Grafana AWS X-Ray data source plugin >=2.13.0 is not compatible with Grafana versions <10.4.x due to a breaking change in UI components.
X-Ray datasource plugin provides a support for AWS X-Ray. Add it as a data source, then you are ready to build dashboards or use Explore with X-Ray to look at traces, analytics, or insights.
- In the side menu under the Configuration link, click on Data Sources.
- Click the Add data source button.
- Select X-Ray in the Distributed tracing section.
Note: If you have issues getting this data source to work and Grafana is giving you undescriptive errors, check your log file (/var/log/grafana/grafana.log).
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The data source name. This is how you refer to the data source in panels and queries. |
| Default | Default data source means that it will be pre-selected for new panels. |
| Default Region | Used in query editor to set region. (can be changed on per query basis) |
| Auth Provider | Specify the provider to get credentials. |
| Credentials profile name | Specify the name of the profile to use (if you use ~/.aws/credentials file), leave blank for default. |
| Assume Role Arn | Specify the ARN of the role to assume. |
| External ID | If you are assuming a role in another account that was created with an external ID, specify the external ID here. |
In this section we will go through the different type of authentication you can use for the AWS X-Ray data source.
Currently all access to X-Ray is done server-side by the Grafana backend using the official AWS SDK. If your Grafana server is running on AWS you can use IAM Roles and authentication will be handled automatically.
See the AWS documentation on IAM Roles
Note: AWS Role Switching is not currently supported.
Grafana needs permissions granted via IAM to be able to read X-Ray data and EC2 tags/instances/regions. You can attach these permissions to IAM roles and utilize Grafana's built-in support for assuming roles.
Here is a basic policy example:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"xray:BatchGetTraces",
"xray:GetTraceSummaries",
"xray:GetTraceGraph",
"xray:GetGroups",
"xray:GetTimeSeriesServiceStatistics",
"xray:GetInsightSummaries",
"xray:GetInsight",
"xray:GetServiceGraph",
"ec2:DescribeRegions"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}If the Auth Provider is Credentials file, Grafana tries to obtain credentials in the following order:
- Hard-code credentials
- Environment variables (
AWS_ACCESS_KEY_IDandAWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY) - Existing default config files
- ~/.aws/credentials
- IAM role for Amazon EC2
See Configuring the AWS SDK for Go in the AWS documentation for more information.
Create a file at ~/.aws/credentials. That is the HOME path for users running grafana-server.
