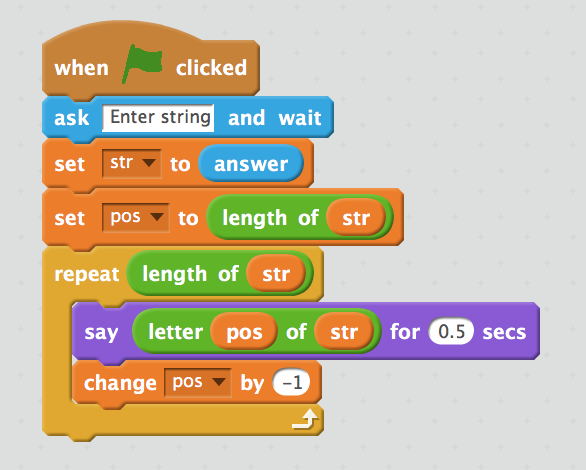
Pseudocode
for pos = str.length downto 1
Say str[pos]
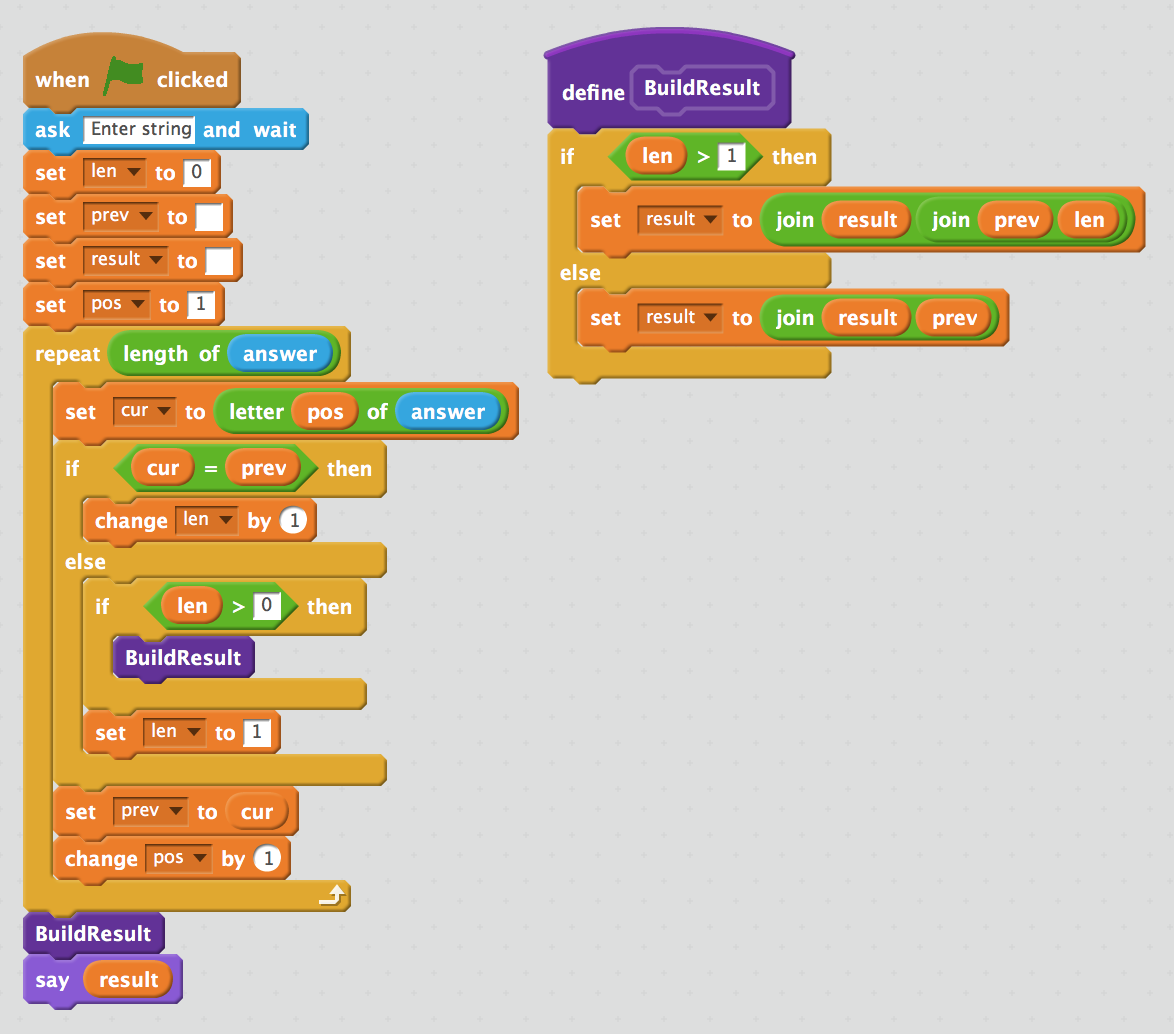
Pseudocode
str2 = ''
for pos = str.length downto 1
str2 = str2 + str[pos]
Say str2
4. Create a new Scratch project, and write your own Vowel-couting program using Figure 8-2. Vowel-counting program in the text book.
Pseudocode
CountVowels(str)
cnt = 0
for pos 1 to str.length
c = str[i].toUpper
if c = 'A' or c = 'E' or c = 'I' or c = 'O' or c = 'U'
cnt = cnt + 1
Say cnt
Pseudocode
IsPalindrome(str)
for pos 1 to str.length/2
if str[pos] != str[str.length + 1 - pos]
Say "No"
break
Say "Yes"
Nice job for solving the homework. This homework was a tough one. So, please don't be discouraged if you didn't finish on time.
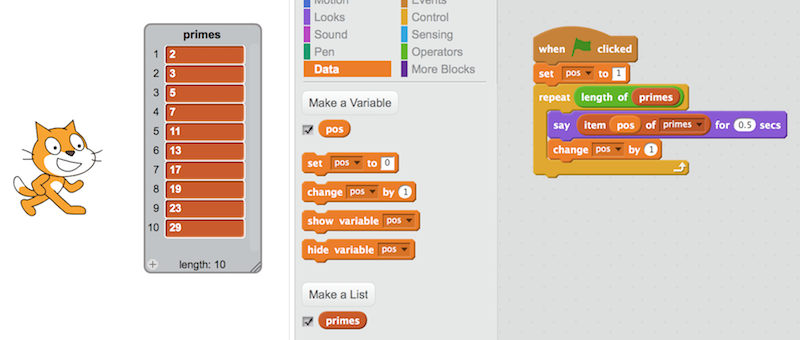
An array is a ordered collection of data. For example, an array can be used for storing the scores of players for a video game.
Let's say you are writing a program that needs to show the following information of Pacman, a classic video game:
- Average score of players
- Best score
- Worst score
GetAverage(Scores)
index = 1
sum = 0
Loop until index = length of Scores
change sum by Array[index]
change index by 1
average = sum / length of Scores
Say "Average is " + average
GetMaximum(Scores)
index = 1
result = Scores[index]
Loop until index = length of Scores
index = index + 1