Note: If the credentials file is in the correct directory, but it is not working, try moving your .aws file to '/usr/share/grafana/'. Make sure your credentials file has at most 0644 permissions.
Example credential file:
[default]
aws_access_key_id = <your access key>
aws_secret_access_key = <your access key>
region = us-west-2The most important field in the query editor is the query type. There are five query types:
- Trace List (Traces in AWS)
- Trace Statistics
- Trace Analytics (Analytics in AWS)
- Insights
- Service map
The Trace List type allows you to search for traces which are shown in a table. Clicking on the trace id in the first column opens the trace on the right side. Notice the query field in the editor. You can write queries, filter expressions, or insert a single trace ID that will be shown in a trace view. You can find more detail about filter expressions in AWS X-Ray documentation.
Note: The Trace List will only show the first 1000 traces.
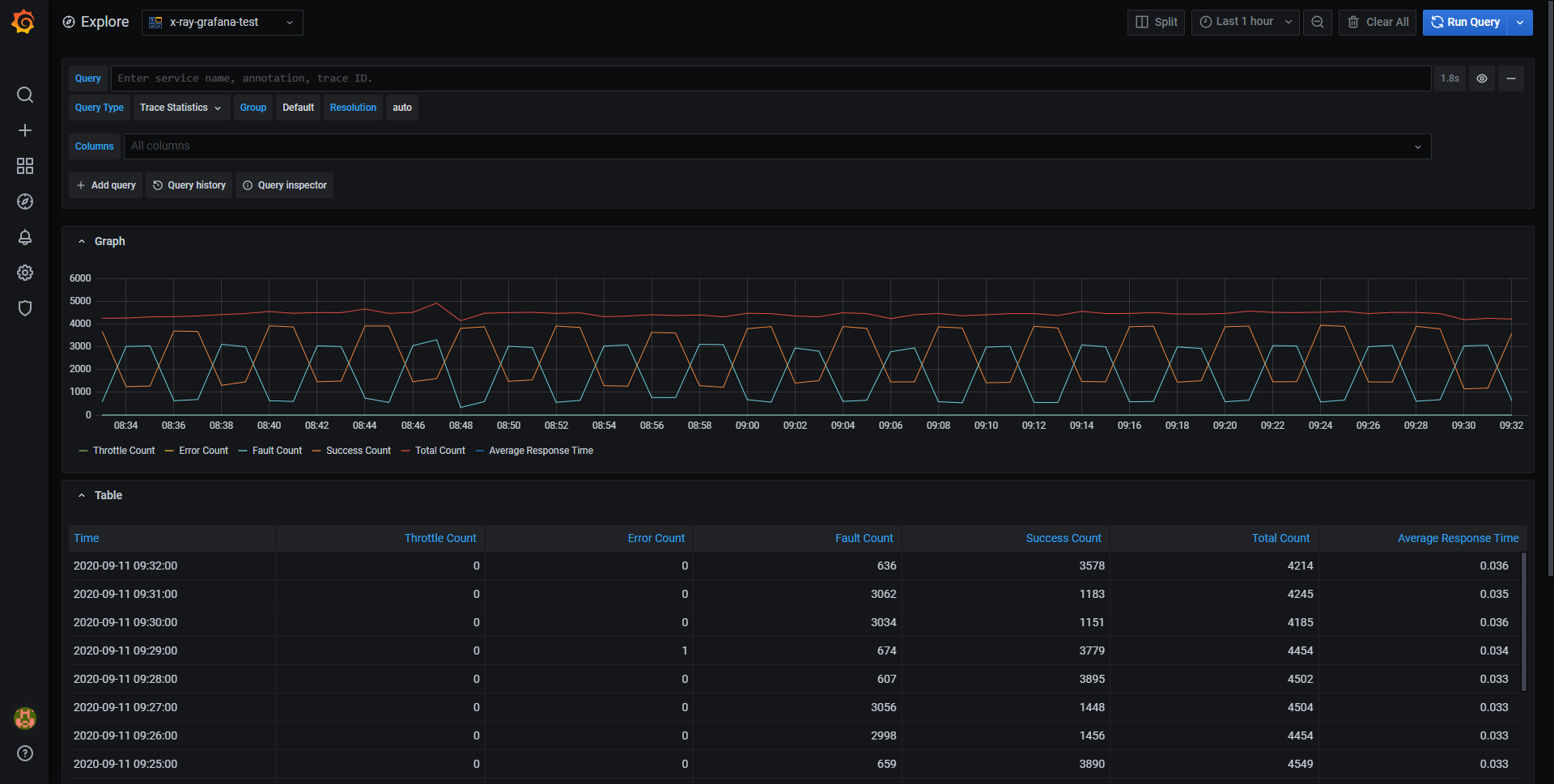
In Trace Statistics you can see a graph and a table showing information about error, fault, throttle, success, and total count. You can use the columns field in the query editor to only see specified columns.
In Trace Analytics you can visualize the following tables:
- Root Cause
- Response Time
- Root Cause Service (Last service in path)
- Path (multiple paths)
- Error
- Root Cause Service (Last service in path)
- Path
- Error Message
- Fault
- Root Cause Service (Last service in path)
- Path
- Error Message
- Response Time
- End user Impact
- URL
- HTTP Status Code
In Insights you can see the summary table for Insights. Clicking the InsightId will take you to AWS console.
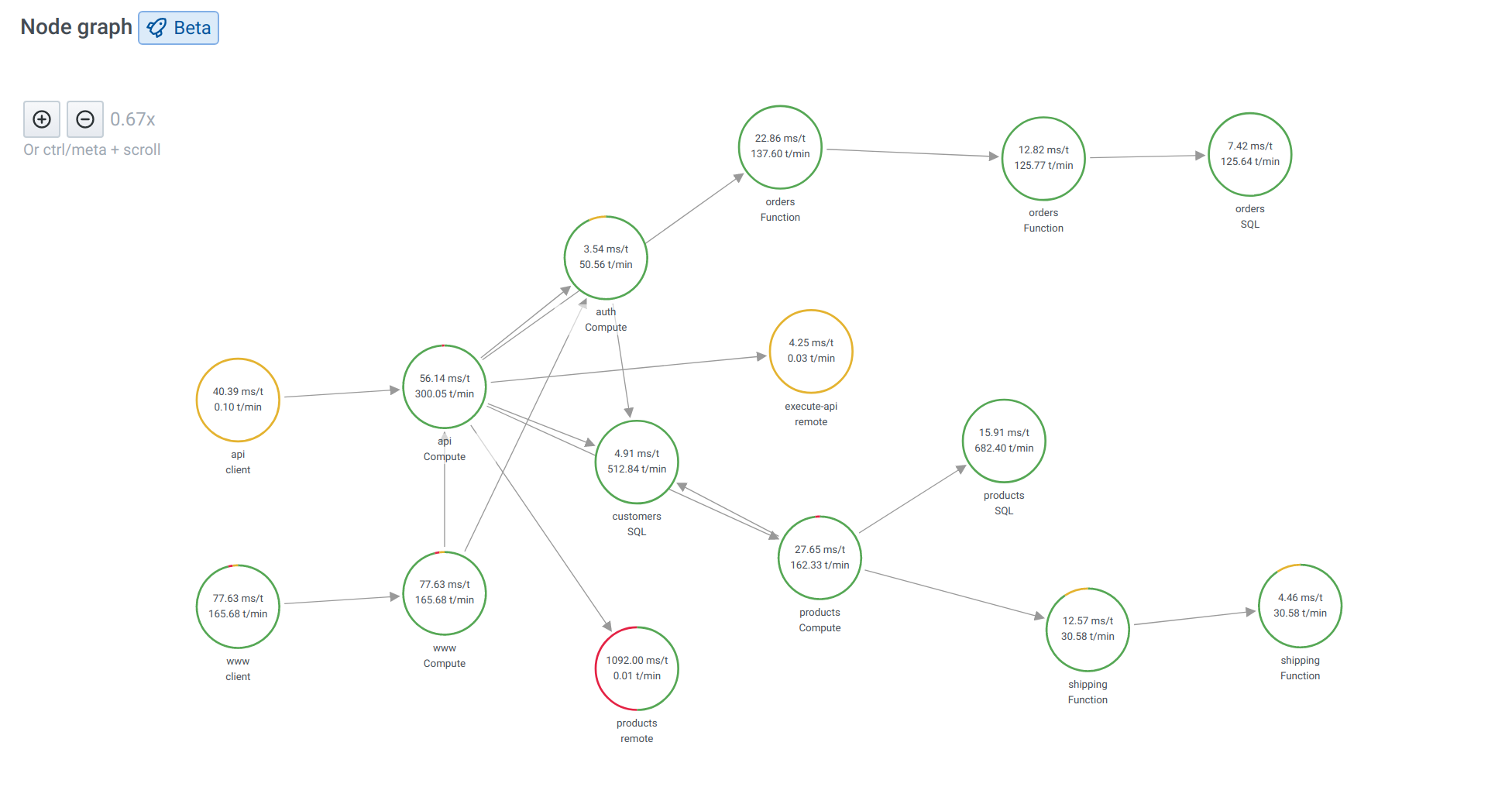
Service map in Grafana enables customers to view a map of their applications built using microservices architecture. Each node on the map represents a service such as an AWS Lambda function or an API running on an API Gateway or DynamoDB table. With this map, customers can easily detect performance issues, or increase in error, fault or throttle rates in any of their services and dive deep into corresponding traces and root cause.
Service Map query type shows the same data as a service map inside X-ray console.
To display the service map:
- Use the Node graph panel visualization in Grafana 7.4 plus.
- Use Explore in Grafana version 7.4 and later.
- Show the data in a simple table. This is the only option if the Node graph panel is unavailable.
You can pan and zoom the view with buttons or use your mouse. For details about the visualization, see Node graph panel.
Similar to X-ray root nodes, nodes in the service map representing the client application are on the left side of the map.
Each service in the map is represented as a circle. Numbers on the inside shows average time per transaction and transactions per minute.
A colored circle around the service also matches colors and meaning from X-ray console representing percentage of requests.