current_score = Scores[index]
if result < current_score
result = current_score
Say "Best score is " + result
GetMinimum(Scores)
index = 1
result = Scores[index]
Loop until index = length of Scores
index = index + 1
current_score = Scores[index]
if result > current_score
result = current_score
Say "Worse score is " + result
Nice job for solving the homework. This homework was an easy one.
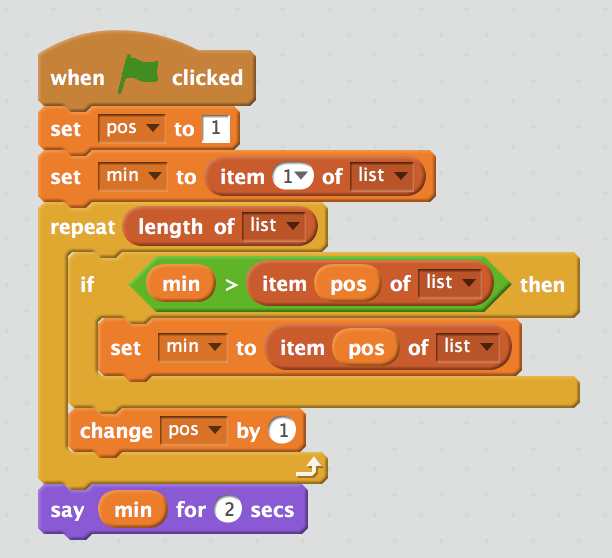
Example:
arr = [7, 2, 1, 5, 3]
min = arr[1]
for pos = 1 to len(arr)
if min > arr[pos]
min = arr[pos]
say min
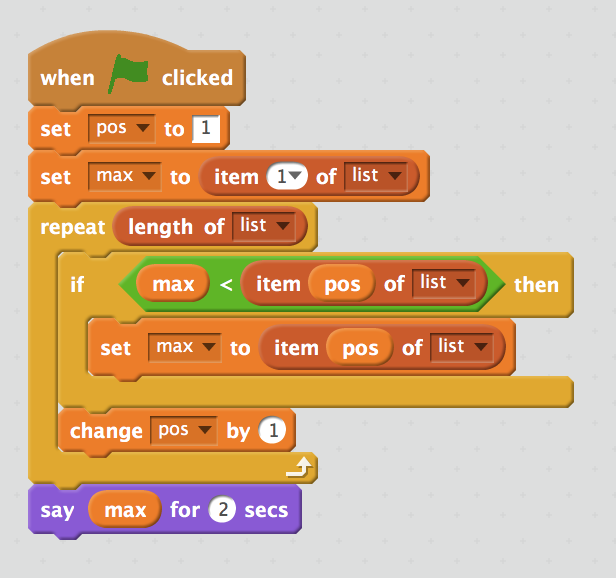
Example:
arr = [7, 2, 1, 5, 3]
max = arr[1]
for pos = 1 to len(arr)
if max < arr[pos]
max = arr[pos]
say max
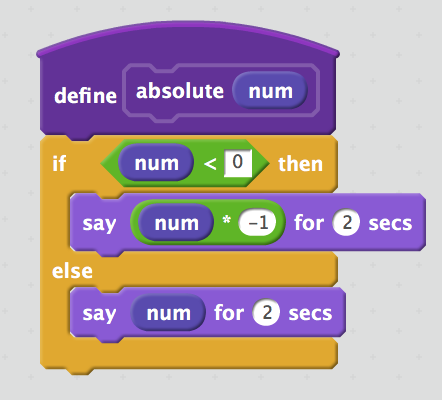
Ask a number, and always return an absolute number.
if num < 0
num = -1 * num
say num
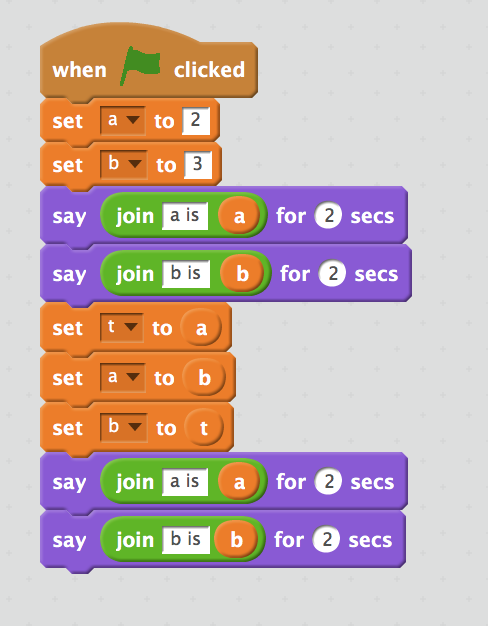
Use a temporary variable!
a = 2
b = 3
t = a
a = b
b = t
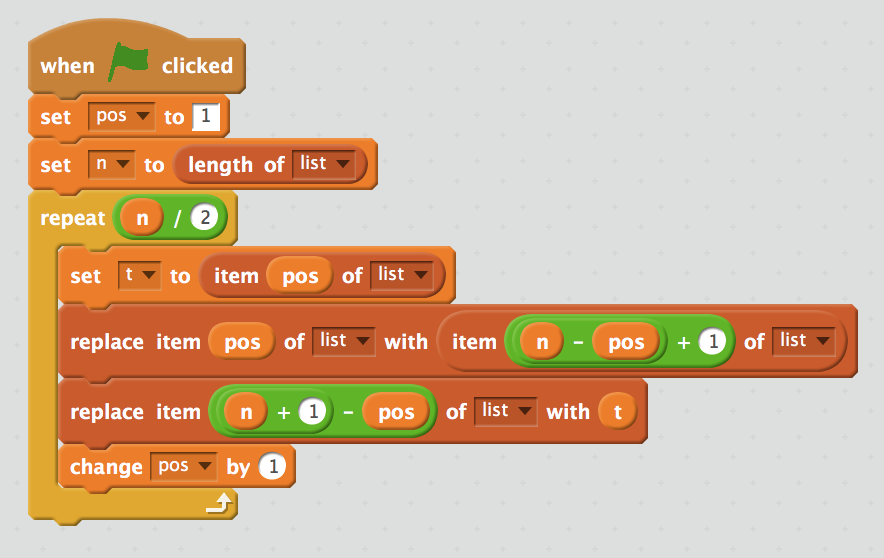
Use swap!
arr = [7, 2, 1, 5, 1]
for pos = 1 to len(arr)/2
swap arr[pos] with arr[len(arr) - pos + 1]