- green = success
- red = fault
- yellow = errors
- purple = throttled responses
Click on the service or the edge to see a context menu with links additional links for quick navigation to other relevant information from X-ray. You can use the links to quickly navigate to a list of all error traces for a particular service and then continue to specific trace.
For more information about Service map, refer to the official AWS X-ray documentation.
Since X-Ray queries can return numeric data, alerts are supported. See the Alerting documentation for more on Grafana alerts.
With AWS X-Ray, there are no upfront fees or commitments. You pay only for what you use, based on the number of traces recorded, retrieved, and scanned. The first 1,000,000 traces retrieved or scanned each month are free. Beyond the free tier, traces scanned cost $0.50 per 1 million traces scanned ($0.0000005 per trace). Please see the X-Ray pricing page for more details.
You can configure data sources using config files with Grafana's provisioning system. For more information regarding how it works and all available settings, see Provision Grafana.
Here are some provisioning examples for this data source.
If you are using the Credentials file authentication type, use a config similar to this:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: X-Ray
type: grafana-x-ray-datasource
jsonData:
authType: credentials
defaultRegion: eu-west-2apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: X-Ray
type: grafana-x-ray-datasource
jsonData:
authType: keys
defaultRegion: eu-west-2
secureJsonData:
accessKey: '<your access key>'
secretKey: '<your secret key>'The X-Ray plugin allows you to monitor traces across multiple AWS accounts within a region with the Cross-Account Observability feature. Using cross-account observability, you can seamlessly search, visualize and analyze AWS traces without worrying about account boundaries.
To enable cross-account observability, first enable the feature in AWS using the official CloudWatch docs, then add two API actions to the IAM policy attached to the role/user running the plugin.
This feature is currently behind the cloudWatchCrossAccountQuerying feature toggle.
You can enable feature toggles through configuration file or environment variables. See configuration [docs]({{< relref "../setup-grafana/configure-grafana/#feature_toggles" >}}) for details. Grafana Cloud users can access this feature by opening a support ticket in the Cloud Portal.
Once the feature is enabled, you will be able to display traces across multiple accounts and filter those traces by account ID. When you select the Service Map query type in Grafana, an account dropdown displays and populates with the account IDs shown in the traces returned in the selected time frame.
You can also add account ID as part of a query filter expression in the Trace List query type.